Abstract
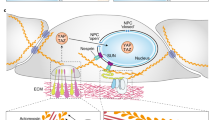
YAP and TAZ are ubiquitously expressed homologous proteins originally identified as penultimate effectors of the Hippo signaling pathway, which plays a key role in maintaining mammalian tissue/organ size. Presently, it is known that YAP/TAZ also interact with various non-Hippo signaling pathways, and have diverse roles in multiple biological processes, including cell proliferation, tissue regeneration, cell lineage fate determination, tumorigenesis, and mechanosensing. In this review, we first examine the various microenvironmental cues and signaling pathways that regulate YAP/TAZ activation, through the Hippo and non-Hippo signaling pathways. This is followed by a brief summary of the interactions of YAP/TAZ with TEAD1-4 and a diverse array of other non-TEAD transcription factors. Finally, we offer a critical perspective on how increasing knowledge of the regulatory mechanisms of YAP/TAZ signaling might open the door to novel therapeutic applications in the interrelated fields of biomaterials, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine and synthetic biology.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webb C, Upadhyay A, Giuntini F, Eggleston I, Furutani-Seiki M, Ishima R, Bagby S (2011) Structural features and ligand binding properties of tandem WW domains from YAP and TAZ, nuclear effectors of the Hippo pathway. Biochemistry 50(16):3300–3309
Lin KC, Park HW, Guan KL (2017) Regulation of the hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD. Trends Biochem Sci 42(11):862–872
Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D et al (2000) TAZ: a novel transcriptional co-activator regulated by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J 19:6778–6791
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A et al (2015) Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347(6220):1260419
Piccolo S, Cordenonsi M, Dupont S (2013) Molecular pathways: YAP and TAZ take center stage in organ growth and tumorigenesis. Clin Cancer Res 19(18):4925–4930
Varelas X (2014) The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development 141(8):1614–1626
Dupont S (2016) Role of YAP/TAZ in cell-matrix adhesion-mediated signalling and mechanotransduction. Exp Cell Res 343(1):42–53
Yu FX, Zhao B, Guan KL (2015) Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell 163(4):811–828
Nardone G, Oliver-De La Cruz J, Vrbsky J, Martini C, Pribyl J, Skládal P, Pešl M, Caluori G, Pagliari S, Martino F, Maceckova Z, Hajduch M, Sanz-Garcia A, Pugno NM, Stokin GB, Forte G (2017) YAP regulates cell mechanics by controlling focal adhesion assembly. Nat Commun. 8:15321
Pardo-Pastor C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Vogel-González M, Serra SA, Afthinos A, Mrkonjic S, Destaing O, Abenza JF, Fernández-Fernández JM, Trepat X, Albiges-Rizo C, Konstantopoulos K, Valverde MA (2018) Piezo2 channel regulates RhoA and actin cytoskeleton to promote cell mechanobiological responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(8):1925–1930
Dupont S, Morsut L, Aragona M, Enzo E, Giulitti S, Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Le Digabel J, Forcato M, Bicciato S, Elvassore N, Piccolo S (2011) Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature 474(7350):179–183
Kim NG, Koh E, Chen X, Gumbiner BM (2011) E-cadherin mediates contact inhibition of proliferation through Hippo signaling-pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(29):11930–11935
Paramasivam M, Sarkeshik A, Yates JR 3rd, Fernandes MJ, McCollum D (2011) Angiomotin family proteins are novel activators of the LATS2 kinase tumor suppressor. Mol Biol Cell 22(19):3725–3733
Zhong W, Tian K, Zheng X, Li L, Zhang W, Wang S, Qin J (2013) Mesenchymal stem cell and chondrocyte fates in a multishear microdevice are regulated by Yes-associated protein. Stem Cells Dev 22(14):2083–2093
Wang KC, Yeh YT, Nguyen P, Limqueco E, Lopez J, Thorossian S, Guan KL, Li YJ, Chien S (2016) Flow-dependent YAP/TAZ activities regulate endothelial phenotypes and atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(41):11525–11530
Wang L, Luo JY, Li B, Tian XY, Chen LJ, Huang Y, Liu J, Deng D, Lau CW, Wan S, Ai D, Mak KK, Tong KK, Kwan KM, Wang N, Chiu JJ, Zhu Y, Huang Y (2016) Integrin-YAP/TAZ-JNK cascade mediates atheroprotective effect of unidirectional shear flow. Nature 540(7634):579–582
Nakajima H, Yamamoto K, Agarwala S, Terai K, Fukui H, Fukuhara S, Ando K, Miyazaki T, Yokota Y, Schmelzer E, Belting HG, Affolter M, Lecaudey V, Mochizuki N (2017) Flow-dependent endothelial YAP regulation contributes to vessel maintenance. Dev Cell 40(6):523–536
Cai H, Xu Y (2013) The role of LPA and YAP signaling in long-term migration of human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Commun Signal 11(1):31
Yu FX, Zhao B, Panupinthu N, Jewell JL, Lian I, Wang LH, Zhao J, Yuan H, Tumaneng K, Li H, Fu XD, Mills GB, Guan KL (2012) Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell 150(4):780–791
Yang X, Shen H, Buckley B, Chen Y, Yang N, Mussell AL, Chernov M, Kobzik L, Frangou C, Han SX, Zhang J (2018) NTRK1 is a positive regulator of YAP oncogenic function. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0609-1
Chen J, Harris RC (2016) Interaction of the EGF receptor and the hippo pathway in the diabetic kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(6):1689–1700
DeRan M, Yang J, Shen CH, Peters EC, Fitamant J, Chan P, Hsieh M, Zhu S, Asara JM, Zheng B, Bardeesy N, Liu J, Wu X (2014) Energy stress regulates hippo-YAP signaling involving AMPK-mediated regulation of angiomotin-like 1 protein. Cell Rep 9(2):495–503
Mo JS, Meng Z, Kim YC, Park HW, Hansen CG, Kim S, Lim DS, Guan KL (2015) Cellular energy stress induces AMPK-mediated regulation of YAP and the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol 17(4):500–510
Moon S, Kim W, Kim S, Kim Y, Song Y, Bilousov O, Kim J, Lee T, Cha B, Kim M, Kim H, Katanaev VL, Jho EH (2017) Phosphorylation by NLK inhibits YAP-14-3-3-interactions and induces its nuclear localization. EMBO Rep 18(1):61–71
Ma B, Chen Y, Chen L, Cheng H, Mu C, Li J, Gao R, Zhou C, Cao L, Liu J, Zhu Y, Chen Q, Wu S (2015) Hypoxia regulates Hippo signalling through the SIAH2 ubiquitin E3 ligase. Nat Cell Biol 17(1):95–103
Kim HB, Kim M, Park YS, Park I, Kim T, Yang SY, Cho CJ, Hwang D, Jung JH, Markowitz SD, Hwang SW, Yang SK, Lim DS, Myung SJ (2017) Prostaglandin E2 activates YAP and a positive-signaling loop to promote colon regeneration after colitis but also carcinogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology 152(3):616–630
Choi HJ, Kim NE, Kim BM, Seo M, Heo JH (2018) TNF-α-induced YAP/TAZ activity mediates leukocyte-endothelial adhesion by regulating vcam1 expression in endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci 19(11):3428
Tharehalli U, Svinarenko M, Kraus JM, Kühlwein SD, Szekely R, Kiesle U, Scheffold A, Barth TFE, Kleger A, Schirmbeck R, Kestler HA, Seufferlein T, Oswald F, Katz SF, Lechel A (2018) YAP activation drives liver regeneration after cholestatic damage induced by Rbpj deletion. Int J Mol Sci 19(12):3801
Flinn MA, Link BA, O’Meara CC (2019) Upstream regulation of the Hippo-Yap pathway in cardiomyocyte regeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol 100:10–11
Gregorieff A, Liu Y, Inanlou MR, Khomchuk Y, Wrana JL (2015) Yap-dependent reprogramming of Lgr5(+) stem cells drives intestinal regeneration and cancer. Nature 526(7575):715–718
Kim W, Jho EH (2018) The history and regulatory mechanism of the Hippo pathway. BMB Rep. 51(3):106–118
Kim Y, Jho EH (2018) Regulation of the Hippo signaling pathway by ubiquitin modification. BMB Rep 51(3):143–150
Deng X, Fang L (2018) VGLL4 is a transcriptional cofactor acting as a novel tumor suppressor via interacting with TEADs. Am J Cancer Res 8(6):932–943
Dobrokhotov O, Samsonov M, Sokabe M, Hirata H (2018) Mechanoregulation and pathology of YAP/TAZ via Hippo and non-Hippo mechanisms. Clin Transl Med 7(1):23
Serrano I, McDonald PC, Lock F, Muller WJ, Dedhar S (2013) Inactivation of the Hippo tumour suppressor pathway by integrin-linked kinase. Nat Commun 4:2976
Kim NG, Gumbiner BM (2015) Adhesion to fibronectin regulates Hippo signaling via the FAK-Src-PI3K pathway. J Cell Biol 210(3):503–515
Elbediwy A, Vincent-Mistiaen ZI, Spencer-Dene B, Stone RK, Boeing S, Wculek SK, Cordero J, Tan EH, Ridgway R, Brunton VG, Sahai E, Gerhardt H, Behrens A, Malanchi I, Sansom OJ, Thompson BJ (2016) Integrin signalling regulates YAP and TAZ to control skin homeostasis. Development 143(10):1674–1687
Fan R, Kim NG, Gumbiner BM (2013) Regulation of Hippo pathway by mitogenic growth factors via phosphoinositide 3-kinase and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(7):2569–2574
Sabra H, Brunner M, Mandati V, Wehrle-Haller B, Lallemand D, Ribba AS, Chevalier G, Guardiola P, Block MR, Bouvard D (2017) β1 integrin-dependent Rac/group I PAK signaling mediates YAP activation of Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) via NF2/merlin. J Biol Chem 292(47):19179–19197
Ladoux B, Nelson WJ, Yan J, Mège RM (2015) The mechanotransduction machinery at work at adherens junctions. Integr Biol (Camb) 7(10):1109–1119
Gladden AB, Hebert AM, Schneeberger EE, McClatchey AI (2010) The NF2 tumor suppressor, Merlin, regulates epidermal development through the establishment of a junctional polarity complex. Dev Cell 19(5):727–739
Yu J, Zheng Y, Dong J, Klusza S, Deng WM, Pan D (2010) Kibra functions as a tumor suppressor protein that regulates Hippo signaling in conjunction with Merlin and Expanded. Dev Cell 18(2):288–299
Gumbiner BM, Kim NG (2014) The Hippo-YAP signaling pathway and contact inhibition of growth. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 4):709–717
Yin F, Yu J, Zheng Y, Chen Q, Zhang N, Pan D (2013) Spatial organization of Hippo signaling at the plasma membrane mediated by the tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2. Cell 154(6):1342–1355
Meng Z, Moroishi T, Mottier-Pavie V, Plouffe SW, Hansen CG, Hong AW, Park HW, Mo JS, Lu W, Lu S, Flores F, Yu FX, Halder G, Guan KL (2015) MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway. Nat Commun 5(6):8357
Dutta S, Mana-Capelli S, Paramasivam M, Dasgupta I, Cirka H, Billiar K, McCollum D (2018) TRIP6 inhibits Hippo signaling in response to tension at adherens junctions. EMBO Rep 19(2):337–350
Yi C, Troutman S, Fera D, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Avila JL, Christian N, Persson NL, Shimono A, Speicher DW, Marmorstein R, Holmgren L, Kissil JL (2011) A tight junction-associated Merlin-angiomotin complex mediates Merlin’s regulation of mitogenic signaling and tumor suppressive functions. Cancer Cell 19(4):527–540
Liem RK (2016) Cytoskeletal integrators: the spectrin superfamily. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8(10):a018259
Wong KK, Li W, An Y, Duan Y, Li Z, Kang Y, Yan Y (2015) β-Spectrin regulates the hippo signaling pathway and modulates the basal actin network. J Biol Chem 290(10):6397–6407
Fletcher GC, Elbediwy A, Khanal I, Ribeiro PS, Tapon N, Thompson BJ (2015) The spectrin cytoskeleton regulates the Hippo signalling pathway. EMBO J 34(7):940–954
Heng BC, Aubel D, Fussenegger M (2013) An overview of the diverse roles of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the pathophysiology of various human diseases. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1676–1694
Xia H, Dai X, Yu H, Zhou S, Fan Z, Wei G, Tang Q, Gong Q, Bi F (2018) EGFR-PI3K-PDK1 pathway regulates YAP signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: the mechanism and its implications in targeted therapy. Cell Death Dis 9(3):269
Hirate Y, Hirahara S, Inoue K, Kiyonari H, Niwa H, Sasaki H (2015) Par-aPKC-dependent and -independent mechanisms cooperatively control cell polarity, Hippo signaling, and cell positioning in 16-cell stage mouse embryos. Dev Growth Differ 57(8):544–556
Suzuki A, Yamanaka T, Hirose T, Manabe N, Mizuno K, Shimizu M, Akimoto K, Izumi Y, Ohnishi T, Ohno S (2001) Atypical protein kinase C is involved in the evolutionarily conserved par protein complex and plays a critical role in establishing epithelia-specific junctional structures. J Cell Biol 152(6):1183–1196
Vorhagen S, Niessen CM (2014) Mammalian aPKC/Par polarity complex mediated regulation of epithelial division orientation and cell fate. Exp Cell Res 328(2):296–302
Yin Y, Sheng J, Hu R, Yang Y, Qing S (2014) The expression and localization of Crb3 in developmental stages of the mice embryos and in different organs of 1-week-old female mice. Reprod Domest Anim 49(5):824–830
Szymaniak AD, Mahoney JE, Cardoso WV, Varelas X (2015) Crumbs3-mediated polarity directs airway epithelial cell fate through the hippo pathway effector yap. Dev Cell 34(3):283–296
Yates LL, Schnatwinkel C, Hazelwood L, Chessum L, Paudyal A, Hilton H, Romero MR, Wilde J, Bogani D, Sanderson J, Formstone C, Murdoch JN, Niswander LA, Greenfield A, Dean CH (2013) Scribble is required for normal epithelial cell-cell contacts and lumen morphogenesis in the mammalian lung. Dev Biol 373(2):267–280
Archibald A, Al-Masri M, Liew-Spilger A, McCaffrey L (2015) Atypical protein kinase C induces cell transformation by disrupting Hippo/Yap signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 26(20):3578–3595
Zhou PJ, Xue W, Peng J, Wang Y, Wei L, Yang Z, Zhu HH, Fang YX, Gao WQ (2017) Elevated expression of Par3 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by forming a Par3/aPKC/KIBRA complex and inactivating the hippo pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):139
Narimatsu M, Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Varelas X, Wrana JL (2015) Distinct polarity cues direct Taz/Yap and TGFβ receptor localization to differentially control TGFβ-induced Smad signaling. Dev Cell 32(5):652–656
Liu J, Li J, Li P, Wang Y, Liang Z, Jiang Y, Li J, Feng C, Wang R, Chen H, Zhou C, Zhang J, Yang J, Liu P (2017) Loss of DLG5 promotes breast cancer malignancy by inhibiting the Hippo signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7(7):42125
Bae SJ, Ni L, Osinski A, Tomchick DR, Brautigam CA, Luo X (2017) SAV1 promotes Hippo kinase activation through antagonizing the PP2A phosphatase STRIPAK. Elife 6:e30278
Boggiano JC, Vanderzalm PJ, Fehon RG (2011) Tao-1 phosphorylates Hippo/MST kinases to regulate the Hippo-Salvador-Warts tumor suppressor pathway. Dev Cell 21(5):888–895
Meng Z, Moroishi T, Mottier-Pavie V, Plouffe SW, Hansen CG, Hong AW, Park HW, Mo JS, Lu W, Lu S, Flores L, Yu FX, Halder G, Guan KL (2015) MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway. Nat Commun 6:8357
Wang W, Xiao ZD, Li X, Aziz KE, Gan B, Johnson RL, Chen J (2015) AMPK modulates Hippo pathway activity to regulate energy homeostasis. Nat Cell Biol 17(4):490–499
Wang W, Huang J, Wang X, Yuan J, Li X, Feng L, Park JI, Chen J (2012) PTPN14 is required for the density-dependent control of YAP1. Genes Dev 26(17):1959–1971
Wilson KE, Li YW, Yang N, Shen H, Orillion AR, Zhang J (2014) PTPN14 forms a complex with Kibra and LATS1 proteins and negatively regulates the YAP oncogenic function. J Biol Chem 289(34):23693–23700
Elosegui-Artola A, Andreu I, Beedle AEM, Lezamiz A, Uroz M, Kosmalska AJ, Oria R, Kechagia JZ, Rico-Lastres P, Le Roux AL, Shanahan CM, Trepat X, Navajas D, Garcia-Manyes S, Roca-Cusachs P (2017) Force triggers YAP nuclear entry by regulating transport across nuclear pores. Cell 171(6):1397–1410
Frey S, Görlich D (2007) A saturated FG-repeat hydrogel can reproduce the permeability properties of nuclear pore complexes. Cell 130:512–523
Furukawa KT, Yamashita K, Sakurai N, Ohno S (2017) The Epithelial Circumferential Actin Belt Regulates YAP/TAZ through Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling of Merlin. Cell Rep 20(6):1435–1447
Domínguez-Calderón A, Ávila-Flores A, Ponce A, López-Bayghen E, Calderón-Salinas JV, Luis Reyes J, Chávez-Munguía B, Segovia J, Angulo C, Ramírez L, Gallego-Gutiérrez H, Alarcón L, Martín-Tapia D, Bautista-García P, González-Mariscal L (2016) ZO-2 silencing induces renal hypertrophy through a cell cycle mechanism and the activation of YAP and the mTOR pathway. Mol Biol Cell 27(10):1581–1595
Schaefer KN, Bonello TT, Zhang S, Williams CE, Roberts DM, McKay DJ, Peifer M (2018) Supramolecular assembly of the beta-catenin destruction complex and the effect of Wnt signaling on its localization, molecular size, and activity in vivo. PLoS Genet 14(4):e1007339
Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E, Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V, Fassina A, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S (2014) YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 158(1):157–170
Oudhoff MJ, Freeman SA, Couzens AL, Antignano F, Kuznetsova E, Min PH, Northrop JP, Lehnertz B, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Vedadi M, Arrowsmith CH, Nishina H, Gold MR, Rossi FM, Gingras AC, Zaph C (2013) Control of the hippo pathway by Set7-dependent methylation of Yap. Dev Cell 26(2):188–194
Liu X, Yang N, Figel SA, Wilson KE, Morrison CD, Gelman IH, Zhang J (2013) PTPN14 interacts with and negatively regulates the oncogenic function of YAP. Oncogene 32(10):1266–1273
Hozumi K (2020) Distinctive properties of the interactions between Notch and Notch ligands. Dev Growth Differ 62(1):49–58
Totaro A, Castellan M, Di Biagio D, Piccolo S (2018) Crosstalk between YAP/TAZ and notch signaling. Trends Cell Biol 28(7):560–573
Li Y, Hibbs MA, Gard AL, Shylo NA, Yun K (2012) Genome-wide analysis of N1ICD/RBPJ targets in vivo reveals direct transcriptional regulation of Wnt, SHH, and hippo pathway effectors by Notch1. Stem Cells 30(4):741–752
Slemmons KK, Crose LES, Riedel S, Sushnitha M, Belyea B, Linardic CM (2017) A novel Notch-YAP circuit drives stemness and tumorigenesis in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Mol Cancer Res 15(12):1777–1791
Lu J, Zhou Y, Hu T, Zhang H, Shen M, Cheng P, Dai W, Wang F, Chen K, Zhang Y, Wang C, Li J, Zheng Y, Yang J, Zhu R, Wang J, Lu W, Zhang H, Wang J, Xia Y, De Assuncao TM, Jalan-Sakrikar N, Huebert RC, Bin Z, Guo C (2016) Notch signaling coordinates progenitor cell-mediated biliary regeneration following partial hepatectomy. Sci Rep 6:22754
Derynck R, Budi EH (2019) Specificity, versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci Signal 12(570):5183
Chaikuad A, Bullock AN (2016) Structural basis of intracellular TGF-β signaling: receptors and smads. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8(11):a022111
Ben Mimoun S, Mauviel A (2018) Molecular mechanisms underlying TGF-ß/Hippo signaling crosstalks—role of baso-apical epithelial cell polarity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 98:75–81
Saito A, Nagase T (2015) Hippo and TGF-β interplay in the lung field. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 309(8):L756–L767
Miranda MZ, Bialik JF, Speight P, Dan Q, Yeung T, Szászi K, Pedersen SF, Kapus A (2017) TGF-β1 regulates the expression and transcriptional activity of TAZ protein via a Smad3-independent, myocardin-related transcription factor-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem 292(36):14902–14920
Wang Y, Tu K, Liu D, Guo L, Chen Y, Li Q, Maiers JL, Liu Z, Shah VH, Dou C, Tschumperlin D, Voneschen L, Yang R, Kang N (2019) p300 acetyltransferase is a cytoplasm-to-nucleus shuttle for SMAD2/3 and TAZ nuclear transport in transforming growth factor β-stimulated hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 70(4):1409–1423
Pefani DE, Pankova D, Abraham AG, Grawenda AM, Vlahov N, Scrace S, O’Neill E (2016) TGF-β targets the hippo pathway scaffold RASSF1A to facilitate YAP/SMAD2 nuclear translocation. Mol Cell 63(1):156–166
Holden JK, Cunningham CN (2018) Targeting the hippo pathway and cancer through the TEAD family of transcription factors. Cancers (Basel). 10(3):81
Yasunami M, Suzuki K, Ohkubo H (1996) A novel family of TEA domain-containing transcription factors with distinct spatiotemporal expression patterns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 228(2):365–370
Moya IM, Halder G (2018) Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0086-y
Oh H, Slattery M, Ma L, White KP, Mann RS (2014) Irvine KD Yorkie promotes transcription by recruiting a histone methyltransferase complex. Cell Rep 8(2):449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.017
Zhu Y, Li D, Wang Y, Pei C, Liu S, Zhang L, Yuan Z, Zhang P (2015) Brahma regulates the Hippo pathway activity through forming complex with Yki-Sd and regulating the transcription of Crumbs. Cell Signal 27(3):606–613
Lin KC, Moroishi T, Meng Z, Jeong HS, Plouffe SW, Sekido Y, Han J, Park HW, Guan KL (2017) Regulation of Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD by p38 MAPK-induced cytoplasmic translocation. Nat Cell Biol 19(8):996–1002
Zhang W, Gao Y, Li P, Shi Z, Guo T, Li F, Han X, Feng Y, Zheng C, Wang Z, Li F, Chen H, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Ji H (2014) VGLL4 functions as a new tumor suppressor in lung cancer by negatively regulating the YAP-TEAD transcriptional complex. Cell Res 24(3):331–343
Lin Z, Guo H, Cao Y, Zohrabian S, Zhou P, Ma Q, VanDusen N, Guo Y, Zhang J, Stevens SM, Liang F, Quan Q, van Gorp PR, Li A, Dos Remedios C, He A, Bezzerides VJ, Pu WT (2016) Acetylation of VGLL4 Regulates Hippo-YAP Signaling and Postnatal Cardiac Growth. Dev Cell 39(4):466–479
Grannas K, Arngården L, Lönn P, Mazurkiewicz M, Blokzijl A, Zieba A, Söderberg O (2015) Crosstalk between Hippo and TGFβ: subcellular Localization of YAP/TAZ/Smad complexes. J Mol Biol 427(21):3407–3415
Brusgard JL, Choe M, Chumsri S, Renoud K, MacKerell AD Jr, Sudol M, Passaniti A (2015) RUNX2 and TAZ-dependent signaling pathways regulate soluble E-Cadherin levels and tumorsphere formation in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 6(29):28132–28150
Lin X, Yang H, Wang L, Li W, Diao S, Du J, Wang S, Dong R, Li J, Fan Z (2019) AP2a enhanced the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting the formation of YAP/RUNX2 complex and BARX1 transcription. Cell Prolif 52(1):e12522
Tomlinson V, Gudmundsdottir K, Luong P, Leung KY, Knebel A, Basu S (2010) JNK phosphorylates Yes-associated protein (YAP) to regulate apoptosis. Cell Death Dis 1:e29
Roperch JP, El Ouadrani K, Hendrix A, Emami S, De Wever O, Melino G, Gespach C (2008) Netrin-1 induces apoptosis in human cervical tumor cells via the TAp73alpha tumor suppressor. Cancer Res 68(20):8231–8239
Bora-Singhal N, Nguyen J, Schaal C, Perumal D, Singh S, Coppola D, Chellappan S (2015) YAP1 regulates OCT4 activity and SOX2 expression to facilitate self-renewal and vascular mimicry of stem-like cells. Stem Cells 33(6):1705–1718
Kuser-Abali G, Alptekin A, Lewis M, Garraway IP, Cinar B (2015) YAP1 and AR interactions contribute to the switch from androgen-dependent to castration-resistant growth in prostate cancer. Nat Commun 1(6):8126
Liu H, Dai X, Cao X, Yan H, Ji X, Zhang H, Shen S, Si Y, Zhang H, Chen J, Li L, Zhao JC, Yu J, Feng XH, Zhao B (2018) PRDM4 mediates YAP-induced cell invasion by activating leukocyte-specific integrin β2 expression. EMBO Rep 19(6):e45180
Panciera T, Azzolin L, Fujimura A, Di Biagio D, Frasson C, Bresolin S, Soligo S, Basso G, Bicciato S, Rosato A, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S (2016) Induction of expandable tissue-specific stem/progenitor cells through transient expression of YAP/TAZ. Cell Stem Cell 19(6):725–737
Ohgushi M, Minaguchi M, Sasai Y (2015) Rho-signaling-directed YAP/TAZ activity underlies the long-term survival and expansion of human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 17(4):448–461
Yang W, Han W, He W, Li J, Wang J, Feng H, Qian Y (2016) Surface topography of hydroxyapatite promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 60:45–53
Zhang Y, Gong H, Sun Y, Huang Y, Fan Y (2016) Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells on grid-topographic surface and evidence for involvement of YAP mediator. J Biomed Mater Res A. 104(5):1143–1152
Qian W, Gong L, Cui X, Zhang Z, Bajpai A, Liu C, Castillo AB, Teo JCM, Chen W (2017) Nanotopographic regulation of human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(48):41794–41806
Hwang JH, Lee DH, Byun MR, Kim AR, Kim KM, Park JI, Oh HT, Hwang ES, Lee KB, Hong JH (2017) Nanotopological plate stimulates osteogenic differentiation through TAZ activation. Sci Rep 7(1):3632
Arslan E, Hatip Koc M, Uysal O, Dikecoglu B, Topal AE, Garifullin R, Ozkan AD, Dana A, Hermida-Merino D, Castelletto V, Edwards-Gayle C, Baday S, Hamley I, Tekinay AB, Guler MO (2017) Supramolecular peptide nanofiber morphology affects mechanotransduction of stem cells. Biomacromol 18(10):3114–3130
Sedlmayer F, Aubel D, Fussenegger M (2018) Synthetic gene circuits for the detection, elimination and prevention of disease. Nat Biomed Eng. 2(6):399–415
Tolle F, Stücheli P, Fussenegger M (2019) Genetic circuitry for personalized human cell therapy. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7(59):31–38
Schütte U, Bisht S, Heukamp LC, Kebschull M, Florin A, Haarmann J, Hoffmann P, Bendas G, Buettner R, Brossart P, Feldmann G (2014) Hippo signaling mediates proliferation, invasiveness, and metastatic potential of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl Oncol 7(2):309–321
Lian I, Kim J, Okazawa H, Zhao J, Zhao B, Yu J, Chinnaiyan A, Israel MA, Goldstein LS, Abujarour R, Ding S, Guan KL (2010) The role of YAP transcription coactivator in regulating stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Genes Dev 24(11):1106–1118
Wang S, Ma K, Chen L, Zhu H, Liang S, Liu M, Xu N (2016) TAZ promotes cell growth and inhibits Celastrol-induced cell apoptosis. Biosci Rep 36(5)
Tian T, Li A, Lu H, Luo R, Zhang M, Li Z (2015) TAZ promotes temozolomide resistance by upregulating MCL-1 in human glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 463(4):638–643
Yagi R, Kohn MJ, Karavanova I, Kaneko KJ, Vullhorst D, DePamphilis ML, Buonanno A (2007) Transcription factor TEAD4 specifies the trophectoderm lineage at the beginning of mammalian development. Development 134(21):3827–3836
Lv XY, Sun W, Su R, Li D, Wang QZ, Musa HH, Chen L, Zhang YF, Wu WZ (2015) Correlation between sheep YAP1 temporal and spatial expression trends and MSTN and MyoG gene expression. Genet Mol Res 14(2):3244–3256
Ralston A, Cox BJ, Nishioka N, Sasaki H, Chea E, Rugg-Gunn P, Guo G, Robson P, Draper JS, Rossant J (2010) Gata3 regulates trophoblast development downstream of Tead4 and in parallel to Cdx2. Development 137(3):395–403
Ribas R, Moncaut N, Siligan C, Taylor K, Cross JW, Rigby PW, Carvajal JJ (2011) Members of the TEAD family of transcription factors regulate the expression of Myf5 in ventral somitic compartments. Dev Biol 355(2):372–380
Liu X, Li H, Rajurkar M, Li Q, Cotton JL, Ou J, Zhu LJ, Goel HL, Mercurio AM, Park JS, Davis RJ, Mao J (2016) Tead and AP1 Coordinate Transcription and Motility. Cell Rep 14(5):1169–1180
Qiao Y, Chen J, Lim YB, Finch-Edmondson ML, Seshachalam VP, Qin L, Jiang T, Low BC, Singh H, Lim CT, Sudol M (2017) YAP regulates actin dynamics through ARHGAP29 and promotes metastasis. Cell Rep 19(8):1495–1502
Ehmer U, Zmoos AF, Auerbach RK, Vaka D, Butte AJ, Kay MA, Sage J (2014) Organ size control is dominant over Rb family inactivation to restrict proliferation in vivo. Cell Rep 8(2):371–381
Shen Z, Stanger BZ (2015) YAP regulates S-phase entry in endothelial cells. PLoS One 10(1):e0117522
Lo Sardo F, Forcato M, Sacconi A, Capaci V, Zanconato F, Di Agostino S, Del Sal G, Pandolfi PP, Strano S, Bicciato S, Blandino G (2017) MCM7 and its hosted miR-25, 93 and 106b cluster elicit YAP/TAZ oncogenic activity in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 38(1):64–75
Wang Z, Wu Y, Wang H, Zhang Y, Mei L, Fang X, Zhang X, Zhang F, Chen H, Liu Y, Jiang Y, Sun S, Zheng Y, Li N, Huang L (2014) Interplay of mevalonate and Hippo pathways regulates RHAMM transcription via YAP to modulate breast cancer cell motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(1):E89–E98
Zhao B, Ye X, Yu J, Li L, Li W, Li S, Yu J, Lin JD, Wang CY, Chinnaiyan AM, Lai ZC, Guan KL (2008) TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev 22(14):1962–1971
Zhang H, Pasolli HA, Fuchs E (2011) Yes-associated protein (YAP) transcriptional coactivator functions in balancing growth and differentiation in skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(6):2270–2275
Xu MZ, Chan SW, Liu AM, Wong KF, Fan ST, Chen J, Poon RT, Zender L, Lowe SW, Hong W, Luk JM (2011) AXL receptor kinase is a mediator of YAP-dependent oncogenic functions in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 30(10):1229–1240
Zhang Y, Xia H, Ge X, Chen Q, Yuan D, Chen Q, Leng W, Chen L (2014) Tang Q1 Bi F. CD44 acts through RhoA to regulate YAP signaling. Cell Signal 26(11):2504–2513
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFC1105303/04), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51772006, 31670993, 51973004, 81991505), Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission Projects (Grant No. Z181100002018001), and Peking University Medicine Fund (Grant Nos. PKU2020LCXQ009, BMU2020PYB029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Boon Chin Heng and Xuehui Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heng, B.C., Zhang, X., Aubel, D. et al. An overview of signaling pathways regulating YAP/TAZ activity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 497–512 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03579-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03579-8