Abstract
Objective
Investigation of functional magnetic resonance (MR) imaging role in early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy (DN) in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) type 2, by quantification of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) values.
Material and methods
10 healthy volunteers and 91 DM type 2 patients were scanned using diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) sequences. Patients were divided into four groups based on the estimated glomerular filtration value (eGFR). ADC and FA values, calculated in six regions of interest in each kidney (cortex and medulla), were compared to eGFR and laboratory parameters of renal function.
Results
ADC values of DM patients were higher in the cortex than in the medulla (p < 0.01), while FA values were higher in the medulla (p = 0.284). Creatinine, cystatin C negatively correlated with ADC (cortex, medulla, parenchyma). Medullary FA were lower in DM patients and positively correlated with the eGFR (p = 0.049). Tractography showed disturbed structure in patients with impaired renal function.
Discussion
Medullary FA value is a more sensitive parameter than parenchymal ADC in the early detection of renal damage in DM patients. ADC and FA values are significant in the diagnosis of DN; further research is needed for the update and refinement of the established recommendations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DN:
-
Diabetic nephropathy
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- GFR:
-
Glomerular filtration rate
- FIESTA:
-
Fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition
- FSPGR:
-
Fast-spoiled gradient
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- Cys C:
-
Cystatin C
- eGFR:
-
Estimate glomerular filtration rate
- CKD-EPI:
-
Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration
References
Lu L, Sedor JR, Gulani V et al (2011) Use of diffusion tensor MRI to identify early changes in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 34(5):476–482
Hueper K, Gutberlet M, Rodt T et al (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography for assessment of renal allograft dysfunction-initial results. Eur Radiol 21(11):2427–2433
Hueper K, Hartung D, Gutberlet M et al (2012) Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging for evaluation of histopathological changes in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Investig Radiol 47(7):430–437
Gaudiano C, Clementi V, Busato F et al (2013) Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of the kidneys: assessment of chronic parenchymal diseases. Eur Radiol 23(6):1678–1685
Caroli A, Schneider M, Friedli I et al (2018) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to assess diffuse renal pathology: a systematic review and statement paper. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33(Suppl 2):ii29–ii40
Liu Z, Xu Y, Zhang J et al (2015) Chronic kidney disease: pathological and functional assessment with diffusion tensor imaging at 3T MR. Eur Radiol 25(3):652–660
Chenevert TL, Galbán CJ, Ivancevic MK et al (2011) Diffusion coefficient measurement using a temperature-controlled fluid for quality control in multicenter studies. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(4):983–987
Gürses B, Kılıçkesmez Ö, Taşdelen N, Fırat Z, Gürmen N (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla MRI: normative values and repeatability of measurements in healthy volunteers. Diagn Interv Radiol 17(4):317–322
Notohamiprodjo M, Glaser C, Herrmann KA et al (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney with parallel imaging: initial clinical experience. Investig Radiol 43(10):677–685
Heusch P, Wittsack HJ, Kröpil P et al (2013) Impact of blood flow on diffusion coefficients of the human kidney: a time-resolved ECG-triggered diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) study at 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 37:233–236
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Oyen RH, Peeters RR (2005) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in healthy volunteers and patients with parenchymal diseases: initial experience. Radiology 235(3):911–917
Ries M, Basseau F, Tyndal B et al (2003) Renal diffusion and BOLD MRI in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Magn Reson Imaging 17(1):104–113
Wang W, Pui MH, Guo Y, Hu X, Wang H, Yang D (2014) MR diffusion tensor imaging of normal kidneys. J Magn Reson Imaging 40(5):1099–1102
Yang D, Ye Q, Williams DS, Hitchens TK, Ho C (2004) Normal and transplanted rat kidneys: diffusion MR imaging at 7 T. Radiology 231(3):702–709
Wang YC, Feng Y, Lu CQ, Ju S (2018) Renal fat fraction and diffusion tensor imaging in patients with early-stage diabetic nephropathy. Eur Radiol 28(8):3326–3334
Ries M, Jones RA, Basseau F, Moonen CT, Grenier N (2001) Diffusion tensor MRI of the human kidney. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:42–49
Fukuda Y, Ohashi I, Hanafusa K et al (2000) Anisotropic diffusion in kidney: apparent diffusion coefficient measurements for clinical use. J Magn Reson Imaging 11(2):156–160
Kataoka M, Kido A, Yamamoto A et al (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging of kidneys with respiratory triggering: optimization of parameters to demonstrate anisotropic structures on fraction anisotropy maps. J Magn Reson Imaging 29(3):736–744
Herget-Rosenthal S (2011) Imaging techniques in the management of chronic kidney disease: current developments and future perspectives. Semin Nephrol 31(3):283–290
Lanzman RS, Ljimani A, Pentang G et al (2013) Kidney transplant: functional assessment with diffusion-tensor MR imaging at 3 T. Radiology 266:218–225
Sigmund EE, Vivier PH, Sui D et al (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion-tensor imaging in renal tissue under hydration and furosemide flow challenges. Radiology 263(3):758–769
Zhang JL, Sigmund EE, Chandarana H et al (2010) Variability of renal apparent diffusion coefficients: limitations of the monoexponential model for diffusion quantification. Radiology 254(3):783–792
Blondin D, Lanzman RS, Klasen J et al (2011) Diffusion-attenuated MRI signal of renal allografts: comparison of two different statistical models. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196(6):W701–W705
Blondin D, Lanzman RS, Mathys C et al (2009) Functional MRI of transplanted kidneys using diffusion-weighted imaging. Rofo 181(12):1162–1167
Thoeny HC, Binser T, Roth B, Kessler TM, Vermathen P (2009) Noninvasive assessment of acute ureteral obstruction with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: a prospective study. Radiology 252(3):721–728
Zhang JL, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H et al (2012) Optimization of b value sampling for diffusion-weighted imaging of the kidney. Magn Reson Med 67(1):89–97
Zheng Z, Shi H, Zhang J, Zhang Y (2014) Renal water molecular diffusion characteristics in healthy native kidneys: assessment with diffusion tensor MR imaging. PLoS ONE 9(12):e113469
Grenier N, Basseau F, Ries M, Tyndal B, Jones R, Moonen C (2003) Functional MRI of the kidney. Abdom Imaging 28(2):164–175
Gaudiano C, Clementi V, Busato F et al (2011) Renal diffusion tensor imaging: is it possible to define the tubular pathway? A case report. Magn Reson Imaging 29(7):1030–1033
Cheung JS, Fan SJ, Chow AM, Zhang J, Man K, Wu EX (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging of renal ischemia reperfusion injury in an experimental model. NMR Biomed 23(5):496–502
Xu X, Fang W, Ling H, Chai W, Chen K (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease: initial study. Eur Radiol 20(4):978–983
Karadeli E, Ulu EM, Yilmaz S, Durukan E (2009) Diffusion-weighted MRI of the kidneys in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: initial experience. Diagn Interv Radiol 15:252–255
Wang W, Pui MH, Guo Y, Wang L, Wang H, Liu M (2014) 3T magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging in chronic kidney disease. Abdom Imaging 39(4):770–775
Çakmak P, Yağcı AB, Dursun B, Herek D, Fenkçi SM (2014) Renal diffusion-weighted imaging in diabetic nephropathy: correlation with clinical stages of disease. Diagn Interv Radiol 20(5):374–378
Zhao J, Wang ZJ, Liu M et al (2014) Assessment of renal fibrosis in chronic kidney disease using diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin Radiol 69(11):1117–1122
Yalçin-Şafak K, Ayyildiz M, Ünel SY, Umarusman-Tanju N, Akça A, Baysal T (2015) The relationship of ADC values of renal parenchyma with CKD stage and serum creatinine levels. Eur J Radiol Open 3:8–11
Goyal A, Sharma R, Bhalla AS, Gamanagatti S, Seth A (2012) Diffusion-weighted MRI in assessment of renal dysfunction. Indian J Radiol Imaging 22(3):155–159
Xu Y, Wang X, Jiang X (2007) Relationship between the renal apparent diffusion coefficient and glomerular filtration rate: preliminary experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(3):678–681
Razek AAKA, Al-Adlany MAAA, Alhadidy AM, Atwa MA, Abdou NEA (2017) Diffusion tensor imaging of the renal cortex in diabetic patients: correlation with urinary and serum biomarkers. Abdom Radiol (NY) 42(5):1493–1500
Chen X, Xiao W, Li X, He J, Huang X, Tan Y (2014) In vivo evaluation of renal function using diffusion weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging in type 2 diabetics with normoalbuminuria versus microalbuminuria. Front Med 8(4):471–476
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Mitsuzaki K, Nakayama Y, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1999) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in diffuse renal disease by diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 9(6):832–837
Muller MF, Prasad PV, Bimmler D, Kaiser A, Edelman RR (1994) Functional imaging of the kidney by means of measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 193(3):711–715
Li Q, Li J, Zhang L, Chen Y, Zhang M, Yan F (2014) Diffusion-weighted imaging in assessing renal pathology of chronic kidney disease: A preliminary clinical study. Eur J Radiol 83(5):756–762
Carbone SF, Gaggioli E, Ricci V, Mazzei F, Mazzei MA, Volterrani L (2007) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of renal function: a preliminary study. Radiol Med 112:1201–1210
Ljimani A, Caroli A, Laustsen C, Francis S, Mendichovszky AI, Bane O et al (2020) Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal diffusion-weighted MRI. MAGMA 33(1):197–198
Kido A, Kataoka M, Yamamoto A, Nakamoto Y, Umeoka S, Koyama T et al (2010) Diffusion tensor MRI of the kidney at 3.0 and 1.5 Tesla. Acta Radiol 51(9):1059–1063
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Anna Caroli from Institute Mario Negri, Medical Imaging Unit, Bergamo, Italy, and Azim Celik, Ph.D, Regional Research Manager—Eastern Europe and Turkey, GE Healthcare, for the help with reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TM took the lead in writing the manuscript, performed the acquisition of the data, processed, analyzed and interpreted the data. ON conceived and supervised the study, processed and analyzed the data, added in interpreting the results, worked on the manuscript. UM drafted the manuscript, designed figures and tables and worked out the technical details. MM contributed to the study by choosing the relevant patients with DM type 2. VT contributed to the statistical analysis of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Funding
No fundings were received for this study.
Research invloving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendices
Appendix
See Figs. 1, 2, Tables 1, 2, 3 and 4.
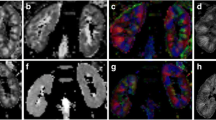
Positions of six ROIs in both kidney’ cortex and medulla (upper, middle, lower pole) on FSPGR T1 weighted FS image (left), complementary ADC map (middle) and FA map (right). Healthy man, 28 years old, BMI 32.1 kg/m2, Cr 75 µmol/l, Cys C 0.843 mg/l, eGFR 124 ml/min/1.73 m2. Preserved corticomedullary differentiation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mrđanin, T., Nikolić, O., Molnar, U. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of renal function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Magn Reson Mater Phy 34, 273–283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-020-00869-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-020-00869-x