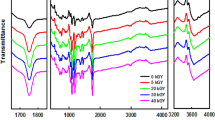
Abstract
Modification of surface of natural fibers by high-energy gamma irradiation (6 MV) is a competent process for enhancing the adhesion between fiber and matrix. Composites reinforced with natural fiber have gained a prominent place in the field of research and innovation due to the advantages such as low cost, lightweight and environment friendly. We have studied the thermal properties of biodegradable composites using biodegradable polymer poly(lactic) acid and fiber of Luffa cylindrica (LC) fabricated by using injection molding technique. Before reinforcement LC fibers are irradiated with gamma rays of 0.5, 1 and 2 Gy using 6 MV linear accelerator at room temperature in the presence of air. The thermal properties like glass transition temperature (Tg), crystallization temperature (Tcc), melting peak temperature (Tm) and thermal stability of the composites are studied using differential scanning calorimetry in the temperature range from 30 to 250 °C and thermogravimetric analysis in temperature range from 20 to 700 °C. The variation of these properties in response to the irradiation dose and fiber loading is analyzed in detail. It is observed that with increase in irradiation dose, glass transition temperature and crystallization temperature are increasing. However, the thermal stability of the composites is found to decrease with increase in irradiation dose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bledzki AK, Gassan J (1999) Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog Polym Sci 24(2):221–274
Vrsaljko D, Grcic I, Guyon C, Schelcher G, Tatoulian M (2016) Designing hydrophobicity of the PLA polymer blend surfaces by ICP etching. Plasma Process Polym 13(9):869–878
Ndiaye D, Tidjani A (2014) Physical changes associated with gamma doses on wood/polypropylene composites. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/62/1/012025
Shahabi S, Najafi F, Majdabadi A, Hooshmand T, Nazarpak MH, Karimi B, Fatemi SM (2014) Effect of gamma irradiation on structural and biological properties of a PLGA-PEG-hydroxyapatite composite. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/420616
Orozco RS, Hernandez PB, Ramirez NF, Morales GR, Luna JS, Montoya AJS (2012) Gamma irradiation induced degradation of orange peels. Energies 5(8):3051–3063
Said HM (2013) Effects of gamma irradiation on the crystallization, thermal and mechanical properties of poly (l-lactic acid)/ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blends. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 6(2):11–20
Egute NS, Forster PL, Parra DF, Fermino DM, Santana S, Lugao AB (2009) Mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene composites with curaua fibre irradiated with gamma radiation. In: International nuclear atlantic conference—INAC 2009. Rio de Janeiro, Associação Brasileira De Energia Nuclear—Aben, ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8
Albano C, Reyes J, Ichazo M, González J, Brito M, Moronta D (2002) Analysis of the mechanical, thermal and morphological behavior of polypropylene compounds with sisal fibre and wood flour, irradiated with gamma rays. Polym Degrad Stab 76(2):191–203
Mazali IO, Alves OL (2005) Morphosynthesis: high fidelity inorganic replica of the fibrous network of loofa sponge (Luffa cylindrica). Ann Braz Acad Sci 77(1):25–31
Parida C, Dash SK, Das SC (2015) Effect of fiber treatment and fiber loading on mechanical properties of Luffa-resorcinol composites. Indian J Mater Sci 2015:6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/658064
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Laboratory of Advanced Research in Polymeric Materials (LARPM), Central Institute of Plastic Engineering and Technology, Government of India for synthesis and characterization of the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parida, C., Mohanta, K.L. & Patra, S. Study of Thermal Behaviour of Poly(Lactic) Acid Composites with Gamma Irradiated Luffa Fiber. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. A Phys. Sci. 91, 597–603 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-020-00705-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-020-00705-w