Abstract
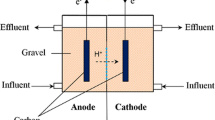
In this study, a single chamber microbial fuel cell (SCMFC) with nano-polypyrrole modified graphite felt as anode- and platinum-coated carbon cloth as cathode was employed to reduce the amount of copper, Cu2+, in synthetic wastewater. The performance of the SCMFC was studied for two inocula, Shewanella putrefaciens and mixed culture. Maximum tolerable concentrations of 50 mg/L and 70 mg/L of copper and power densities of 0.33 W/m2 and 0.304 W/m2 were achieved, respectively, for the pure and mixed cultures. The study shows that microbial tolerance level towards the toxicity of metal strongly influences the MFC performance and the pure culture showed better performance than mixed culture over the Cu toxicity. This study exhibits the possibility of using single chamber microbial fuel cell for treating wastewater containing copper.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cristiani, P.; Carvalho, M.L.; Guerrini, E.; Daghio, M.; Santoro, C.; Li, B.: Bioelectrochemistry cathodic and anodic bio fi lms in single chamber. Microbial Fuel Cells 9, 6–13 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2013.01.005
Feng, C.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Lang, X.; Fan, S.: A dual-chamber microbial fuel cell with conductive film-modified anode and cathode and its application for the neutral electro-Fenton process. Electrochim. Acta 55, 2048–2054 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.11.033
Mustakeem, M.: Electrode materials for microbial fuel cells: nanomaterial approach. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 4, 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40243-015-0063-8
Tang, X.; Li, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, W.; Ng, H.Y.: Conductive polypyrrole hydrogels and carbon nanotubes composite as an anode for microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv. 5, 50968–50974 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA06064H
Mathuriya, A.S.; Yakhmi, J.V.: Microbial fuel cells to recover heavy metals. Environ. Chem. Lett. 12, 483–494 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-014-0474-2
Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Puranik, S.; Lei, Y.; Vadas, T.; Li, B.: Metals as electron acceptors in single-chamber microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 269, 430–439 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.06.117
Abourached, C.; Catal, T.; Liu, H.: Efficacy of single-chamber microbial fuel cells for removal of cadmium and zinc with simultaneous electricity production. Water Res. 51, 228–233 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.062
Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Kong, F.: Copper removal and microbial community analysis in single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 253, 372–377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.046
Rikame, S.S.; Mungray, A.A.; Mungray, A.K.: Modification of anode electrode in microbial fuel cell for electrochemical recovery of energy and copper metal. Electrochim. Acta 275, 8–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.04.141
Rodenas, M.; Peter, H.; Van der Weijden, R.; Saakes, M.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Sleutels, T.H.J.A.: High rate copper and energy recovery in microbial fuel cells. Front. Microbiol. 6, 1–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00527
Roshan, V.; Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Ming, Y.; Tseng, M.: Comparative bioelectricity production from various wastewaters in microbial fuel cells using mixed cultures and a pure strain of Shewanella oneidensis. Bioresour. Technol. 104, 315–323 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.129
Sumisha, A.; Haribabu, K.: Modification of graphite felt using nano polypyrrole and polythiophene for microbial fuel cell applications-a comparative study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43, 3308–3316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.175
Sekar, A.D.; Jayabalan, T.; Muthukumar, H.; Chandrasekaran, N.I.; Mohamed, S.N.; Matheswaran, M.: Enhancing power generation and treatment of dairy waste water in microbial fuel cell using Cu-doped iron oxide nanoparticles decorated anode. Energy 173, 80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.01.102
Singh, S.; Park, I.S.; Shin, Y.; Lee, Y.S.: Comparative study on antimicrobial efficiency of AgSiO2, ZnAg and AgZeolite for the application of fishery plastic container. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 4, 180 (2015)
Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Li, X.: Electrode modification and optimization in air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 15, 1349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071349
Yang, S.; Jia, B.; Liu, H.: Effects of the Pt loading side and cathode-biofilm on the performance of a membrane-less and single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 1197–1202 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.08.005
Liu, H.; Logan, B.E.: Electricity generation using an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4040–4046 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/es0499344
Vullo, D.L.; Ceretti, H.M.; Daniel, M.A.; Ramírez, S.A.M.; Zalts, A.: Cadmium, zinc and copper biosorption mediated by Pseudomonas veronii 2E. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 5574–5581 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.060
Mahmoudkhani, R.; Torabian, A.; Hassani, A.H.; Mahmoudkhani, R.: Copper, cadmium and ferrous removal by membrane bioreactor. APCBEE Procedia. 10, 79–83 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcbee.2014.10.020
Katsou, E.; Malamis, S.; Loizidou, M.: Performance of a membrane bioreactor used for the treatment of wastewater contaminated with heavy metals. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 4325–4332 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anappara, S., Kanirudhan, A., Prabakar, S. et al. Energy Generation in Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell from Pure and Mixed Culture Bacteria by Copper Reduction. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 7719–7724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04832-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04832-9