Abstract
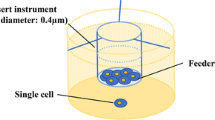
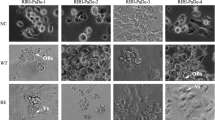
In this paper, four established cell lines derived from newly hatched larvae of Papilio demoleus Linnaeus and 57 single-cell clones derived from the 3 lines were used as test materials. Recombinant β-galactosidase baculovirus AcMNPV-Gal was used to infect the P. demoleus L. cell lines and the single-cell clones, and recombinant protein expression in each cell line was detected and compared. Three clonal cell lines, RIRI-PaDe-1-C1, RIRI-PaDe-2-C6 and RIRI-PaDe-3-C52, which showed significantly higher β-galactosidase expression levels than those of the parental cell lines, were selected. Five types of commercial serum-free media for insect cells, Express Five SFM, Ex-Cell 405, Sf-900III SFM, Sf-900II SFM and HyClone Serum-Free Media, were used to adapt RIRI-PaDe-2-C6 cells and RIRI-PaDe-3-C52 cells to serum-free culture conditions, and the growth characteristics of the cells and the exogenous protein expression characteristics before and after adaptation were compared. The results showed that RIRI-PaDe-2-C6 cells could stably proliferate in Ex-Cell 405, RIRI-PaDe-3-C52 cells could stably proliferate in Express Five SFM and Ex-Cell 405, and the rate of proliferation of and the level of expression of β-galactosidase in RIRI-PaDe-3-C52 cells were significantly increased in Express Five SFM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MOI:
-
Multiplicity of infection
References
Chen YR, Solter LF, Chien TY, Jiang MH, Lin HF, Fan HS, Lo CF, Wang CH (2009) Characterization of a new insect cell line (NTU-YB) derived from the common grass yellow butterfly, Eurema hecabe (Linnaeus) (Pieridae: Lepidoptera) and its susceptibility to microsporidia. J Invertebr Pathol 102(3):256–262
Ding WF, Feng Y, Zhang X, Li X, Wang CY (2013) Establishment and characterization of a cell line developed from the neonate larvae of Papilio demoleus Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 49(2):108–113
Ding WF, Zhang X, Li X, Liu ZG (2018) Expression of three reporter genes in four cell lines developed from Papilio demoleus Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 54(3):194–199
Drugmand J-C, Schneider Y-J, Agathos SN (2012) Insect cells as factories for biomanufacturing. Biotechnol Adv 30(5):1140–1157
Granados RR, Li GX, Blissard GW (2007) Insect cell culture and biotechnology. Virol Sin 22(2):83–93
Granados RR, Li GX, Derksen ACG, McKenna KA (1994) A new insect cell line from Trichoplusia ni (BTI-Tn-5B1-4) susceptible to Trichoplusia ni single enveloped nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Invertebr Pathol 64(3):260–266
Ikonomou L, Bastin G, Schneider YJ, Agathos SN (2001) Design of an efficient medium for insect cell growth and recombinant protein production. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37(9):549–559
Liu ZG, Ding WF, Xie SC, Sun N, Zhang X, Li X, Feng Y (2018) Establishment and characterization of cell clones from the Papilio cell line RIRI-PaDe-3 by a high-efficiency clonal method. Cytotechnology 70(4):1235–1245
Matsumura T, Tatsumi K, Noda Y, Nakanishi N, Okonogi A, Hirano K, Liu L, Osumi T, Tada T, Kotera H (2014) Single-cell cloning and expansion of human induced pluripotent stem cells by a microfluidic culture device. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 453(1):131–137
Mena JA, Kamen AA (2014) Insect cell technology is a versatile and robust vaccine manufacturing platform. Expert Rev Vaccines 10(7):1063–1081
Mitsuhashi J (1972) Primary culture of the haemocytopoietic tissue of Papilio xuthus Linne. Appl Entomol Zool 7(1):39–41
Mitsuhashi J (1973) Establishment of cell lines from the pupal ovaries of the swallow tail, Papilio xuthus Linne: Lepidoptera: Papilionidae. Appl Entomol Zool 8(2):64–72
Pan MH, Cai XJ, Liu M, Lv J, Tang H, Tan J, Lu C (2010) Establishment and characterization of an ovarian cell line of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Tissue Cell 42(1):42–46
Siissalo S, Laitinen L, Koljonen M, Vellonen K-S, Kortejärvi H, Urtti A, Hirvonen J, Kaukonen AM (2007) Effect of cell differentiation and passage number on the expression of efflux proteins in wild type and vinblastine-induced Caco-2 cell lines. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 67(2):548–554
Swiech K, Picanço-Castro V, Covas DT (2012) Human cells: new platform for recombinant therapeutic protein production. Protein Expr Purif 84(1):147–153
Yuan WT, Ju CY, Yi TC, Shuo CW, Villaflores O (2012) A bi-cistronic baculovirus expression vector for improved recombinant protein production. Bioeng Bugs 3(2):127–130
Zhang X, Feng Y, Ding WF, Chen XM, Wang CY, Ma T (2011) Establishment and characterization of an embryonic cell line from Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47(4):327–332
Zhang X, Feng Y, Ding WF, Chen XM, Wang CY, Ma T (2012) Characterization of a new insect cell line that is derived from the neonate larvae of Papilio xuthus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) and its susceptibility to AcNPV. Tissue Cell 44(3):137–142
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Non-profit Research Institution of CAF (No. CAFYBB2016ZD005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, WF., Liu, ZG., Sun, N. et al. Screening of single-cell clonal lines from Papilio demoleus Linnaeus cell lines for exogenous protein expression and adaptation in serum-free culture. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 56, 444–451 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00484-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00484-z