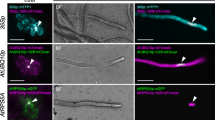
Abstract
CRISPR/Cas9 technology is a powerful tool for improving crop genetic traits. However, CRISPR/Cas9 system for efficient expression of cotton germ cells has still not been established. In this study, we developed a tissue-specific vectors to drive Cas9 expression with GhPLIMP2b and GhMYB24 promoters and established the effective method to transform cotton pollen by Agrobacterium vacuum infiltration. GhPLIMP2b and GhMYB24 promoters of cotton pollen were cloned into Cas9 expression vectors. The sgRNAs targetting to CLA1, ERA1 and GGB (drought-resistant negative regulation genes) were designed and constructed into GhPLIMP2b and GhMYB24 promoter vectors. Cotton pollens were tranformed by Agrobacterium vacuum infiltration with GhPLIMP2b and GhMYB24 promoter vectors. The results of clone sequencing shown that mutation types of the sequence were mainly base substitutions wth the frequency from 3.29 to 6.45%. Eleven potential off-target sites were chosen and two sites were observed. Our results indicated that GhPLIM2bP::Cas9 and GhMYB24P::Cas9 editing vectors achieved targeted edition of endogenous genes in cotton pollen, but there were a few off-target effects. This study provides an effective gene-editing system for the rapid acquisition of cotton mutants using pollen as a transgenic receptor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin NA, Ahmad N, Wu N, Pu X, Ma T, Du Y, Bo X, Wang N, Sharif R, Wang P (2019) CRISPR-Cas9 mediated targeted disruption of FAD2-2 microsomal omega-6 desaturase in soybean (Glycine maxL.). BMC Biotechnol 19:1–10
Anzu O, Taj A, Nikolai B, Niharika S, Nathan SW, Elise JT, Ute B, Peter L, Ryan W (2019) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of Ms1 enables the rapid generation of male-sterile hexaploid wheat lines for use in hybrid seed production. Plant Biotechnol J 17:1905–1913
Arnaud D, Déjardin A, Leplé JC, Lesage-Descauses MC, Pilate G (2007) Genome-wide analysis of LIM gene family in Populus trichocarpa, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Oryza sativa. DNA Res 14:103–116
Belhaj K, Chaparro-Garcia A, Kamoun S, Nekrasov V (2013) Plant genome editing made easy: targeted mutagenesis in model and crop plants using the CRISPR/Cas system. Plant Methods 9:10
Bortesi L, Fischer R (2015) The CRISPR/Cas9 system for plant genome editing and beyond. Biotechnol Adv 33:41–52
Chen XG, Lu XK, Shu N, Wang S, Wang JJ, Wang DL, Guo LX, Ye WW (2017) Targeted mutagenesis in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44304
Eliasson Å, Gass N, Mundel C, Baltz R, Kräuter R, Evrard JL, Steinmetz A (2000) Molecular and expression analysis of a LIM protein gene family from flowering plants. Mol Gen Genet 264:257–267
Gao W, Long L, Tian XQ, Xu FC, Liu J, Singh PK, Botella JR, Song CP (2017) genome editing in cotton with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.0136
Hwang HH, Yu M, Lai EM (2017) Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation: biology and applications. Arabidopsis Book. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0186
Janga MR, Campbell LM, Rathore KS (2017) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in upland cotton (Gossypiumhirsutum L.). Plant Mol Biol 94:349–360
Jiang WZ, Zhou HB, Bi HH, Fromm ME, Yang B, Weeks DP (2013) Demonstration of CRISPR/Cas9/sgRNA-mediated targeted gene modification in Arabidopsis, tobacco, sorghum and rice. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt780
Lei JF, Wu J, Chen XJ, Yu TP, Ni ZY, Li Y, Zhang JS, Liu XD (2015) Cloning and functional analysis of cotton U6 promoter with high transcription activity in cotton pollen. Sci Agric Sin 48:3794–3802
Li JF, Norville JE, Aach J, McCormack M, Zhang D, Bush J, Church GM, Sheen J (2013a) Multiplex and homologous recombination-mediated genome editing in Arabidopsis and Nicotianabenthamiana using guide RNA and Cas9. Nat Biotechnol 31:688–691
Li Y, Jiang J, Du ML, Li L, Wang XL, Li XB (2013b) A cotton gene encoding MYB-Like transcription factor is specifically expressed in pollen and is involved in regulation of late anther/pollen development. Plant Cell Physiol 54:893–906
Li C, Unver T, Zhang BH (2017) A high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9 system for targeted mutagenesis in cotton (Gossypium hirsutumL.). Sci Rep 7:43902
Li JY, Lei JF, Dai PH, Yao R, Qu YY, Chen QJ, Li Y, Liu XD (2018a) Establishment of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system based on GbU6 promoters in cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.). J Crop Sci 44:227–235
Li C, Hao MY, Wang WX, Wang H, Chen F, Chu W, Zhang BH, Mei DS, Cheng HT, Hu Q (2018b) An efficient CRISPR/Cas9 platform for rapidly generating simultaneous mutagenesis of multiple gene homoeologs in allotetraploid oilseed rape. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00442
Liang Z, Zhang K, Chen KL, Gao CX (2014) Targeted mutagenesis in Zea mays using TALENs and the CRISPR/Cas system. J Genet Genom 41:63–68
Ma X, Zhang Q, Zhu Q, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z, Li H, Lin Y, Xie Y, Shen R, Chen S, Wang Z, Chen Y, Guo J, Chen L, Zhao X, Dong Z, Liu YG (2015) A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Mol Plant 8:1274–1284
Mao YF, Zhang ZJ, Feng ZY, Wei PL, Zhang H, Botella JR, Zhu JK (2016) Development of germ-line-specific CRISPR-Cas9 systems to improve the production of heritable gene modifications in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol J 14:519–532
Osakabe Y, Liang ZC, Ren C, Nishitani C, Osakabe K, Wada M, Komori S, Malnoy M, Velasco R, Poli M (2018) CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in apple and grapevine. Nat Protoc 13:2844–2863
Schreiber DN, Dresselhaus T (2003) In vitro pollen germination and transient transformation of Zea mays and other plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 21:31–41
Wang YP, Cheng X, Shan QW, Zhang Y, Liu JX, Gao CX, Qiu JL (2014) Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powderymildew. Nat Biotechnol 32:947–951
Wang ZP, Xing HL, Dong L, Zhang HY, Han CY, Wang XC, Chen QJ (2015) Egg cell-specific promoter-controlled CRISPR/Cas9 efficiently generates homozygous mutants for multiple target genes in Arabidopsis in a single generation. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0715-0
Wang W, Akhunova A, Chao S, Akhunov E (2016) Optimizing multiplex CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing for wheat. Bio Rxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/051342
Wang DD, Samsulrizal N, Yan C, Allcock NS, Craigon J, Blanco-Ulate B, Ortega-Salazar I, Marcus SE, Bagheri HM, Perez-Fons L, Fraser PD, Foster T, Fray RG, Knox JP, Seymour GB (2018) Characterisation of CRISPR mutants targeting genes modulating pectin degradation in ripening tomato. Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01187
Wang C, Liu Q, Shen Y, Hua YF, Wang JJ, Lin JR, Wu MG, Sun TT, Cheng ZK, Mercier R, Wang KJ (2019) Clonal seeds from hybrid rice by simultaneous genome engineering of meiosis and fertilization genes. Nat Biotechnol 37:283–286
Xie KB, Yang YN (2013) RNA-guided genome editing in plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Mol Plant 6:1975–1983
Xie SS, Shen B, Zhang CB, Huang XX, Zhang YL (2014) sgRNAcas9: a software package for designing CRISPR sgRNA and evaluating potential off-target cleavage sites. PLoS ONE 9:1–9
Xie XR, Ma XL, Zhu QL, Zeng DC, Li GS, Liu YG (2017) CRISPR-GE: a convenient software toolkit for CRISPR-based genome editing. Mol Plant 10:1246–1249
Yan LH, Wu YR, Li HJ, Yang WC, Wei SW, Hu RL, Xie Q (2015) High efficiency genome editing in Arabidopsis using Yao promoter-driven CRISPR/Cas9 system. Mol Plant 8:1820–1823
Ye JR, Xu ML (2012) Actin bundler PLIM2s are involved in the regulation of pollen development and tube growth in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 169:516–522
Zhang SJ, Zhang RZ, Song GQ, Gao J, Li W, Han XD, Chen ML, Li YL, Li GY (2018) Targeted mutagenesis using the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated CRISPR-Cas9 system in common wheat. BMC Plant Biol 18:1–12
Zhao X, Meng ZG, Wang Y, Chen WJ, Sun CJ, Cui B, Cui JH, Yu ML, Zeng ZH, Guo SD, Luo D, Cheng Jeery Q, Zhang R, Cui HX (2017) Pollen magnetofection for genetic modification with magnetic nanoparticles as gene carriers. Nat Plant 3:956–964
Zhu SH, Yu XL, Li YJ, Sun YQ, Zhu QH, Sun J (2018) Highly efficient targeted gene editing in upland cotton using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Int J Mol Sci 19:3000
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (316604330); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYYJ201701); Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region postgraduate research and innovation project (XJ2019G131); Xinjiang Agricultural University cotton team development fund (XNMH2019003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XDL and JFL designed the experiment; JFL, PHD, JYL, MY, XQL, WQZ, GTZ and WZG performed the experiments and analyzed the data; JFL and XDL wrote the manuscript. All the authors agreed on the contents of the paper and post no conflicting interest.
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, J., Dai, P., Li, J. et al. Tissue-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 System of Cotton Pollen with GhPLIMP2b and GhMYB24 Promoters. J. Plant Biol. 64, 13–21 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09272-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09272-4