Abstract
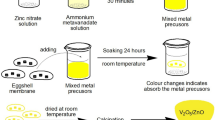
The following study was performed chiefly to analyze the antimicrobial activity of CdO/ZnO-ESM nanocomposites. A unique method was used for the synthesis of CdO/ZnO-ESM nanocomposites using an eggshell membrane as a bio-template which acts as both reducing and stabilizing agents; whereas cadmium nitrate and zinc nitrate were employed as metal precursors. The prepared samples were characterized by the following techniques such as TGA, PXRD, DRS–UV–Visible reflectance, FT-IR, HR-SEM, EDAX, Zeta potential, and Photoluminescence analysis. The prepared samples were subsequently tested for antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus sp.) and Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella enterica, and Vibrio sp.) using agar well diffusion method. The minimum inhibitory concentration was determined by the broth microdilution method. The maximum inhibition zone of 24 mm, was observed in Salmonella enterica at a concentration (30 μg/mL) of CdO/ZnO-ESM nanocomposites, while the highest MIC value was observed in Bacillus sp. at a concentration (1.95 μg/mL) of these nanocomposites. The result of this study showed that CdO/ZnO-ESM nanocomposites have an exceptional antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Azam, A.S. Ahmed, M. Oves, M.S. Khan, S.S. Habib, A. Memic, Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: a comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 6003–6009 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s35347
V. Staníc, S.B. Tanaskovíc, Antibacterial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicity 11, 241–274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819943-5.00011-7
R. Kumar, A. Umar, G. Kumar, H.S. Nalwa, Antimicrobial properties of nanomaterials: a review. Ceram. Int. 43, 3940–3961 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.12.062
K. Kannan, D. Radhika, K.K. Sadasivuni, K. Raghava-Reddy, A.V. Raghu, Nanostructured metal oxides and its hybrids for biomedical applications. Adv. Coll. Interface. Sci. 281, 102178 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102178
S. Cheemadan, M. Krishnan, A.J. Rathinam, M.C.S. Kumar, Biocidal properties of sputtered CdO:ZnO multi-component thin films for potential use in pathogenic bacteria control. Mater. Res. Express 6, 104009 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab3cbe
E. Khalili, S.A. Hassanzadeh Tabrizi, ZnO-CdO nanocomposite: microemulsion synthesis and dye removal ability. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 81, 475–482 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4211-0
A.H. Hateem, T. Ekhlass, W.M. Mohammed, M.M. Saleh, Green synthesis of CdO nanoparticles by olive leaf extract and their biological effectiveness. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 23(1), 138–141 (2019)
T.V.M. Sreekanth, M. Pandurangan, G.R. Dillip, D.H. Kim, Y.R. Lee, Toxicity and efficacy of CdO nanostructures on the MDCK and Caki-2cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 164, 174–181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.09.028
T. Bhuyan, K. Mishra, M. Khanuja, R. Prasad, A. Varma, Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 32, 55–61 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.12.053
N.M. Al-Hada, H. Mohamed Kamari, C.A.C. Abdullah, E. Saion, A.H. Shaari, Z.A. Talib, K.A. Matori, Down-top nanofabrication of binary (CdO)x (ZnO)1–x nanoparticles and their antibacterial Activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 8309–8323 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S150405
K. Karthik, S. Dhanuskodi, C. Gobinath, S. Sivaramakrishnan, Microwave-assisted synthesis of CdO-ZnO nanocomposite and its antibacterial activity against human pathogens. Spectrochim. Acta A 139, 7–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.11.079
E. Mosquera, I. del Pozo, M. Morel, Structure and red shift of optical band gap in CdO–ZnO nanocomposite synthesized by the sol gel method. J. Solid-State Chem. 206, 265–271 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2013.08.025
C.V. Reddy, B. Babu, J. Shim, Synthesis, optical properties and efficient photocatalytic activity of CdO/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 112, 20–28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.09.003
S. Rajaboopathi, S. Thambidurai, Green synthesis of seaweed surfactant based CdO-ZnO nanoparticles for better thermal and photocatalytic activity. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17(12), 1622–1638 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2017.09.006
M.M. Raman, S.B. Khan, H.M. Marwani, A.M. Asiri, K.A. Alarmy, M.A. Rub, A. Khan, A.A.P. Khan, N. Azum, Facile synthesis of doped ZnO-CdO nanotubes as solid phase adsorbent and efficient solar photo-catalyst applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 1622–1638 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.09.059
P. Margan, M. Haghighi, Sono-coprecipitation synthesis and physicochemical characterization of CdO-ZnO nanophotocatalyst for removal of acid orange 7 from wastewater. Ultrason. Sonochem. 40, 323–332 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.07.003
M. Mahendiran, J.J. Mathen, M. Racik, J. Madhavan, M.V. Antony-Raj, Investigation of structural, optical and electrical properties of transition metal oxide semiconductor CdO-ZnO nanocomposite and its effective role in the removal of water contaminants. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 126, 322–334 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.11.012
B.O. Godfrey, W.B. Henry, Structural and optical characterization of CdO-ZnO nanocomposite deposited by sol-gel method. Int. Res. J. Multidiscip. Sci. Technol. 2(3), 15–19 (2018)
Z.N. Abdul-Ameer, I.R. Agool, Structural and optical properties of ZnO-CdO nanocomposite using electrodeposition method. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astronomy 63, 127–133 (2016)
C. Karunakaran, A. Vijayabalan, P. Vinayagamoorthy, CdO-implanted hexagonal ZnO nanoplatelets: red-shifted emission and enhanced charge carrier-resistance and bacteria-inactivation. Appl. Phys. A 125, 14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2318-6
P. Senthil Kumar, M. Selvakumar, P. Bhagabati, B. Bharathi, S. Karuthapandian, S. Balakumar, CdO/ZnO nanohybrids: Facile synthesis and morphologically enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv. 4, 32977–32986 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA02502D
S.P. Meshram, J.D. Ambekar, I.S. Mulla, D.P. Amalnerkar, P.V. Adhyapak, Synthesis and characterization of CdO–ZnO nanocomposite for degradation of reactive red 198 under ultrasound irradiation. J. Nanoeng. Nanomanuf. 4, 127–134 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnan.2014.1181
J.K. Rajput, T.K. Pathak, V. Kumar, H.C. Swart, L.P. Purohit, Liquid petroleum gas sensing application of ZnO/CdO:ZnO nanocomposite at low temperature. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 80035 (1942). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5028869
R. Saravanan, F. Gracia, M.M. Khan, V. Poornima, V.K. Gupta, V. Narayanan, A. Stephenh, ZnO/CdO nanocomposite for textile effluent degradation and electrochemical detection. J. Mol. Liq. 209, 374–380 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.05.040
G. Somasundaram, J. Rajana, J. Poul, Effect of calcination process on CdO-ZnO nanocomposite by honey-assisted combustion method for antimicrobial performances. Toxicol. Res 7, 779–879 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TX00059J
S.S. Khan, Enhancement of visible light photocatalytic activity of CdO modified ZnO nanohybrid particles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 142, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.11.001
A. Umar, M.S. Akhtar, M.S. Al-Assiri, A.E. Al-Salami, S.H. Kim, Composite CdO-ZnO hexagonal nanocones: efficient materials for photovoltaic and sensing applications. Ceram. Int. 44, 5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.098
R.A. Zargar, A.H. Shah, M. Arora, F.A. Mir, Crystallographic, spectroscopic and electrical study of ZnO:CdO nanocomposite-coated films for photovoltaic applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 6631–6636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03823-9
T. Sinha, M. Ahmaruzzaman, High-value utilization of egg shell to synthesize Silver and Gold-Silver core shell nanoparticles and their application for the degradation of hazardous dyes from aqueous phase-A green approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 453, 115–131 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.053
J. Celina Selvakumari, S.T. Nishanthi, J. Dhanalakshmi, M. Ahila, D. Pathinettam Padiyan, Bio-active synthesis of tin oxide nanoparticles using eggshell membrane for energy storage application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 441, 530–537 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.043
S. Albohani, M.M. Sundaram, D.W. Laird, Egg shell membrane template stabilises formation of β-NiMoO4 nanowires and enhances hybrid supercapacitor behaviour. Mater. Lett. 236, 64–68 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.10.034
P.S. Devi, S. Banerjee, S.R. Chowdhury, G.S. Kumar, Eggshell membrane: a natural biotemplate to synthesize fluorescent gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2, 11578–11585 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RA21053C
B. Zheng, L. Qian, H. Yuan, D. Xiaoa, X. Yangc, M.C. Paaud, M.M.F. Choid, Preparation of gold nanoparticles on eggshell membrane and their biosensing application. Talanta 82(1), 177–183 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.04.014
Q. Dong, Su Huilan, Di Zhang, Na Zhu, X. Guo, Biotemplate-directed assembly of porous SnO2 nanoparticles into tubular hierarchical structures. Scr. Mater. 55(9), 799–802 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.07.012
S. Fan, M. Zhao, L. Ding, J. Liang, J. Chen, Y. Li, S. Chen, Synthesis of 3Dhierarchical porous Co3O4 film by egg shell membrane for non-enzymatic glucose detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 775, 52–57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.05.035
J. Li, D. Zhai, F. Lv, Yu Qingqing, H. Ma, J. Yin, Z. Yi, M. Liu, J. Chang, Wu Chengtie, Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposite for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 36, 254–266 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.011
M. Liang, Su Rongxin, W. Qi, Yu Yanjun, L. Wang, Z. He, Synthesis of well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles on eggshell membrane for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 1639–1647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7847-y
M. Prekajski, B. Babic, D. Bucevac, J. Pantíc, J. Gulicovski, M. Miljkovic, B. Matovíc, Synthesis and characterization of biomorphic CeO2 obtained by using egg shell membrane as template. Process. Appl. Ceram. 8(2), 81–85 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2298/PAC1402081P
Qi Wang, C. Ma, J. Tang, C. Zhang, L. Ma, Eggshell membrane-templated MnO2 nanoparticles: facile synthesis and tetracycline hydrochloride decontamination. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 255 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2679-y
R. Camaratta, A.N. Correia-Lima, M.D. Reyes, M.A. Hernández-Fenollosa, J. Orozco-Messana, C.P. Bergmann, Microstructural evolution and optical properties of TiO2 synthesized by eggshell Membrane templating for DSSCs application. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(4), 1569–1574 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.12.047
Q. Dong, H. Su, J. Xu, D. Zhang, R. Wang, Synthesis of biomorphic ZnO interwoven microfibers using eggshell membrane as the biotemplate. Mater. Lett. 61(13), 2714–2717 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.06.091
N. Song, H. Jiang, T. Cui, L. Chang, X. Wang, Synthesis and enhanced gas-sensing properties of mesoporous hierarchical α-Fe2O3 architectures from an eggshell membrane. Micro Nano Lett. 7(9), 943–946 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2012.0631
X. He, D.-P. Yanga, X. Zhang, M. Liu, Z. Kang, C. Lin, N. Jia, R. Luque, Waste eggshell membrane-templated CuO-ZnO nanocomposite with enhanced adsorption, catalysis and antibacterial properties for water purification. Chem. Eng. J. 369, 621–633 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.047
C. Vlgas, S. Machado-de-Souza, E.F.A. Smania, A. Smania Jr., Screening methods to determine antibacterial activity of natural products. Braz. J. Microbiol. 38, 369–380 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822007000200034
S.D. Sarker, L. Nahar, Y. Kumarasamy, Microtitre plate-based antibacterial assay incorporating resazurin as an indicator of cell growth, and its application in the in vitro antibacterial screening of phytochemicals. Methods 42, 321–324 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.01.006
N. Thovhogi, E. Park, E. Manikandan, M. Maaza, A. Gurib-Fakim, Physical properties of CdO nanoparticles synthesized by green chemistry via Hibiscus Sabdariffa flower extract. J. Alloys Compd. 655, 314–320 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.063
P. Senthil Kumar, M. Selvakumar, S. Ganesh-Babu, S. Karuthapandian, S. Chattopadhyay, P. Senthil Kumar, M. Selvakumar, S. Ganesh Babu, S. Karuthapandian, S. Chattopadhyay, CdO nanospheres: Facile synthesis and bandgap modification for the superior photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 151, 45–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.03.047
N.C.S. Selvam, R.T. Kumar, K. Yogeenth, L. John-Kennedy, G. Sekaran, J. Judith Vijaya, Simple and rapid synthesis of cadmium oxide (CdO) nanospheres by a microwave-assisted combustion method. Powder Technol. 211(2–3), 250–255 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2011.04.031
N.D. Krupa, R. Vimala, Evaluation of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) sol–gel coatings, modified with green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles for combating microfouling. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 61, 728–735 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.01.013
S. Jafarirad, M. Mehrabi, B. Divband, M. Kosari-Nasab, Biofabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using fruit extract of Rosa canina and their toxic potential against bacteria: a mechanistic approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 59, 296–302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.09.089
N. Supraja, T.N. Prasad, T. Giridhara-Krishna, E. David, Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of Boswellia ovalifoliolata stem bark-extract-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 581–590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0472-0
K. Qi, B. Cheng, Yu Jiaguo, W. Ho, Review on the improvement of the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 727, 792–820 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.142
Acknowledgements
The author, Dr. K. Venkatachalam gratefully acknowledges the financial assistance from the Department of Science and Technology, India for the DST-SERB Project (Ref. No. EEQ/2016/000559, Date.: 06.02.2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PSSS—conceptualization; methodology; formal analysis; investigation; writing original draft preparation; writing-review and editing. GSC—investigation and methodology. DG—data curation. PP—providing laboratory for testing antimicrobial activity. VK—funding acquisition; visualization; supervision and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundara Selvam, P.S., Chinnadurai, G.S., Ganesan, D. et al. Cadmium Oxide-Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites Synthesized Using Waste Eggshell Membrane and Its In-Vitro Assessments of the Antimicrobial Activities and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 816–835 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01688-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01688-2