Abstract
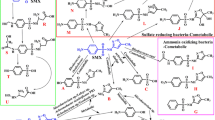
A gram-positive gabapentin-degrading bacteria strain N.ISM.1 was isolated from the pharmaceutical plant soil. According to the analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequence, the strain was categorized as a Micrococcus luteus. Though the strain N.ISM.1 is capable of degrading gabapentin (GABA), this compound cannot provide enough carbon source for the isolated strain. M. luteus N.ISM.1 degrades GABA in the presence of glucose. The greater the concentration of secondary simpler carbon source (glucose) for cometabolism, the greater the biodegradation of GABA is. Around 97% of GABA was degraded within a course of 40 days after using 150 mg/L glucose as cometabolic simpler carbon source. M. luteus N.ISM.1 is a promising microorganism for the biodegradation of an anticonvulsant drug GABA contaminated environment and with the aid of cometabolic activity of glucose (150 mg/L) the degradation achieved perfection. GABA biodegradation metabolites were identified by a liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. This is the very first report of GABA biodegradation as per our concern.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Daughton, C.G. and Ternes, T.A., Environ. Health Perspect., 1999, vol. 107, suppl. 6, pp. 907–938.
Reis, P.J., Reis, A.C., Ricken, B., Kolvenbach, B.A., Manaia, C.M., Corvini, P.F., and Nunes, O.C., J. Hazard. Mater., 2014, vol. 280, pp. 741–749.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Nielsen, S.N., Lanzky, P.F., Ingerslev, F., Lützhøft, H.H., and Jørgensen, S.E., Chemosphere, 1998, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 357–393.
Kümmerer, K., Chemosphere, 2009, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 417–434.
Carta, M.G., Hardoy, M.C., Hardoy, M.J., Grunze, H., and Carpiniello, B., J., Affect Disord., 2003, vol. 75, no. 1, pp. 83–91.
Happe, S., Sauter, C., Klösch, G., Saletu, B., and Zeitlhofer, J., 2003, Neuropsychobiology, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 82–86.
Lai, F.Y., Ort, C., Gartner, C., Carter, S., Prichard, J., Kirkbride, P., et al., Water Res., 2011, vol. 45, no. 15, pp. 4437–4448.
Drug Prescription Report. Current Data, Expenses, Trends and Comments, Schwabe, U. and Paffrath, D., Eds., Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer–Verlag, 2010.
Ebert, I., Amato, R., Hein, A., and Konradi, S., Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Avoiding, Reducing, Monitoring, Federal Environmental Agency, Dessau–Rosslau: Umweltbunesarnt, 2014.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R.M., and Guwy, A.J., 2009, Environ. Pollut., vol. 157, no. 6, pp. 1778–1786.
Ferrer, I., Barber, L.B., and Thurman, E.M., Sci. Total Environ., 2013, vol. 461, pp. 519–527.
Morasch, B., Bonvin, F., Reiser, H., Grandjean, D., De Alencastro, L.F., Perazzolo, C., et al., Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2010, vol. 29, no. 8. pp. 1658–1668.
Zour, E., Lodhi, S.A., Nesbitt, R.U., Silbering, S.B., and Chaturvedi, P.R., Pharmac. Res., 1992, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 595–600.
Herrmann, M., Menz, J., Olsson, O. and Kümmerer, K., Water Res., 2015, vol. 85, pp. 11–21.
Marchlewicz, A., Domaradzka, D., Guzik, U., and Wojcieszyńska, D., Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 2016, vol. 227, no. 6, p. 197.
Tarafdar, A., Sinha, A., Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2017, vol. 24, pp. 10373–10380.
Garrity, G.M., Bell, J.A., and Lilburn, T.G., Taxonomic Outline of the Prokaryotes. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, New York: Springer, 2004.
Vandamme, P. and Coenye, T., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 2285–2289.
Vaneechoutte, M., Kämpfer, P., De Baere, T., Falsen, E. and Verschraegen, G., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 317–327.
Tarafdar, A., Sarkar, T.K., Chakraborty, S., Sinha, A., and Masto, R.E., Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety, 2018, vol. 157, pp. 327–334.
Moaledj, K., J. Microbiol. Methods, 1986, vol. 5, nos. 5–6, pp. 353–310.
Faller, A.N.T.O.N. and Schleifer, K.H., J. Clin. Microbiol., 1981, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 1031–1035.
Kämpfer, P., Steiof, M., and Dott, W., Microb. Ecol., 1991, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 227–251.
Gerhard, P., Murray, R.G., Wood, W.A. and Krieg, N.R., Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology, Washington DC: American Society of Microbiology, 1994, pp. 611–654.
Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics, Stackebrandt, E. and Goodfellow, M., Eds., New York: Wiley, 1991, pp. 115–175.
Kim, O.S., Cho, Y.J., Lee, K., Yoon, S.H., Kim, M., Na, H., et al., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2012, vol. 62, no. 3, pp. 716–721.
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N.P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P.A., McWilliam, H., et al., Bioinformatics, 2007, vol. 23, no. 21, pp. 2947–2948.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K., Mol. Biol. Evol., 2016, vol. 33, no. 7, pp. 1870–1874.
Greń, I., Wojcieszyńska, D., Guzik, U., Perkosz, M., and Hupert-Kocurek, K., 2010, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 289–295.
Smejkal, C.W., Vallaeys, T., Burton, S.K., and Lappin-Scott, H.M., Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 272–277.
Tarafdar, A., Sinha, A., Masto, R.E., Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 65, pp. 327–334.
Tobajas, M., Monsalvo, V.M., Mohedano, A.F., and Rodriguez, J.J., J. Environ. Manag., 2012, vol. 95, pp. S116–S121.
Zhang, G., Yang, X., Xie, F., Chao, Y., and Qian, S., World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2009, vol. 25 no. 7, pp. 1169–1174.
Li, A., Cai, R., Cui, D., Qiu, T., Pang, C., Yang, J., et al., J. Envon. Sci., 2013, vol. 25 no. 11, pp. 2281–2290.
Buchicchio, A., Bianco, G., Sofo, A., Masi, S., and Caniani, D., Sci. Total Environ., 2016, vol. 557, pp. 733–739.
Funding
The authors thank the financial support from Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad under Junior Research Fellowship scheme funded by Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Government of India, New Delhi, for carrying out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamal, N., Tarafdar, A., Sinha, A. et al. Effect of Glucose Cometabolism on Biodegradation of Gabapentin (an Anticonvulsant Drug) by Gram-Positive Bacteria Micrococcus luteus N.ISM.1. Appl Biochem Microbiol 56, 433–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683820040067
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683820040067