Abstract
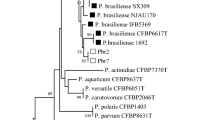
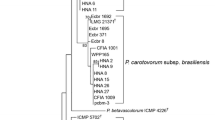
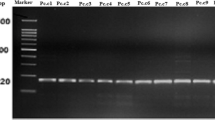
In this study, potato plants displaying symptoms of blackleg and soft rot were collected in Guangdong Province, China, and the causative bacterial pathogens were isolated from symptomatic tissues. In total, five pathogenic isolates (Po-2, Po-3, Po-4, Po-10, and Po-11) were selected and preliminarily identified as Pectobacterium spp. based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing and detection of the pectate-lyase gene using species-specific primers. Physiological and biochemical tests revealed that the five isolates grew at 37 °C, utilized D-galactose, D-lactose, maltose, melibiose, raffinose, sodium citrate, sucrose and trehalose, but not inosine, inulin, malonate, sorbitol and were sensitive to erythromycin. All isolates were negative for acid production from α-methyl glucoside and production of reducing substances from sucrose. In addition, Po-2, Po-3, and Po-4 utilized Tween 80 and produced indole but did not utilize arabinose, while Po-10 and Po-11 did not use Tween 80 and did not produce indole but utilized arabinose. Pathogenicity assays showed that Po-2, Po-3, and Po-4 infected 32 plant species across 19 families, while Po-10 and Po-11 infected 24 species from 17 families. 16S rDNA and phylogenetic analysis based on eight housekeeping genes (acnA, gapA, icdA, mdh, mtlD, pgi, proA, and rpoS) showed that Po-2, Po-3, and Po-4 clustered with Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis assignments confirmed using specific primer sets BR1f/L1r, while Po-10 and Po-11 clustered with Pectobacterium parmentieri. This is the first detailed report on P. carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis and P. parmentieri as causative agents of potato blackleg and soft rot in China.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker GC, Smith JJ, Cowan DA (2003) Review and re-analysis of domain-specific 16S primers. J Microbiol Methods 55:541–555
Czajkowski R, Pérombelon MCM, van Veen JA, van der Wolf JM (2011) Control of blackleg and tuber soft rot of potato caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya species: a review: contro of Dickeya and Pectobacterium species in potato. Plant Pathol 60:999–1013
Czajkowski R, Pérombelon M, Jafra S, Lojkowska E, Potrykus M, van der Wolf J, Sledz W (2015) Detection, identification and differentiation of Pectobacterium and Dickeya species causing potato blackleg and tuber soft rot: a review. Ann Appl Biol 166(1):18–38
Darrasse A, Priou S, Kotoujansky A, Bertheau Y (1994) PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism of a pel gene as a tool to identify Erwinia carotovora in relation to potato diseases. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(5):1437–1443
De Boer SH, Li X, Ward LJ (2012) Pectobacterium spp.associated with bacterial stem rot syndrome of potato in Canada. Phytopathology 102:937–947
Duarte V, De Boer SH, Ward LJ, De Oliveira AM (2004) Characterization of atypical Erwinia carotovora strains causing blackleg of potato in Brazil. J Appl Microbiol 96:535–545
Feil EJ, Holmes EC, Bessen DE, Chan MS, Day NPJ, Enright MC, Goldstein R, Hood DW, Kalia W, Moore CE, Zhou JJ, Spratt BG (2001) Recombination within natural populations of pathogenic bacteria: short-term empirical estimates and long-term phylogenetic consequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:182–187
Gallelli A, Galli M, De Simone D, Zaccardelli M, Loreti S (2009) Phenotypic and genetic variability of Pectobacterium carotovorum isolated from artichoke in the Sele valley. J Plant Pathol 91:757–761
Gallois A, Samson R, Ageron E, Grimont PAD (1992) Erwinia carotovora subsp. odorifera subsp. nov., associated with odorous soft rot of chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:582–588
Gardan L, Gouy C, Christen R, Samson R (2003) Elevation of three subspecies of Pectobacterium carotovorum to species level: Pectobacterium atrosepticum sp nov., Pectobacterium betavasculorum sp nov and Pectobacterium wasabiae sp nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(2):381–391
Golkhandan E, Kamaruzaman S, Sariah M, Abidin MAZ, Nasehi A (2013) Characterization of Malaysian Pectobacterium spp. from vegetables using biochemical, molecular and phylogenetic methods. Eur J Plant Pathol 137(3):431–443
Khayi S, Cigna J, Chong TM, Laurent AQ, Chan KG, Helias V, Faure D (2016) Transfer of the potato plant isolates of Pectobacterium wasabiae to Pectobacterium parmentieri sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:5379–5383
Kim MH, Min SC, Kim BK, Choi HJ, Hahn JH, Kim C, Kang MJ, Kim SH, Park DS (2012) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of Pectobacterium wasabiae using YD repeat protein gene-based primers. Plant Dis 96(2):253–257
Koh YJ, Kim GH, Lee YS, Sohn SH, Koh HS, Kwon S, Heu S, Jung JS (2012) Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp.actinidiae subsp. nov., a new bacterial pathogen causing canker-like symptoms in yellow kiwifruit, Actinidia chinensis. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 40:1–11
Lan WW, Nishiwaki Y, Akino S, Kondo N (2013) Soft rot of root chicory in Hokkaido and its causal bacteria. J Gen Plant Pathol 79:182–193
Lee DH, Kim JB, Lim JA, Han SW, Heu S (2014) Genetic diversity of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis isolated in Korea. Plant Pathol J 30(2):117–124
Ma B, Hibbing ME, Kim HS, Reedy RM, Yedidia I, Breuer J, Breuer J, Glasner JD, Perna NT, Kelman A, Charkowski AO (2007) Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot enterobacterial genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya. Phytopathology 97:1150–1163
McNally RR, Curland RD, Webster BT, Robinson AP, Ishimaru CA (2017) First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis causing blackleg and stem rot in commercial and seed potato fields in Minnesota and North Dakota. Plant Dis 101:1672–1672
Moleleki LN, Onkendi EM, Mongae A, Kubheka GC (2013) Characterization of Pectobacterium wasabiae causing blackleg and soft rot diseases in South Africa. Eur J Plant Pathol 135:279–288
Moretti C, Fakhr R, Cortese C, De Vos P, Cerri M, Geagea L, Cleenwerck I, Buonaurio R (2016) Pectobacterium aroidearum and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum as causal agents of potato soft rot in Lebanon. Eur J Plant Pathol 144(1):205–211
Naas H, Sebaihia M, Orfei B, Rezzonico F, Buonaurio R, Moretti C (2018) Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum as causal agents of potato soft rot in Algeria. Eur J Plant Pathol 151:1027–1034
Nabhan AS, De Boer HS, Maiss E, Wydra K (2012a) Taxonomic relatedness among Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp.brasiliense subsp. nov. J Appl Microbiol 113:904–913
Nabhan S, Wydra K, Linde M, Debener T (2012b) The use of two complementary DNA assays, AFLP and MLSA, for epidemic and phylogenetic studies of pectolytic enterobacterial strains, with focus on the heterogeneous species Pectobacterium carotovorum. Plant Pathol 61:498–508
Nabhan S, De Boer SH, Maiss E, Wydra K (2013) Pectobacterium aroidearum sp. nov., a soft rot pathogen with preference for monocotyledonous plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(7):2520–2525
Nazerian E, Sijam K, Ahmad ZAM, Keshavarz K (2011) Characterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum causing a new soft rot disease on okra in Malaysia. J Gen Plant Pathol 77:292–294
Ngoc Ha VT, Voronina MV, Kabanova AP, Shneider MM, Korzhenkov AA, Toschakov SV, Miroshnikov KK, Miroshnikov KA, Ignatov AN (2018) First report of Pectobacterium parmentieri causing stem rot disease of potato in Russia. Plant Dis 103:1
Nykyri J, Niemi O, Koskinen P, Nokso–Koivisto J, Pasanen M, Broberg M, Petri PI, Liisa PH, Pirhonen M, Palva ET, Tyler B (2012) Revised phylogenyand novel horizontally acquired virulence determinants of the model soft rot phytopathogen Pectobacterium wasabiae SCC3193. PLoS Pathology 8:e1003013
Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA (2000) Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 405:299–304
Onkendi EM, Moleleki LN (2014) Characterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and brasiliense from diseased potatoes in Kenya. Eur J Plant Pathol 139:557–566
Ozturk M, Aksoy HM, Ozturk S, Potrykus M, Lojkowska E (2016) First report of potato blackleg and soft rot caused by Pectobacterium wasabiae in Turkey. New Dis Rep 34:17
Pasanen M, Laurila J, Brader G, Palva ET, Ahola V, van der Wolf J, Hannukkala A, Pirhonen M (2013) Characterisation of Pectobacterium wasabiae and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum isolates from diseased potato plants in Finland. Ann Appl Biol 163(3):403–419
Pérombelon MCM (2002) Potato disease caused by soft rot Erwinias: an overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol 51:1–12
Pitman AR, Harrow SA, Visnovsky SB (2010) Genetic characterisation of Pectobacterium wasabiae causing soft rot disease of potato in New Zealand. Eur J Plant Pathol 126:423–435
Schaad NW, Jones JB, Chun W (2001) Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, Third edn. APS Press, St. Paul
Toth IK, van der Wolf JM, Saddler G, Lojkowska E, Hélias V, Pirhonen M, Tsror Lahkim L, Elphinstone JG (2011) Dickeya species: an emerging problem for potato production in Europe. Plant Pathol 60:385–399
van der Merwe JJ, Coutinho TA, Korsten L, van der Waals JE (2010) Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis causing blackleg on potatoes in South Africa. Eur J Plant Pathol 126(2):175–185
van der Wolf JM, Nijhuis EH, Kowalewska MJ, Saddler GS, Parkinson N, Elphinstone JG, Pritchard L, Tothn IK, Lojkowska E, Potrykus M, Waleron M, de Vos P, Cleenwerck I, Pirhonen M, Garlant L, Hélias V, Pothier JF, Pflüger V, Duffy B, Tsror L, Manulis S (2014) Dickeya solani sp. nov., a pectinolytic plant-pathogenic bacterium isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(3):768–774
Waleron M, Waleron K, Lojkowska E (2013) Occurrence of Pectobacterium wasabiae in potato field samples. Eur J Plant Pathol 137:149–158
Waleron M, Waleron K, Lojkowska E (2014) Characterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp.odoriferum causing soft rot of stored vegetables. Eur J Plant Pathol 139(3):457–469
Waleron M, Waleron K, Lojkowska E (2015) First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense causing soft rot on potato and other vegetables in Poland. Plant Dis 99:1271–1271
Zhao YQ, Dou J, Geng GM, Tian YL, Fan JQ, Li X, Hu BS (2018) First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense causing blackleg and stem rot on potato in China. Plant Dis 102:1653
Acknowledgments
We thank Tamsin Sheen, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest of China(201303015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
all authors have received research grants from College of Agriculture, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China; and Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Microbial Signals and Disease Control, Guangzhou, China. All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li-ping, W., Min, Z., Min-hua, R. et al. Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis and Pectobacterium parmentieri as causal agents of potato blackleg and soft rot in China. J Plant Pathol 102, 871–879 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-020-00597-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-020-00597-0