Abstract
Glycosylphosphatidylinositols (GPIs) anchored proteins are commonly localized onto lipid rafts. These extracellular proteins participate in a variety of cellular functions, including as receptors for viruses and toxins. Intracellular trafficking of World Health Organization recognized mosquito-larvicidal BinAB toxin is mediated via GPI-anchored Cqm1 receptor protein in Culex mosquitoes. We confirmed conformational change in Cqm1 dimer on interaction with BinA/BinB proteins by dynamic light scattering, modelling of hydrodynamic parameters using the atomic structures, and synchrotron Small Angle solution X-ray scattering (SAXS). A reliable model of the receptor–BinB complex was also constructed from joint SAXS/SANS refinement. We confirmed electrostatic interactions of the Cqm1 ectodomain with lipid rafts reconstituted in model membranes and report receptor-dependent impairment of model liposomes by BinA/B proteins. Liposomal disruption was toxin concentration-dependent as monitored by the release of encapsulated carboxyfluorescein dye. Interestingly, BinA alone, without BinB, showed efficient efflux of the fluorescent dye in agreement with the reported high larvicidal activity of BinA variants. The study provides insight into BinA/B toxin internalization mechanism in the membrane model that is toxin internalization is mediated via receptor-dependent pore formation mechanism. It also suggests a tangible and environmentally safe strategy for control of mosquito population.
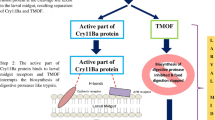
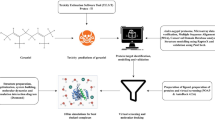
Graphic Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Small Angle solution Scattering (SAXS and SANS) data for Cqm1 (SAXS), BinB (SAXS), BinB–Cqm1 complex (SAXS) and BinB–Cqm1 complex (SANS) have been submitted to the Small Angle Scattering Biological Data Bank (SASBDB; https://www.sasbdb.org; Valentini et al. 2015) with submission Ids SASDHR8, SASDHS8, SASDHT8 and SASDHU8, respectively.
References
Baker NA, Sept D, Joseph S, Holst MJ, McCammon JA (2001) Electrostatics of nanosystems: application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10037–10041
Banerjee P, Wehle M, Lipowsky R, Santer M (2018) A molecular dynamics model for glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol anchors: "flop down" or "lollipop"? PhysChemChemPhys 20:29314–29324
Berry C (2012) The bacterium, Lysinibacillus sphaericus, as an insect pathogen. J Invertebr Pathol 109:1–10
Bideshi DK, Park HW, Hice RH, Wirth MC, Federici BA (2017) Highly effective broad spectrum chimeric larvicide that targets vector mosquitoes using a lipophilic protein. Sci Rep 7:11282
Charles J, Silvafilha M, Nielsenleroux C, Humphreys M, Berry C (1997) Binding of the 51- and 42-kDa individual components from the crystal toxin to mosquito larval midgut membranes from and sp. (Diptera: Culicidae). FEMS Microbiol Lett 156(1):153–159
Colletier JP, Sawaya MR, Gingery M, Rodriguez JA, Cascio D, Brewster AS, Michels-Clark T, Hice RH, Coquelle N, Boutet S, Williams GJ, Messerschmidt M, DePonte DP, Sierra RG, Laksmono H, Koglin JE, Hunter MS, Park HW, Uervirojnangkoorn M, Bideshi DK, Brunger AT, Federici BA, Sauter NK, Eisenberg DS (2016) De novo phasing with X-ray laser reveals mosquito larvicide BinAB structure. Nature 539:43–47
Cooper ST, McNeil PL (2015) Membrane Repair: Mechanisms and Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 95:1205–1240
de Almeida RF, Fedorov A, Prieto M (2003) Sphingomyelin/phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol phase diagram: boundaries and composition of lipid rafts. Biophys J 85:2406–2416
Ferreira LM, Romão TP, Nascimento NA, Costa Mda C, Rezende AM, de-Melo-Neto OP, Silva-Filha MH (2014) Non conserved residues between Cqm1 and Aam1 mosquito α-glucosidases are critical for the capacity of Cqm1 to bind the Binary toxin from Lysinibacillus sphaericus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 50:34–42
Franke D, Petoukhov MV, Konarev PV, Panjkovich A, Tuukkanen A, Mertens HDT, Kikhney AG, Hajizadeh NR, Franklin JM, Jeffries CM, Svergun DI (2017) ATSAS 2.8: a comprehensive data analysis suite for small-angle scattering from macromolecular solutions. J Appl Crystallogr 50:1212–1225
Gao H, Shi W, Freund LB (2005) Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9469–9474
Hire RS, Hadapad AB, Dongre TK, Kumar V (2009) Purification and characterization of mosquitocidal Bacillus sphaericus BinA protein. J invert Patholog 101:106–111
Jesorka A, Orwar O (2008) Liposomes: technologies and analytical applications. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif) 1:801–832
Jiménez-García B, Bernadó P, Fernández-Recio J (2020) Structural characterization of protein–protein interactions with pyDockSAXS. Methods Mol Biol 2112:131–144
Kale A, Hire RS, Hadapad AB, D'Souza SF, Kumar V (2013) Interaction between mosquito-larvicidal Lysinibacillus sphaericus binary toxin components: analysis of complex formation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43:1045–1054
Kozakov D, Hall DR, Xia B, Porter KA, Padhorny D, Yueh C, Beglov D, Vajda S (2017) The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nat Protoc 12:255–278
Lorent JH, Levental I (2015) Structural determinants of protein partitioning into ordered membrane domains and lipid rafts. Chem Phys Lipids 192:23–32
Lorent JH, Diaz-Rohrer B, Lin X et al (2017) Structural determinants and functional consequences of protein affinity for membrane rafts. Nat Commun 8:1219
Ortega A, Amorós D, García de la Torre J (2011) Prediction of hydrodynamic and other solution properties of rigid proteins from atomic- and residue-level models. Biophys J 101:892–898
Parker MW, Feil SC (2005) Pore-forming protein toxins: from structure to function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 88:91–142
Paladino S, Sarnataro D, Pillich R, Tivodar S, Nitsch L, Zurzolo C (2004) Protein oligomerization modulates raft partitioning and apical sorting of GPI-anchored proteins. J Cell Biol 167:699–709
Pandey B, Aarthy M, Sharma M, Singh SK, Kumar V (2020) Computational analysis identifies druggable mutations in human rBAT mediated Cystinuria. J Biomol Struct Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1784792
Pauchet Y, Luton F, Castella C, Charles JF, Romey G, Pauron D (2005) Effects of a mosquitocidal toxin on a mammalian epithelial cell line expressing its target receptor. Cell Microbiol 7:1335–1344
Paulick MG, Bertozzi CR (2008) The glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor: a complex membrane-anchoring structure for proteins. Biochemistry 47:6991–7000
Petoukhov MV, Konarev PV, Kikhney AG, Svergun DI (2007) ATSAS 2.1 - towards automated and web-supported small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Cryst 40:s223–s228
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Schwartz JL, Potvin L, Coux F et al (2001) Permeabilization of model lipid membranes by Bacillus sphaericus mosquitocidal binary toxin and its individual components. J Membr Biol 184:171–183
Sezgin E, Levental I, Mayor S, Eggeling C (2017) The mystery of membrane organization: composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:361–374
Sharma M, Kumar V (2019) Crystal structure of BinAB toxin receptor (Cqm1) protein and molecular dynamics simulations reveal the role of unique Ca(II) ion. Int J Biol Macromol 140:1315–1325
Sharma M, Hire RS, Hadapad AB, Gupta GD, Kumar V (2017) PEGylation enhances mosquito-larvicidal activity of lysinibacillus sphaericus binary toxin. Bioconjug Chem 28:410–418
Sharma M, Gupta GD, Kumar V (2018a) Mosquito-larvicidal BinA toxin displays affinity for glycoconjugates: proposal for BinA mediated cytotoxicity. J Invertebr Pathol 156:29–40
Sharma M, Gupta GD, Kumar V (2018b) Receptor protein of Lysinibacillus sphaericus mosquito-larvicidal toxin displays amylomaltase activity. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 93:37–46
Sharma M, Aswal VK, Kumar V, Chidambaram R (2020) Small-angle neutron scattering studies suggest the mechanism of BinAB protein internalization. IUCrJ 7:166–172
Silva-Filha MH, Nielsen-LeRoux C, Charles JF (1999) Identification of the receptor for Bacillus sphaericus crystal toxin in the brush border membrane of the mosquito Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:711–721
Singkhamanan K, Promdonkoy B, Srikhirin T, Boonserm P (2013) Amino acid residues in the N-terminal region of the BinB subunit of Lysinibacillus sphaericus binary toxin play a critical role during receptor binding and membrane insertion. J Invertebr Pathol 114:65–70
Svergun DI (1999) Restoring low resolution structure of biological macromolecules from solution scattering using simulated annealing. Biophys J 76:2879–2886
Svergun D, Barberato C, Koch MHJ (1995) CRYSOL: a program to evaluate X-ray solution scattering of biological macromolecules from atomic coordinates. J Appl Cryst 28:768–773
Trewhella J, Duff AP, Durand D, Gabel F, Guss JM, Hendrickson WA, Hura GL, Jacques DA, Kirby NM, Kwan AH, Pérez J, Pollack L, Ryan TM, Sali A, Schneidman-Duhovny D, Schwede T, Svergun DI, Sugiyama M, Tainer JA, Vachette P, Westbrook J, Whitten AE (2017) publication guidelines for structural modelling of small-angle scattering data from biomolecules in solution: an update. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 73:710–728
Valentini E, Kikhney AG, Previtali G, Jeffries CM, Svergun DI (2015) SASBDB, a repository for biological small-angle scattering data. Nucleic Acids Res 43:357–363
World Health Organization (1985) Informal consultation on the development of Bacillus sphaericus as a microbial larvicide. TDR/BCV/Sphaericus/85.3. World Health Organization, Geneva.
Yokouchi Y, Tsunoda T, Imura T, Yamauchi H, Yokoyama S, Sakai H, Abe M (2001) Effect of adsorption of bovine serum albumin on liposomal membrane characteristics. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 20:95–103
Zhang H (2017) Thin-film hydration followed by extrusion method for liposome preparation. Methods Mol Biol 1522:17–22
Zhang S, Li J, Lykotrafitis G, Bao G, Suresh S (2009) Size-dependent endocytosis of nanoparticles. Adv Mater 21:419–424
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor R. Chidambaram for encouragement and useful discussions. We also thank Drs. Debasis Sen, Avik Das and Rahul Singh, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, for the kind help of SAXS data acquisition on Indus-2 synchrotron.
Funding
The research was funded by the Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VK conceived and designed the research, analysed data and wrote the manuscript. MS purified the proteins. MS and AK planned and performed liposomal study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All the authors agree on publication of the manuscript.
Ethical Approval
No animals or humans have been used in the study. Ethics approval are not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M., Kumar, A. & Kumar, V. Liposome-Based Study Provides Insight into Cellular Internalization Mechanism of Mosquito-Larvicidal BinAB Toxin. J Membrane Biol 253, 331–342 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-020-00131-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-020-00131-4