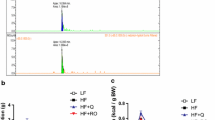
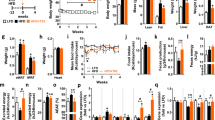
Abstract
We studied the effects of quercetin (Q) on the behavioral responses and integral and metabolic indices in male db/db mice genetically predisposed to obesity and C57Bl/6J mice fed a diet with an excessive energy value. We examined forepaw grip strength, exploratory activity, anxiety, and short-term memory, as well as integral and biochemical indices, and the contents of leptin, ghrelin, and IL-10. We found differences between two models of obesity in the integral and biochemical indices and behavioral responses to Q treatment. In the db/db mice, they were associated with knockout of the Lepr gene encoding the leptin receptor, which prevented the neurotropic and regulatory functions of leptin. These effects of Q detected should be considered when justifying the dose and timing of this nutraceutical in clinical practice.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Apryatin, S.A., Shipelin, V.A., Sidorova, Yu.S., Petrov, N.A., Gmoshinskii, I.V., and Nikityuk, D.B., Interspecific differences in behavioral responses and neuromotorics between laboratory rodents receiving rations with easily digested carbohydrates, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2018, vol. 165, no. 1, pp. 5–9.
Bojanowska, E. and Ciosek, J., Can we selectively reduce appetite for energy-dense foods? An overview of pharmacological strategies for modification of food preference behavior, Curr. Neuropharmacol., 2016, vol. 14, no. 22, pp. 118–142. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X14666151109103147
Castrejón-Tellez, V., Rodríguez-Pérez, J.M., Pérez-Torres, I., Perez- Hernández, N., Cruz-Lagunas, A., Guarner-Lans, V., and Rubio-Ruiz, M.E., The effect of resveratrol and quercetin treatment on PPAR mediated uncoupling protein (UCP-) 1, 2, and 3 expression in visceral white adipose tissue from metabolic syndrome rats, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2016, vol. 17, no. 7, p. 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071069
Chen, H.-W., Tsai, C.-W., Yang, J.-J., and Liu, C.-T., The combined effects of garlic oil and fish oil on the hepatic antioxidant and drug-metabolizing enzymes of rats, Br. J. Nutr., 2003, vol. 89, no. 2, pp. 189–200. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN2002766
Cinque, S., Zoratto, F., Poleggi, A., Leo, D., Cerniglia, L., Cimino, S., Tambelli, R., Alleva, E., Gainetdinov, R.R., Laviola, G., and Adriani, W., Behavioral phenotyping of dopamine transporter knockout rats: compulsive traits, motor stereotypies, and anhedonia, Front. Psychiatry, 2018, vol. 9, no. 43, pp. 1–13.
Deck, C.A., Honeycutt, J.L., Cheung, E., Reynolds, H.M., and Borski, R.J., Assessing the functional role of leptin in energy homeostasis and the stress response in vertebrates, Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne), 2017, vol. 8, p. 63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00063
Edwards, R.L., Lyon, T., Litwin, S.E., Rabovsky, A., Symons, J.D., and Jalili, T., Quercetin reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects, J. Nutr., 2007, vol. 137, pp. 2405–2411. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.11.2405
Efimova, E.V., Gainetdinov, R.R., Budygin, E.A., and Sotnikova, T.D., Dopamine transporter mutant animals: a translational perspective, J. Neurogenet., 2016, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 5–15.
Egert, S., Boesch-Saadatmandi, C., Wolffram, S., Rimbach, G., and Muller, M.J., Serum lipid and blood pressure responses to quercetin vary in overweight patients by apolipoprotein E genotype, J. Nutr., 2010, vol. 140, pp. 278–284.
Horio, Y., Hayashi, T., Kuno, A., and Kunimoto, R., Cellular and molecular effects of sirtuins in health and disease, Clin. Sci. (Lond.), 2011, vol. 121, no. 5, pp. 191–203. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20100587
Hosoi, T. and Maffei, M., Editorial: leptin resistance in metabolic disorders: possible mechanisms and treatments, Front Endocrinol. (Lausanne), 2017, vol. 8, p. 300. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00300
Hsu, T.M., Hahn, J.D., Konanur, V.R., Noble, E.E., Suarez, A.N., Thai, J., Nakamoto, E.M., and Kanoski, S.E., Hippocampus ghrelin signaling mediates appetite through lateral hypothalamic orexin pathways, Elife, 2015, vol. 4, e11190. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11190
Kobayashi, K., Forte, T.M., Taniguchi, S., Ishida, B.Y., Oka, K., and Chan, L., The db/db mouse, a model for diabetic dyslipidemia: molecular characterization and effects of western diet feeding, Metabolism, 2000, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 22–31.
Kobori, M., Masumoto, S., Akimoto, Y., and Oike, H., Chronic dietary intake of quercetin alleviates hepatic fat accumulation associated with consumption of a Western-style diet in C57/BL6J mice, Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 2011, vol. 55, pp. 530–540. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201000392
Kravchenko, L.V., Aksenov, I.V., Trusov, N.V., Guseva, G.V., and Avren’eva, L.I., Effect of the amount of fat in the diet on the activity of enzymes involved in metabolism of xenobiotics and antioxidant defense in rats, Vopr. Pitan., 2012, vol. 81, no. 1, рр. 24–29.
López-Jaramillo, P., Gómez-Arbeláez, D., López-López, J., López-López, C., Martínez-Ortega, J., Gómez-Rodríguez, A., and Triana-Cubillos, S., Leptin/adiponectin ratio in metabolic syndrome and diabetes, Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Invest., 2014, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2013-0053
Mzhel’skaya, K.V., Shipelin, V.A., Apryatin, S.A., Soto, S.Kh., Shumakova, A.A., Evstratova, V.S., Kirbaeva, N.V., Trusov, N.V., and Gmoshinskii, I.V., The influence of a diet with excess fats and carbohydrates on the neuromotor function and cognitive, integral, and biochemical parameters of rats and mice of various lines, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2018, vol. 104, no. 4, pp. 452–465.
Ouchi, N., Parker, J.L., Lugus, J.J., and Walsh, K., Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 85–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2921
Panchal, S.K., Poudyal, H., and Brown, L., Quercetin ameliorates cardiovascular, hepatic, and metabolic changes in diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats, J. Nutr., 2012, vol. 142, no. 6, pp. 1026–1032. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.157263
Pérez-Pérez, A., Vilariño-García, T., Fernández-Riejos, P., Martín-González, J., Segura-Egea, J.J., and Sánchez-Margalet, V., Role of leptin as a link between metabolism and the immune system, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 2017, vol. 35, pp. 71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.03.001
Perry, M.L., Leinninger, G.M., Chen, R., Luderman, K.D., Yang, H., Gnegy, M.E., Myers, M.G., Jr., and Kennedy, R.T., Leptin promotes dopamine transporter and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in the nucleus accumbens of Sprague–Dawley rats, J. Neurochem., 2010, vol. 114, no. 3, pp. 666–674. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06757.x
Rodgers, J.T. and Puigserver, P., Fasting-dependent glucose and lipid metabolic response through hepatic sirtuin 1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2007, vol. 104, no. 31, pp. 12861–12866. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20100587
Roslyi, I.M., Abramov, S.V., and Pokrovskii, V.I., Enzymemia—adaptive mechanism or a cytolysis marker?, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 2002, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 3–9.
Roslyi, I.M., Biokhimicheskie pokazateli v meditsine i biologii (Biochemical Indicators in Medicine and Biology), Moscow: Med. Inform. Agentstvo, 2015.
Tomankova, V., Anzenbacher, P., and Anzenbacherova, E., Effects of obesity on liver cytochromes P450 in various animal models, Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech. Repub., 2017, vol. 161, no. 2, pp. 144–151. https://doi.org/10.5507/bp.2017.026
Tran, L.T., Yuen, V.G., and McNeill, J.H., The fructose-fed rat: a review on the mechanisms of fructose-induced insulin resistance and hypertension, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 2009, vol. 332, pp. 145–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0184-4
Wong, S.K., Chin, K.-Y., Suhaimi, F.H., Fairus, A., and Ima-Nirwana, S., Animal models of metabolic syndrome: a review, Nutr. Metab., 2016, vol. 13, p. 65.
Yamamoto, H., Schoonjans, K., and Auwerx, J., Sirtuin functions in health and disease, Mol. Endocrinol., 2007, vol. 21, no. 8, pp. 1745–1755. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0079
Zhao, Y., Chen, B., Shen, J., Wan, L., Zhu, Y., Yi, T., and Xiao, Z., The beneficial effects of quercetin, curcumin, and resveratrol in obesity, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2017, vol. 2017, p. 1459497. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1459497
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 17-16-01043 (“The Search for the Effector Metabolic Components Regulated by Nutritional Factors in Obesity for the Development of Innovative Specialized Foods”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. Experiments with animals were performed according to the Order of the Ministry of Health Care of the Russian Federation no. 199n, April 1, 2016 “On Approval of the Rules of Good Laboratory Practice.” The design of the experiment was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Federal Research Center for Nutrition, Biotechnology, and Food Safety (Protocol no. 4 of April 20, 2017).
Additional information
Translated by M. Stepanichev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apryatin, S.A., Shipelin, V.A., Trusov, N.V. et al. The Effect of Quercetin on Metabolism and Behavioral Responses in Mice with Normal and Impaired Leptin Reception. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 47, 407–416 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359020040020
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359020040020