Abstract
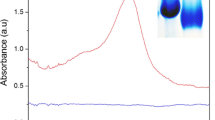
A hydrothermal method has been employed to synthesize a green and one-pot carbon dots-based sensor for ratiometric monitoring and imaging lysosomal pH in living cells. The carbon dots were directly functionalized by abundant amino groups during synthesis and exhibited dual emission bands at 439 and 550 nm under single-wavelength excitation of 380 nm without any additional modification. In addition to its small size, the established sensor had good biocompatibility. Owing to its abundant amino groups and good hydrophilicity, the sensor is able to target lysosome with high Pearson’s colocalization coefficients (0.935 and 0.924) and responds to change of lysosomal pH in living cells. It also had excellent pH sensitivity and reversibility, and anti-interference capability, thus enabling sensing pH change in intracellular environment in real time, as demonstrated by successful monitoring of lysosomal pH changes during lysosomal alkalization, dexamethasone-induced stimulation, and stress in Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 cells (blue channel, excitation = 405 nm and emission = 419–459 nm bandpass; and yellow channel, excitation = 405 nm and emission = 530–570 nm bandpass).

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shrode LD, Tapper H, Grinstein S (1997) Role of intracellular pH in proliferation, transformation, and apoptosis. J Bioenerg Biomembr 29(4):393–399
Kennedy RT, Lan H, Aspinwall CA (1996) Extracellular pH is required for rapid release of insulin from Zn−insulin precipitates in β-cell secretory vesicles during exocytosis. J Am Chem Soc 118(7):1795–1796
Simon S, Roy D, Schindler M (1994) Intracellular pH and the control of multidrug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(3):1128–1132
Lakadamyali M, Rust MJ, Babcock HP, Zhuang XW (2003) Visualizing infection of individual influenza viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(16):9280–9285
Zhang XM, Lin YX, Gillies RJ (2010) Tumor pH and its measurement. J Nucl Med 51(8):1167–1170
Wan QQ, Chen SM, Shi W, Li LH, Ma HM (2014) Lysosomal pH rise during heat shock monitored by a lysosome-targeting near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent probe. Angew Chem-Int Edit 53(41):10916–10920
Li G, Zhu D, Xue L, Jiang H (2013) Quinoline-based fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection of lysosomal pH. Org Lett 15(19):5020–5023
Turk B, Turk V (2009) Lysosomes as “suicide bags” in cell death: myth or reality? J Biol Chem 284(33):21783–21787
Wang L, Fan ZC, Zhang JY, Changyi YZ, Huang CY, Gu YJ, Xu ZY, Tang ZJ, Lu WY, Wei XB, Li C (2015) Evaluating tumor metastatic potential by imaging intratumoral acidosis via pH-activatable near-infrared fluorescent probe. Int J Cancer 136(4):E107–E116
Li HJ, Du JZ, Liu J, Du XJ, Shen S, Zhu YH, Wang XY, Ye XD, Nie SM, Wang J (2016) Smart superstructures with ultrahigh pH-sensitivity for targeting acidic tumor microenvironment: instantaneous size switching and improved tumor penetration. ACS Nano 10(7):6753–6761
Han JY, Burgess K (2010) Fluorescent indicators for intracellular pH. Chem Rev 110(5):2709–2728
Tang B, Yu F, Li P, Tong LL, Duan X, Xie T, Wang X (2009) A near-infrared neutral pH fluorescent probe for monitoring minor pH changes: imaging in living HepG2 and HL-7702 cells. J Am Chem Soc 131(8):3016–3023
Yang LM, Li N, Pan W, Yu ZZ, Tang B (2015) Real-time imaging of mitochondrial hydrogen peroxide and pH fluctuations in living cells using a fluorescent nanosensor. Anal Chem 87(7):3678–3684
Myochin T, Kiyose K, Hanaoka K, Kojima H, Terai T, Nagano T (2011) Rational design of ratiometric near-infrared fluorescent pH probes with various pK(a) values, based on aminocyanine. J Am Chem Soc 133(10):3401–3409
Tantama M, Hung YP, Yellen G (2011) Imaging intracellular pH in live cells with a genetically encoded red fluorescent protein sensor. J Am Chem Soc 133(26):10034–10037
Esposito A, Gralle M, Dani MAC, Lange D, Wouters FS (2008) pHlameleons: a family of FRET-based protein sensors for quantitative pH imaging. Biochemistry 47(49):13115–13126
Huang J, Ying L, Yang XH, Yang YJ, Quan K, Wang H, Xie N, Ou M, Zhou QF, Wang KM (2015) Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pH values in living cells by dual-fluorophore-labeled i-motif nanoprobes. Anal Chem 87(17):8724–8731
Shi W, Li XH, Ma HM (2012) A tunable ratiometric pH sensor based on carbon nanodots for the quantitative measurement of the intracellular pH of whole cells. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 51(26):6432–6435
Zhang YA, Guo S, Cheng SB, Ji XH, He ZK (2017) Label-free silicon nanodots featured ratiometric fluorescent aptasensor for lysosomal imaging and pH measurement. Biosens Bioelectron 94:478–484
Pramanik S, Roy S, Mondal A, Bhandari S (2019) A two- target responsive reversible ratiometric pH nanoprobe: a white light emitting quantum dot complex. Chem Commun 55(30):4331–4334
Yuan FL, Li SH, Fan ZT, Meng XY, Fan LZ, Yang SH (2016) Shining carbon dots: synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Nano Today 11(5):565–586
Han M, Zhu SJ, Lu SY, Song YB, Feng TL, Tao SY, Liu JJ, Yang B (2018) Recent progress on the photocatalysis of carbon dots: classification, mechanism and applications. Nano Today 19:201–218
Nie H, Li MJ, Li QS, Liang SJ, Tan YY, Sheng L, Shi W, Zhang SXA (2014) Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing. Chem Mat 26(10):3104–3112
E S, Mao QX, Yuan XL, Kong XL, Chen XW, Wang JH (2018) Targeted imaging of the lysosome and endoplasmic reticulum and their pH monitoring with surface regulated carbon dots. Nanoscale 10(26):12788–12796
Guo S, Sun Y, Geng X, Yang R, Xiao L, Qu L, Li Z (2020) Intrinsic lysosomal targeting fluorescent carbon dots with ultrastability for long-term lysosome imaging. J Mater Chem B 8(4):736–742
Zhang QQ, Yang T, Li RS, Zou HY, Li YF, Guo J, Liu XD, Huang CZ (2018) A functional preservation strategy for the production of highly photoluminescent emerald carbon dots for lysosome targeting and lysosomal pH imaging. Nanoscale 10(30):14705–14711
Zhang FM, He X, Ma PY, Sun Y, Wang XH, Song DQ (2018) Rapid aqueous synthesis of CuInS/ZnS quantum dots as sensor probe for alkaline phosphatase detection and targeted imaging in cancer cells. Talanta 189:411–417
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun HC, Wang HY, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 52(14):3953–3957
Liu JJ, Li DW, Zhang K, Yang MX, Sun HC, Yang B (2018) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped conjugated carbonized polymer dots with 31% efficient red emission for in vivo imaging. Small 14(15):10
Lu WJ, Jiao Y, Gao YF, Qiao J, Mozneb M, Shuang SM, Dong C, Li CZ (2018) Bright yellow fluorescent carbon dots as a multifunctional sensing platform for the label-free detection of fluoroquinolones and histidine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(49):42915–42924
Wang H, Li ZH, Gao F, Zhao JQ, Zhu MX, He X, Niu N, Zhao W (2016) Immunoprotection of recombinant Eg.P29 against Echinococcus granulosus in sheep. Vet Res Commun 40(2):73–79
Peng JF, He XX, Wang KM, Tan WH, Wang Y, Liu Y (2007) Noninvasive monitoring of intracellular pH change induced by drug stimulation using silica nanoparticle sensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 388(3):645–654
Bao BQ, Yang ZY, Liu YF, Xu Y, Gu BB, Chen J, Su P, Tong L, Wang LH (2019) Two-photon semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as a new platform for imaging of intracellular pH variation. Biosens Bioelectron 126:129–135
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Developing Foundation of Jilin Province of China (No. 20180201050YY), Industrial Innovation Funds of Jilin Province of China (No. 2018C034-1), and Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (No. 101832018C172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 512 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., He, X., Huang, Y. et al. Lysosome-targeted ratiometric fluorescent sensor for monitoring pH in living cells based on one-pot-synthesized carbon dots. Microchim Acta 187, 478 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04462-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04462-w