Abstract
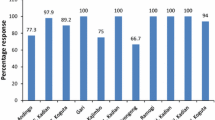
The high-altitude regions of Himalaya are among the best indicators of climate change yet noticeable for the lack of climate monitoring stations. However, they support ethnic communities whose livelihood activities are climate driven. Consequently, these communities are keen observers of the same and documenting their perception on changing climate is now an important area of global research. Therefore, the present study was conducted with the prime objective of documenting the climate change perception of Bhangalis—a resident community of western Himalaya, and analyzing variation in their perceptions in relation to age and gender. For this, respondent surveys (household, n = 430; individual interviews, n = 240) were carried out and the collected data were subjected to statistical analyses. The study also validated the perception of Bhangalis using the available weather data (1974–2017) through the Mann-Kendall test. The results reveal that Bhangalis perceived 11 indicators of changing climate, of which decrease in snowfall was the most prominent (reported by ~ 97% of the respondents). The perceptions varied between the two genders with males having significantly higher proportion of responses for all the 11 indicators. Similarly, differences in perception among the age groups were also observed, elderly people reported higher proportion of climate change indicators as compared to respondents of lower age. Notably, patterns of temperature and rainfall perceptions by the Bhangalis agreed with the trends of meteorological data. This highlights the importance of the study in documenting knowledge of ethnic communities especially from areas that lack monitoring stations. It argues for involving them in climate change programs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IPCC:
-
Intergovernmental panel on climate change
- FAO:
-
Food and Agriculture Organization
- EIA:
-
Environmental impact assessment
- %:
-
Percentage
- ha:
-
Hectare
- °C:
-
Degree Celsius
- mm:
-
Millimeters
- ~:
-
Approximately
- b :
-
Coefficient
- p :
-
Probability value
- *:
-
Significant value
References
Agho, K., Stevens, G., Taylor, M., Barr, M., & Raphael, B. (2010). Population risk perceptions of global warming in Australia. Environmental Research, 110(8), 756–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2010.09.007.
Aitsi-Selmi, A., Egawa, S., Sasaki, H., Wannous, C., & Murray, V. (2015). The Sendai framework for disaster risk reduction: renewing the global commitment to people’s resilience, health, and well-being. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 6(2), 164–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13753-015-0050-9.
Akerlof, K., Maibach, E. W., Fitzgerald, D., Cedeno, A. Y., & Neuman, A. (2013). Do people “personally experience” global warming, and if so how, and does it matter? Global Environmental Change, 23(1), 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2012.07.006.
Alessa, L., Kliskey, A., Williams, P., & Barton, C. M. (2008). Perception of change in freshwater in remote resource-dependent Arctic communities. Global Environmental Change, 18, 153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2007.05.007.
Anwar, M. R., Liu, D., Farquharson, R., Macadam, I., Abadi, A., Finlayson, J., Wang, B., & Ramilan, T. (2015). Climate change impacts on phenology and yields of five broadacre crops at four climatologically distinct locations in Australia. Agricultural Systems, 132, 133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2014.09.010.
Archie, K., Dilling, L., Milford, J., & Pampel, F. (2012). Climate change and western public lands: a survey of US federal land managers on the status of adaptation efforts. Ecology and Society, 17(4), 20. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-05187-170420.
Battaglini, A., Barbeau, G., Bindi, M., & Badeck, F. (2009). European winegrowers’ perceptions of climate change impact and options for adaptation. Regional Environmental Change, 9(2), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-008-0053-9.
Belay, A., Recha, J. W., Woldeamanuel, T., & Morton, J. F. (2017). Smallholder farmers’ adaptation to climate change and determinants of their adaptation decisions in the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Agriculture & Food Security, 6(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-017-0100-1.
Berkes, F., & Jolly, D. (2002). Adapting to climate change: social-ecological resilience in a Canadian western Arctic community. Conservation Ecology, 5(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-00342-050218.
Bhati, J. P., & Zingel, W. P. (1997). Natural resource use pattern in Western Himalayan agriculture: implications for biodiversity conservation and sustainable development. Conservation and Economic Evaluation of Biodiversity, 2, 575–588.
Bhattacharjee, A., Anadón, J. D., Lohman, D. J., Doleck, T., Lakhankar, T., Shrestha, B. B., Thapa, P., Devkota, D., Tiwari, S., Jha, A., Siwakoti, M., Devkota, N. R., Jha, P. K., & Krakauer, N. Y. (2017). The impact of climate change on biodiversity in Nepal: current knowledge, lacunae, and opportunities. Climate, 5(4), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5040080.
Bhattarai, B., Beilin, R., & Ford, R. (2015). Gender, agrobiodiversity, and climate change: a study of adaptation practices in the Nepal Himalayas. World Development, 70, 122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2015.01.003.
Boko, M., Niang, I., Nyong, A., Vogel, C., Githeko, A., Medany, M., Osman-Elasha, B., Tabo, R., & Yanda, P. (2007). Contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In M. L. Parry, O. F. Canziani, J. P. Palutikof, P. J. Van der Linden, & C. E. Hanson (Eds.), Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability (pp. 433–467). Cambridge: Cambridge university press.
Butt, T. A., McCarl, B. A., Angerer, J., Dyke, P. T., & Stuth, J. W. (2005). The economic and food security implications of climate change in Mali. Climatic Change, 68(3), 355–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-005-6014-0.
Byg, A., & Salick, J. (2009). Local perspectives on a global phenomenon—Climate change in eastern Tibetan villages. Global Environmental Change, 19(2), 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2009.01.010.
CBS (2017). National climate change impact survey 2016. A statistical report, Central Bureau of Statistics, Kathmandu, Nepal.
Chaudhary, P., & Bawa, K. S. (2011). Local perceptions of climate change validated by scientific evidence in the Himalayas. Biology Letters, 7(5), 767–770. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2011.0269.
Choubin, B., Alamdarloo, E. H., Mosavi, A., Hosseini, F. S., Ahmad, S., Goodarzi, M., & Shamshirband, S. (2019). Spatiotemporal dynamics assessment of snow cover to infer snowline elevation mobility in the mountainous regions. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 167, 102870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102870.
Christian, N. G. (2014). The impact of climate change on African traditional religious practices. Journal of Earth Science and Climatic Change, 5(7), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7617.1000209.
DADO. (2017). Annual report (online). District Agriculture Development Office.http://www.dadojumla.gov.np. Accessed 21 June 2020
Das, P. K., Dutta, D., Sharma, J. R., & Dadhwal, V. K. (2016). Trends and behavior of meteorological drought (1901–2008) over Indian region using standardized precipitation–evapotranspiration index. International Journal of Climatology, 36(2), 909–916. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4392.
Davidson, D. J., & Freudenburg, W. R. (1996). Gender and environmental risk concerns: a review and analysis of available research. Environment and Behavior, 28(3), 302–339. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013916596283003.
de Moor, N. (2011). Labour migration for vulnerable communities: a strategy to adapt to a changing environment. Working Paper No. 101/2011. Bielefeld: Center on Migration, Citizenship and Development (COMCAD), Bielefeld University.
Deressa, T. T., Hassan, R. M., & Ringler, C. (2011). Perception of and adaptation to climate change by farmers in the Nile basin of Ethiopia. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 149(01), 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859610000687.
EIA. (2006). EIA report of Lambadug hydro-electric power project (25MW) District Kangra (H.P.)
FAO. (2015). Mapping the vulnerability of mountain peoples to food insecurity. Rome.
Fitter, A. H., & Fitter, R. S. R. (2002). Rapid changes in flowering time in British plants. Science, 296(5573), 1689–1691. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071617.
Gebrehiwot, T., & Van Der Veen, A. (2013). Farm level adaptation to climate change: the case of farmer’s in the Ethiopian Highlands. Environmental Management, 52(1), 29–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0039-3.
Gómez-Baggethun, E., Reyes-García, V., Olsson, P., & Montes, C. (2012). Traditional ecological knowledge and community resilience to environmental extremes: a case study in Doñana, SW Spain. Global Environmental Change, 22(3), 640–650. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-06288-180472.
Goswami, B. N., Venugopal, V., Sengupta, D., Madhusoodanan, M. S., & Xavier, P. K. (2006). Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science, 314(5804), 1442–1445. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1132027.
Gremer, J. R., Bradford, J. B., Munson, S. M., & Duniway, M. C. (2015). Desert grassland responses to climate and soil moisture suggest divergent vulnerabilities across the southwestern United States. Global Change Biology, 21(11), 4049–4062. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13043.
Grobar, L. M. (2019). Policies to promote employment and preserve cultural heritage in the handicraft sector. International Journal of Cultural Policy, 25(4), 515–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286632.2017.1330887.
Grothmann, T., & Patt, A. (2005). Adaptive capacity and human cognition: the process of individual adaptation to climate change. Global Environmental Change, 15(3), 199–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2005.01.002.
Gupta, K.K. (2004). Draft management plan of Dhauladhar wildlife sanctuary (2004–2014). Palampur. Available from corresponding author of this article.
Gupta, A. K., Negi, M., Nandy, S., Alatalo, J. M., Singh, V., & Pandey, R. (2019). Assessing the vulnerability of socio-environmental systems to climate change along an altitude gradient in the Indian Himalayas. Ecological Indicators, 106, 105512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105512.
Habtemariam, L. T., Gandorfer, M., Kassa, G. A., & Heissenhuber, A. (2016). Factors influencing smallholder farmers’ climate change perceptions: a study from farmers in Ethiopia. Environmental Management, 58(2), 343–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-016-0708-0.
Hartter, J., Stampone, M. D., Ryan, S. J., Kirner, K., Chapman, C. A., & Goldman, A. (2012). Patterns and perceptions of climate change in a biodiversity conservation hotspot. PLoS One, 7(2), e32408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032408.
Hik, D. S., & Willaimson, S. N. (2019). Need for mountain weather stations climb. Science, 366(6449), 1083. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz7450.
Ibáñez, I., Primack, R. B., Miller-Rushing, A. J., Ellwood, E., Higuchi, H., Lee, S. D., Kobori, H., & Silander, J. A. (2010). Forecasting phenology under global warming. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, B: Biological Sciences, 365(1555), 3247–3260.
IPCC. (2007). In: Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., et al. (Eds.), Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the 92 R. Krishnan et al. fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (p. 996) Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, USA: Cambridge University Pres.
IPCC. (2014). Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part A: global and sectoral aspects. Contribution of working group II to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [Field CB, Barros V, Dokken D J, Mach KJ, Mastrandrea MD, Bilir TE, Chatterjee M, Ebi KL, Estrada YO, Genova RC, Girma B, Kissel ES, Levy AN, MacCracken S, MPR. White LL (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1–32.
IPCC. (2019). Summary for policymakers. In: IPCC special report on the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate [Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D.C., Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Mintenbeck, K., Nicolai, M., Okem, A., Petzold, J., Rama, B., Weyer, N. (eds.)]. In press.
Isa, S. F. M., Azhar, A. T. S., & Aziman, M. (2018). Design, operation and construction of a large rainfall simulator for the field study on acidic barren slope. Civil Engineering Journal, 4(8), 1851–1857. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-03091119.
Jena, P. K. (2008). Globalization of Indian handicrafts: a human development approach. Orissa Review, 19–25.
Kassie, B. T., Hengsdijk, H., Rötter, R., Kahiluoto, H., Asseng, S., & Van Ittersum, M. (2013). Adapting to climate variability and change: experiences from cereal-based farming in the Central Rift and Kobo Valleys, Ethiopia. Environmental Management, 52(5), 1115–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0145-2.
Kathayat, G. R., & Gautam, D. B. (2016). Ten years agriculture development plan of Jumla district. Kathmandu: District Agriculture Development Committee.
Klein, G., Vitasse, Y., Rixen, C., Marty, C., & Rebetez, M. (2016). Shorter snow cover duration since 1970 in the Swiss Alps due to earlier snowmelt more than to later snow onset. Climatic Change, 139(3-4), 637–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-016-1806-y.
Körner, C. (2004). Mountain biodiversity, its causes and function. Ambio, 13(sp13), 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/0044-7447-33.sp13.11.
Kosmowski, F., Leblois, A., & Sultan, B. (2016). Perceptions of recent rainfall changes in Niger: a comparison between climate-sensitive and non-climate sensitive households. Climatic Change, 135(2), 227–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1562-4.
Krosnick, J. A., Holbrook, A. L., Lowe, L., & Visser, P. S. (2006). The origins and consequences of democratic citizens’ policy agendas: a study of popular concern about global warming. Climatic Change, 77(1–2), 7–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9068-8.
Landis, D. A., Gardiner, M. M. D., Vander Werf, W., & Swinton, S. M. (2008). Increasing corn for the biofuel production reduces biocontrol services in agricultural landscapes. PNAS, 105, 20552–20557. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804951106.
Lee, J. H., Hancock, M. G., & Hu, M. C. (2014). Towards an effective framework for building smart cities: Lessons from Seoul and San Francisco. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 89, 80–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2013.08.033.
Li, C., Tang, Y., Luo, H., Di, B., & Zhang, L. (2013). Local farmers’ perceptions of climate change and local adaptive strategies: a case study from the Middle Yarlung Zangbo River Valley, Tibet, China. Environmental Management, 52(4), 894–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0139-0.
Liere, K. D. V., & Dunlap, R. E. (1980). The social bases of environmental concern: a review of hypotheses, explanations and empirical evidence. Public Opinion Quarterly, 44(2), 181–197. https://doi.org/10.1086/268583.
Liu, Z., Smith, W. J., & Safi, A. S. (2014). Rancher and farmer perceptions of climate change in Nevada, USA. Climatic Change, 122(1–2), 313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-013-0979-x.
Lobell, D. B., Bänziger, M., Magorokosho, C., & Vivek, B. (2011). Nonlinear heat effects on African maize as evidenced by historical yield trials. Nature Climate Change, 1(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1043.
Macchi, M., Gurung, A. M., & Hoermann, B. (2015). Community perceptions and responses to climate variability and change in the Himalayas. Climate and Development, 7(5), 414–425. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2014.966046.
Maddison, D. (2007). The perception of and adaptation to climate change in Africa. The World Bank.
Malka, A., Krosnick, J. A., & Langer, G. (2009). The association of knowledge with concern about global warming: Trusted information sources shape public thinking. Risk Analysis, 29(5), 633–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2009.01220.
Manandhar, S., Vogt, D. S., Perret, S. R., & Kazama, F. (2011). Adapting cropping systems to climate change in Nepal: a cross-regional study of farmers’ perception and practices. Regional Environmental Change, 11(2), 335–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-010-0137-1.
Manandhar, S., Pratoomchai, W., Ono, K., Kazama, S., & Komori, D. (2015). Local people’s perceptions of climate change and related hazards in mountainous areas of northern Thailand. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 11, 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0139-0.
Maponya, P., & Mpandeli, S. (2013). Perception of farmers on climate change and adaptation in Limpopo Province of South Africa. Journal of Human Ecology, 42(3), 283–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/09709274.2013.11906602.
Martin, G.J. (1995). Ethnobotany: a methods manual. Routledge.
McCright, A. M. (2010). The effects of gender on climate change knowledge and concern in the American public. Population and Environment, 32(1), 66–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11111-010-0113-1.
Menzel, A., Sparks, T. H., Estrella, N., & Roy, D. B. (2006). Altered geographic and temporal variability in phenology in response to climate change. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 15(5), 498–504. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-822x.2006.00247.x.
Mertz, O., Mbow, C., Reenberg, A., & Diouf, A. (2009). Farmers’ perceptions of climate change and agricultural adaptation strategies in rural Sahel. Environmental Management, 43(5), 804–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-008-9197-0.
Miller-Rushing, A. J., Inouye, D. W., & Primack, R. B. (2008). How well do first flowering dates measure plant responses to climate change? The effects of population size and sampling frequency. Journal of Ecology, 96(6), 1289–1296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2008.01436.x.
Mitter, H., Larcher, M., Schönhart, M., Stöttinger, M., & Schmid, E. (2019). Exploring farmers’ climate change perceptions and adaptation intentions: empirical evidence from Austria. Environmental Management, 63(6), 804–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-019-01158-7.
Mukerjee, P., Sogani, R., Gurung, N., Rastogi, A., & Swiderska, K. (2018). Smallholder farming systems in the Indian Himalayas: key trends and innovations for resilience. IIED Country Report. IIED, London.
Mulenga, B. P., Wineman, A., & Sitko, N. J. (2017). Climate trends and farmers’ perceptions of climate change in Zambia. Environmental Management, 59(2), 291–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-016-0780-5.
Myers, N., Mittermeier, R., Mittermeier, C. G., Da Fonseca, G. A., & Kent, J. (2000). Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403(6772), 853–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002501.
Negi, V. S., Maikhuri, R. K., Pharswan, D., Thakur, S., & Dhyani, P. P. (2017). Climate change impact in the Western Himalaya: people’s perception and adaptive strategies. Journal of Mountain Science, 14(2), 403–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3814-1.
Obianyo, J. I. (2019). Effect of salinity on evaporation and the water cycle. Emerging Science Journal, 3(4), 255–262. https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2019-01188.
Oo, H. T., Zin, W. W., & Kyi, C. C. T. (2020). Analysis of streamflow response to changing climate conditions using SWAT model. Civil Engineering Journal, 6(2), 194–209. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2020-03091464.
Ouyang, W., Gao, X., Hao, Z., Liu, H., Shi, Y., & Hao, F. (2017). Farmland shift due to climate warming and impacts on temporal-spatial distributions of water resources in a middle-high latitude agricultural watershed. Journal of Hydrology, 547, 156–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.050.
Pandey, R., Aretano, R., Gupta, A. K., Meena, D., Kumar, B., & Alatalo, J. M. (2017). Agroecology as a climate change adaptation strategy for smallholders of Tehri-Garhwal in the Indian Himalayan Region. Small-scale Forestry, 16(1), 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11842-016-9342-1.
Pandey, R., Kumar, P., Archie, K. M., Gupta, A. K., Joshi, P. K., Valente, D., & Petrosillo, I. (2018). Climate change adaptation in the Western-Himalayas: Household level perspectives on impacts and barriers. Ecological Indicators, 84, 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.08.021.
Parry, M., Parry, M.L., Canzian, O., Palutikof, J., Van der Linden, P., & Hanson, C. (Eds.). (2007) Climate change 2007-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: working group II contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4). Cambridge University Press.
Pirnia, A., Darabi, H., Choubin, B., Omidvar, E., Onyutha, C., & Haghighi, A. T. (2019). Contribution of climatic variability and human activities to stream flow changes in the Haraz River basin, northern Iran. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 25, 12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2019.05.001.
Prokopy, L. S., Arbuckle, J. G., Barnes, A. P., Haden, V. R., Hogan, A., Niles, M. T., & Tyndall, J. (2015). Farmers and climate change: A cross-national comparison of beliefs and risk perceptions in high-income countries. Environmental Management, 56(2), 492–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-015-0504-2.
Quarrie, J. (Ed.). (1992). Earth summit 1992: the United Nations conference on environment and development. Rio de Janeiro: Regency Press.
Ranjitkar, S., Luedeling, E., Shrestha, K. K., Guan, K., & Xu, J. (2013). Flowering phenology of tree rhododendron along an elevation gradient in two sites in the Eastern Himalayas. International Journal of Biometeorology, 57(2), 225–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-012-0548-4.
Rashid, I., Romshoo, S. A., Chaturvedi, R. K., Ravindranath, N. H., Sukumar, R., Jayaraman, M., Vijaya Lakshmi, T., & Sharma, J. (2015). Projected climate change impacts on vegetation distribution over Kashmir Himalayas. Climatic Change, 132(4), 601–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1456-5.
Ravera, F., Martín-López, B., Pascual, U., & Drucker, A. (2016). The diversity of gendered adaptation strategies to climate change of Indian farmers: a feminist intersectional approach. Ambio, 45(3), 335–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-016-0833-2.
Roco, L., Engler, A., Bravo-Ureta, B. E., & Jara-Rojas, R. (2015). Farmers’ perception of climate change in Mediterranean Chile. Regional Environmental Change, 15(5), 867–879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0669-x.
Salick, J., Fang, Z., & Byg, A. (2009). Eastern Himalayan alpine plant ecology, Tibetan ethnobotany, and climate change. Global Environmental Change, 19(2), 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2009.01.008.
Sen, P. K. (1968). Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Amer Statistical Assos, 63, 1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.2307/2285891.
Sen, S. M., & Kansal, A. (2019). Achieving water security in rural Indian Himalayas: a participatory account of challenges and potential solutions. Journal of Environmental Management, 245, 398–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.132.
Sharma, R. K., & Shrestha, D. G. (2016). Climate perceptions of local communities validated through scientific signals in Sikkim Himalaya, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(10), 578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5582-y.
Sharma, A., Thakur, D., & Uniyal, S. K. (2019). Plant derived utility products: knowledge comparison across gender, age and education from a tribal landscape of western Himalaya. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 15, 67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-019-0346-8.
Shea, M. M., & Thornton, T. F. (2019). Tracing country commitment to indigenous peoples in the UN framework convention on climate change. Global Environmental Change, 58, 101973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2019.101973.
Shrestha, U. B., Gautam, S., & Bawa, K. S. (2012). Widespread climate change in the Himalayas and associated changes in local ecosystems. PLoS One, 7(5), e36741. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036741.
Shrestha, U.B., Shrestha, A.M., Aryal, S., Shrestha, S., Gautam, M.S., Ojha, H. (2019a). Climate change in Nepal: a comprehensive analysis of instrumental data and people’s perceptions. Climatic Change, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-019-02418-5.
Shrestha, S., Chapagain, P. S., & Ghimire, M. (2019b). Gender perspective on water use and management in the context of climate change: a case study of Melamchi watershed area, Nepal. SAGE Open, 9(1), 2158244018823078. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244018823078.
Shukla, R., Chakraborty, A., Sachdeva, K., & Joshi, P. K. (2018). Agriculture in the western Himalayas–an asset turning into a liability. Development in Practice, 28(2), 318–324. https://doi.org/10.1080/09614524.2018.1420140.
Singh, R., Wagener, T., Werkhoven, K. V., Mann, M. E., & Crane, R. (2011). A trading-space-for-time approach to probabilistic continuous streamflow predictions in a changing climate–accounting for changing watershed behavior. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 15(11), 3591–3603. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-3591-2011.
Sujakhu, N. M., Ranjitkar, S., Niraula, R. R., Pokharel, B. K., Schmidt-Vogt, D., & Xu, J. (2016). Farmers’ perceptions of and adaptations to changing climate in the Melamchi valley of Nepal. Mountain Research and Development, 36(1), 15–31. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-15-00032.1.
Tambe, S., Kharel, G., Arrawatia, M. L., Kulkarni, H., Mahamuni, K., & Ganeriwala, A. K. (2012). Reviving dying springs: climate change adaptation experiments from the Sikkim Himalaya. Mountain Research and Development, 32(1), 62–73.
Thakur, D., Sharma, A., & Uniyal, S. K. (2017). Why they eat, what they eat: patterns of wild edible plants consumption in a tribal area of Western Himalaya. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 13(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-017-0198-z.
Tiwari, P. C., & Joshi, B. (2012). Environmental changes and sustainable development of water resources in the Himalayan headwaters of India. Water Resources Management, 26(4), 883–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9825-y.
Trinh, T. Q., Rañola Jr., R., Camacho, L. D., & Simelton, E. (2018). Determinants of farmers’ adaptation to climate change in agricultural production in the central region of Vietnam. Land Use Policy, 70, 224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.10.023.
Uddin, M. N., Bokelmann, W., & Dunn, E. S. (2017). Determinants of farmers’ perception of climate change: A case study from the coastal region of Bangladesh. American Journal of Climate Change, 6(01), 151. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajcc.2017.61009.
Ullah, H., Rashid, A., Liu, G., & Hussain, M. (2018). Perceptions of mountainous people on climate change, livelihood practices and climatic shocks: a case study of Swat District, Pakistan. Urban Climate, 26, 244–257.
Uniyal, S.K., & Singh, R.D. (2013). Vegetation characteristics, floral diversity and resource use in Western Himalaya. Climate Change and its Ecological Implications for the Western Himalaya. pp 162–179.
Uniyal, S. K., & Uniyal, A. (2009). Climate change and large-scale degradation of spruce: Common pattern across the globe. Climate Research, 38(3), 261–263. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr00792.
Uniyal, S. K., Awasthi, A., & Rawat, G. S. (2003). Developmental processes, changing lifestyle and traditional wisdom: analyses from western Himalaya. Environmentalist, 23(4), 307–312. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ENVR.0000031408.71386.b4.
Uniyal, S. K., Singh, K. N., Jamwal, P., & Lal, B. (2006). Traditional use of medicinal plants among the tribal communities of Chhota Bhangal, Western Himalaya. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 2(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4269-2-14.
van Gevelt, T., Abok, H., Bennett, M. M., Fam, S. D., George, F., Kulathuramaiyer, N., Low, C. T., & Zaman, T. (2019). Indigenous perceptions of climate anomalies in Malaysian Borneo. Global Environmental Change, 58, 101974.
Walther, G. R., Post, E., Convey, P., Menzel, A., Parmesan, C., Beebee, T. J., Fromentin, J. N., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., & Bairlein, F. (2002). Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature, 416(6879), 389. https://doi.org/10.1038/416389a.
Wester, P.A., Mishra, A., Mukherji, A.B., & Shrestha (eds) (2019). The Hindu Kush Himalaya assessment—mountains, climate change, sustainability and people, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham.
Xu, J., & Grumbine, R. E. (2014). Building ecosystem resilience for climate change adaptation in the Asian highlands. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 5(6), 709–718. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.302.
Xu, J., Grumbine, R. E., Shrestha, A., Eriksson, M., Yang, X., Wang, Y. U. N., & Wilkes, A. (2009). The melting Himalayas: cascading effects of climate change on water, biodiversity, and livelihoods. Conservation Biology, 23(3), 520–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2009.01237.x.
Ziell, C., Estrella, N., Kostova, M., Koch, E., & Menzel, A. (2009). Influence of altitude on phenology of selected plant species in the Alpine region (1971–2000). Climate Research, 39(3), 227–234. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr00822.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director CSIR-IHBT for the facilities and the administrative authorities of Panjab University for the support. Faculty members of the high-altitude biology division are acknowledged for their support. Er. Amit Kumar is thanked for helping the authors in map preparation. We are thankful to the Editor-in-Chief and two anonymous reviewers whose comments helped in improving the earlier draft of the manuscript. This is IHBT communication number 4304.
Funding
This study was financially supported by The Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change via the NMHS project GAP-0199.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 83 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Batish, D.R. & Uniyal, S.K. Documentation and validation of climate change perception of an ethnic community of the western Himalaya. Environ Monit Assess 192, 552 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08512-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08512-x