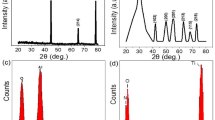
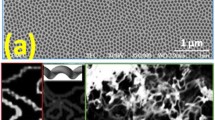
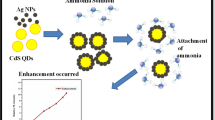
Abstract
A low-angle–dependent photonic crystal hydrogel (LAD-PCH) material was developed to simultaneously detect and remove uranyl ions (UO22+). Different from traditional SiO2 photonic crystal hydrogel with the problem of angle dependency, the LAD-PCH material overcomes the restriction of observation direction. The LAD-PCH is a composite material with the photonic crystal array of 180-nm monodisperse CdS@SiO2 particles embedded into the functional hydrogel. As one UO22+ can bind to multiple carboxyl groups and amide groups, the functional hydrogel fabricated by acrylic acid and acrylamide will shrink after chelating. These changes in the hydrogel volume alter the array spacing and trigger a blue shift of diffraction wavelength and naked-eye visual color changes of LAD-PCH. The color can vary from orange-red to orange, yellow, green, and cyan, corresponding to the determination range of 100 pM–100 μM. The LAD-PCH material detects UO22+ sensitively as the lowest detectable concentration is about 100 pM, and removes UO22+ high-efficiently as the maximum adsorption capacity of U(VI) is about 1010 mg g−1 at 298 K. This LAD-PCH material is convenient and has potential to simultaneously monitor and remove UO22+ from uranium-polluted water.

Schematic representation of the low-angle–dependent photonic crystal hydrogel (LAD-PCH) material for UO22+ detection and removal: The structural colors of LAD-PCH material overcome the restriction of observation angles. After the ligands complex with UO22+, the networks of LAD-PCH show different degrees of shrinkage; these volume changes of hydrogel trigger obvious naked-eye visual color changes of LAD-PCH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowart JB, Burnett WC (1994) The distribution of uranium and thorium decay-series radionuclides in the environment—a review. J Environ Qual 23(4):651–662. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1994.00472425002300040005x
Wang KX, Chen JS (2011) Extended structures and physicochemical properties of uranyl-organic compounds. Acc Chem Res 44(7):531–540. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar200042t
Rathore D (2008) Advances in technologies for the measurement of uranium in diverse matrices. Talanta 77(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.06.019
Santos JS, Teixeira LS, Dos Santos WN, Lemos VA, Godoy JM, Ferreira SL (2010) Uranium determination using atomic spectrometric techniques: an overview. Anal Chim Acta 674(2):143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.06.010
Farzin L, Shamsipur M, Sheibani S, Samandari L, Hatami Z (2019) A review on nanomaterial-based electrochemical, optical, photoacoustic and magnetoelastic methods for determination of uranyl cation. Microchim Acta 186(5):289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3426-5
Wang J, Zhuang S (2019) Extraction and adsorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution using affinity ligand-based technologies: an overview. Rev Environ Sci Bio:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-019-09507-y
Zhang Z, Zhang D, Shi C, Liu W, Chen L, Miao Y, Diwu J, Li J, Wang S (2019) 3, 4-Hydroxypyridinone-modified carbon quantum dot as a highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for the rapid detection of uranyl ions. Environ Sci-Nano 6(5):1457–1465. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EN00148D
Yun W, Chen L, Yi Z, Yi Y, Tang Y, Yang L (2019) Entropy-driven catalytic reaction-induced hairpin structure switching for fluorometric detection of uranyl ions. Microchim Acta 186(9):653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3767-0
Xiong XH, Yu ZW, Gong LL, Tao Y, Gao Z, Wang L, Yin WH, Yang LX, Luo F (2019) Ammoniating covalent organic framework (COF) for high-performance and selective extraction of toxic and radioactive uranium ions. Adv Sci 6(16):1900547. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201900547
Ge J, Yin Y (2011) Responsive photonic crystals. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(7):1492–1522. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200907091
Zhao Y, Xie Z, Gu H, Zhu C, Gu Z (2012) Bio-inspired variable structural color materials. Chem Soc Rev 41(8):3297–3317. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15267c
Fenzl C, Hirsch T, Wolfbeis OS (2014) Photonic crystals for chemical sensing and biosensing. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(13):3318–3335. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201307828
Kanai T, Yano H, Kobayashi N, Sawada T (2017) Enhancement of thermosensitivity of gel-immobilized tunable colloidal photonic crystals with anisotropic contraction. ACS Macro Lett 6(11):1196–1200. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.7b00780
Ye BF, Zhao YJ, Cheng Y, Li TT, Xie ZY, Zhao XW, Gu ZZ (2012) Colorimetric photonic hydrogel aptasensor for the screening of heavy metal ions. Nanoscale 4(19):5998–6003. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr31601c
Yan D, Li R, Lu W, Piao C, Qiu L, Meng Z, Wang S (2019) Flexible construction of cellulose photonic crystal optical sensing nano-materials detecting organic solvents. Analyst 144(6):1892–1897. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN01236A
Chen Q, Shi W, Cheng M, Liao S, Zhou J, Wu Z (2018) Molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogel sensor for optical detection of L-histidine. Microchim Acta 185(12):557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3080-3
Xiao F, Li G, Wu Y, Chen Q, Wu Z, Yu R (2016) Label-free photonic crystal-based β-lactamase biosensor for β-lactam antibiotic and β-lactamase inhibitor. Anal Chem 88(18):9207–9012. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02457
Li G, Xiao F, Liao S, Chen Q, Zhou J, Wu Z, Yu R (2018) Label-free 2D colloidal photonic crystal hydrogel biosensor for urea and urease inhibitor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 277:591–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.059
Su X, Xia H, Zhang S, Tang B, Wu S (2017) Vivid structural colors with low angle dependence from long-range ordered photonic crystal films. Nanoscale 9(9):3002–3009. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR07523A
Xiao F, Sun Y, Du W, Shi W, Wu Y, Liao S, Wu Z, Yu R (2017) Smart photonic crystal hydrogel material for uranyl ion monitoring and removal in water. Adv Funct Mater 27(42):1702147. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201702147
Zhan Q, Qian J, Li X, He S (2009) A study of mesoporous silica-encapsulated gold nanorods as enhanced light scattering probes for cancer cell imaging. Nanotechnology 21(5):055704. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/21/5/055704
Guerrero-Martínez A, Pérez-Juste J, Liz-Marzán LM (2010) Recent progress on silica coating of nanoparticles and related nanomaterials. Adv Mater 22(11):1182–1195. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200901263
Guo P, Xu J, Zhuang X, Hu W, Zhu X, Zhou H, Tang L, Pan A (2013) Surface plasmon resonance enhanced band-edge emission of CdS-SiO2 core-shell nanowires with gold nanoparticles attached. J Mater Chem C 1(3):566–571. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TC00088A
Zhu S, Leng Y, Yan M, Tuo X, Yang J, Almásy L, Tian Q, Sun G, Zou L, Li Q (2018) Bare and polymer coated iron oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles for effective removal of U(VI) from acidic and neutral aqueous medium. Appl Surf Sci 447:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.016
Zhang S, Shu X, Zhou Y, Huang L, Hua D (2014) Highly efficient removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solutions using poly (acrylic acid)-functionalized microspheres. Chem Eng J 253:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.036
Wang F, Xue Y, Lu B, Luo H, Zhu J (2019) Fabrication and characterization of angle-independent structurally colored films based on CdS@SiO2 nanospheres. Langmuir 35(14):4918–4926. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04193
Wang Z, Chen J, Xue X, Hu Y (2007) Synthesis of monodispersed CdS nanoballs through γ-irradiation route and building core-shell structure CdS@SiO2. Mater Res Bull 42(12):2211–2218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2007.01.002
Zhao J, Yu K, Hu Y, Li S, Tan X, Chen F, Yu Z (2011) Discharge behavior of mg-4 wt% Ga-2 wt% hg alloy as anode for seawater activated battery. Electrochim Acta 56(24):8224–8231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.06.065
Mayonado G, Mian SM, Robbiano V, Cacialli F (2015) Investigation of the Bragg-Snell Law in photonic crystals. American Assoc of Phy Teachers under a Creative Commons Attr 30 license. https://doi.org/10.1119/bfy.2015.pr.015
Su X, Jiang Y, Sun X, Wu S, Tang B, Niu W, Zhang S (2017) Fabrication of tough photonic crystal patterns with vivid structural colors by direct handwriting. Nanoscale 9(45):17877–17883. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR06570A
Su X, Chang J, Wu S, Tang B, Zhang S (2016) Synthesis of highly uniform Cu2O spheres by a two-step approach and their assembly to form photonic crystals with a brilliant color. Nanoscale 8(11):6155–6161. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR08401F
Ulusoy Hİ, Şimşek S (2013) Removal of uranyl ions in aquatic mediums by using a new material: gallocyanine grafted hydrogel. J Hazard Mater 254:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.04.004
WHO (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. World Health Organization Publication, Geneva
Xu M, Wang T, Gao P, Zhao L, Zhou L, Hua D (2019) Highly fluorescent conjugated microporous polymers for concurrent adsorption and detection of uranium. J Mater Chem A 7(18):11214–11222. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA11764K
Cui W, Zhang C, Jiang W, Li F, Liang R, Liu J, Qiu J (2020) Regenerable and stable sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks for selective detection and extraction of uranium. Nat Commun 11(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14289-x
Zhang C, Cui W, Jiang W, Li F, Wu Y, Liang R, Qiu J (2020) Simultaneous sensitive detection and rapid adsorption of UO22+ based on a post-modified sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic framework. Environ Sci-Nano 7:842–850. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EN01225G
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21874037 and 21675045) and the International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Projects of China (2012DFR40480).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 25711 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, W., Cheng, M., Chen, Q. et al. Low-angle–dependent CdS@SiO2 photonic crystal hydrogel material for visual detection and removal of uranyl ions. Microchim Acta 187, 476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04456-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04456-8