Abstract
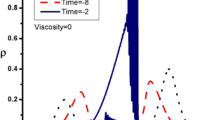
The nonlinear propagation of self-gravitational shock structures (SGSSs) in a self-gravitating, super-dense, degenerate quantum plasma system (containing non-degenerate extremely heavy nuclei and ultra-relativistic degenerate electrons) has been investigated. The well-known reductive perturbation technique, which is valid in the small but finite amplitude limit, has been used to examine the nonlinear propagation of these SGSSs in such degenerate quantum plasma systems. The nonlinear dynamics of these SGSSs has been found to be governed by the Burgers equation, which is derived analytically and solved numerically in planar coordinates. These SGSSs in such plasma systems are shown to be formed due to the presence of a viscous force (which is the source of dissipation) acting on inertial extremely heavy nuclei species of the plasma system. The fundamental properties (viz., amplitude, width, speed, etc.) of these SGSSs are influenced in the ultra-relativistic limit. Our considered plasma model and the numerical analysis of the Burgers equation can be applied to astrophysical compact objects like neutron stars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. S. Goldberg and M. D. Scadron, Physics of Stellar Evolution and Cosmology (Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York, 1987), p. 202.
S. Chandrasekhar, Philos. Mag. 11, 592 (1931).
S. Chandrasekhar, Astrophys. J. 74, 81 (1931).
S. Chandrasekhar, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 170, 405 (1935).
S. Chandrasekhar, An Introduction to the Study of Stellar Structure (Dover, New York, 1939), p. 412.
S. Chandrasekhar, Phys. Rev. Lett. 12, 114 (1964).
S. Chandrasekhar and R. F. Tooper, Astrophys. J. 139, 1396 (1964).
D. Koester and G. Chanmugam, Rep. Prog. Phys. 53, 837 (1990).
S. L. Shapiro and S. A. Teukolsky, Black Holes, White Dwarfs, and Neutron Stars: The Physics of Compact Objects (Wiley, New York, 1983).
E. Garcia-Berro et al., Nature (London) 465, 194 (2010).
W. F. El-Taibany and A. A. Mamun, Phys. Rev. E 85, 026406 (2012).
N. Roy, M. S. Zobaer and A. A. Mamun, J. Mod. Phys. 3, 850 (2012).
A. Rahman, S. Ali, A. Mushtaq and A. Qamar, J. Plasma Phys. 79, 817 (2013).
A. A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 24, 102306 (2017).
B. Hosen, M. Amina and A. A. Mamun, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 69, 1762 (2016).
S. A. Ema, M. R. Hossen and A. A. Mamun, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 55, 551 (2015).
M. Asaduzzaman, A. Mannan and A. A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 24, 052102 (2017).
R. H. Fowler, J. Astrophys. Astron. 15, 115 (1994).
M. R. Hossen, L. Nahar and A. A. Mamun, Phys. Scr. 89, 105603 (2014).
M. S. Zobaer, N. Roy and A. A. Mamun, Astrophys. Space Sci. 343, 675 (2013).
R. P. Drake, Phys. Plasmas 16, 055501 (2009).
R. P. Drake, Phys. Today 63, 28 (2010).
P. K. Shukla and B. Eliasson, Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 885 (2011).
A. A. Mamun, M. Amina and R. Schlickeiser, Phys. Plasmas 23, 094503 (2016).
A. A. Mamun, M. Amina and R. Schlickeiser, Phys. Plasmas 24, 042307 (2017).
Acknowledgments
M. Asaduzzaman is grateful to the Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh, for its financial support through National Science and Technology (NST) fellowship and to the Khulna University of Engineering and Technology (Khulna, Bangladesh) for the study leave during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asaduzzaman, M., Mamun, A.A. Self-Gravitational Shock Structures in Self-Gravitating, Super-Dense, Degenerate Quantum Plasmas. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 77, 111–115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.111