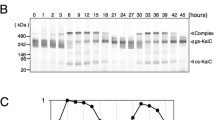
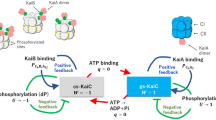
Abstract
The cyanobacterial circadian clock is the most well-understood and simplest biological time-keeping system. Its oscillator consists of three proteins: KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC. When combined together in a test tube, the Kai proteins produce a free-running 24-h cycle of rhythmic auto-phosphorylation and auto-dephosphorylation. To generate a robust circadian rhythm of the in vitro reaction mixture, KaiC, the core oscillator protein, must be purified with an untraditional approach, since even the smallest amount of impurity can hinder its post-translational activities. Until recently, series of fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) columns (glutathione S-transferase (GST), anion exchange (Q), and desalting columns) have been used to purify the oscillator proteins, often requiring laborious elution processes. Although the common methodology has already been established, whether the purified KaiC can produce robust oscillations remains to be verified. Here we emphasize the significance of eliminating the Q step and lengthening the step of removing the non-specifically bound impurities on the GST column for generating a rhythmic KaiC phosphorylation in vitro. These findings demonstrate the potential for shortening the amount of time and effort it takes to purify proteins without compromising its quality.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cohen, S.E. and Golden, S.S., Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2015, vol. 79, no. 4, pp. 373–385.
Tomita, J., Nakajima, M., Kondo, T., and Iwasaki, H., Science, 2005, vol. 307, no. 5707, pp. 251–254.
Nakajima, M., Imai, K., Ito, H., Nishiwaki, T., Murayama, Y., Iwasaki, H., et al., Science, 2005, vol. 308, no. 5720, pp. 414–415.
Dong, G., Kim, Y.I., and Golden, S.S., Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 2010, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 619–625.
Kaur, M., Ng, A., Kim, P., Diekman, C., and Kim, Y.-I. J. Biol. Rhythms, 2019, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 218–223.
Kim, Y.I., Dong, G., Carruthers, C.W., Jr., Golden, S.S., and LiWang, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, vol. 105, no. 35, pp. 12825–12830.
Jeong, Y.M., Dias, C., Diekman, C., Brochon, H., Kim, P., Kaur, M., et al., J. Biol. Rhythms, 2019, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 380–390.
Chang, Y.G., Cohen, S.E., Phong, C., Myers, W.K., Kim, Y.I., Tseng, R., et al., Science, 2015, vol. 349, no. 6245, pp. 324–328.
Kim, Y.I., Boyd, J.S., Espinosa, J., and Golden, S.S., Methods Enzymol., 2015, vol. 551, pp. 153–173.
Zhang, X., Dong, G., and Golden, S.S., Mol. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 658–668.
Mittal, M. K., Misra, S., Owais, M., and Goyal, N., Protein Expr. Purif., 2005, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 279–286.
Nishiwaki, T., Satomi, Y., Nakajima, M., Lee, C., Kiyohara, R., Kageyama, H., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, vol. 101, no. 38, pp. 13927–13932.
Rial, D.V. and Ceccarelli, E.A., Protein Expr. Purif., 2002, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 503–507.
Kitayama, Y., Iwasaki, H., Nishiwaki, T., and Kondo, T., EMBO J., 2003, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 2127–2134.
Nishiwaki, T., Satomi, Y., Kitayama, Y., Terauchi, K., Kiyohara, R., Takao, T., and Kondo, T., EMBO J., 2007, vol. 26, no. 17, pp. 4029–4037.
Snijder, J., Burnley, R.J., Wiegard, A., Melquiond, A.S.J., Bonvin, A.M.J.J., Axmann, I.M., and Heck, A.J.R., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, vol. 111, no. 4, pp. 1379.
Chen, Q., Liu, S., Yang, L., Zhang, L., and Li, J. Data Brief, 2018, vol. 18, pp. 241–247.
Mukaiyama, A., Ouyang, D., Furuike, Y., and Akiyama, S., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, vol. 131, pp. 67–73.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank H. Nim for insightful discussion and A. Ng, E. Kim, and M. Bartley for technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by New Jersey Institute of Technology (USA) start-up grant to Y.I. Kim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, P., Kaszuba, A., Jang, HI. et al. Purification of GST-Fused Cyanobacterial Central Oscillator Protein KaiC. Appl Biochem Microbiol 56, 395–399 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683820040092
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683820040092