Abstract
Background
It has comprehensively been acknowledged that a genetic contribution, especially in immune inflammatory players, such as interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, are critically involved in the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease (CAD). This meta-analysis study aimed to reach a conclusive understanding of the role of genetic polymorphisms, including IL6 gene C572G (rs1800796) and G174C (rs1800795) as well as TNFA gene G238A (rs361525) and G308A (rs1800629) in susceptibility to CAD.
Methods
Two major databases, namely MEDLINE and Scopus, were searched to find the studies surveying the mentioned polymorphisms and CAD susceptibility up to July 2020. Association comparison between the polymorphisms and CAD susceptibility were assessed using pooled odds ratio (OR) and their corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
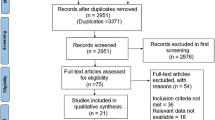
This meta-analysis study was conducted on 69 papers (73 population studies), comprising 5062 patients and 8446 controls for IL6 gene rs1800796 (17 studies), 13801 patients and 16215 controls for IL6 gene rs1800795 (38 studies), 1439 patients and 2850 controls for TNFA gene rs361525 (5 studies), and 5051 patients and 3958 controls for TNFA gene rs1800629 (13 studies), according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. There were statistically positive association between all genetic comparisons of IL6 gene rs1800795 polymorphism and the CAD risk. Moreover, the recessive model (CC vs. CG + GG) in IL6 gene rs1800796 polymorphism had marginally significant association with decreased risk of CAD. None of the TNFA gene polymorphisms were associated with CAD risk.
Conclusions
The meta-analysis revealed the positive association of IL6 gene rs1800795 polymorphism in susceptibility to CAD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- SNPs:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
References
Harky A, Noshirwani A, Karadakhy O, Ang J. Comprehensive literature review of anomalies of the coronary arteries. J Cardiac Surg. 2019;34(11):1328–43.
Figura N, Palazzuoli A, Vaira D, Campagna M, Moretti E, Iacoponi F, et al. Cross-sectional study: CagA–positive Helicobacter pylori infection, acute coronary artery disease and systemic levels of B-type natriuretic peptide. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:251–7.
Jia S-J, Niu P-P, Cong J-Z, Zhang B-K, Zhao M. TLR4 signaling: a potential therapeutic target in ischemic coronary artery disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;23:54–9.
Sanjadi M, Rezvanie Sichanie Z, Totonchi H, Karami J, Rezaei R, Aslani S. Atherosclerosis and autoimmunity: a growing relationship. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21:908–21.
Yeganeh F, Mousavi SMJ, Hosseinzadeh-Sarband S, Ahmadzadeh A, Bahrami-Motlagh H, Hoseini MHM, et al. Association of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV mRNA level in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with disease activity and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:3183–90.
Said MA, van de Vegte YJ, Zafar MM, van der Ende MY, Raja GK, Verweij N, et al. Contributions of interactions between lifestyle and genetics on coronary artery disease risk. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019;21:89.
Mahalle N, Garg M, Kulkarni M, Naik S. Association of inflammatory cytokines with traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors in indians with known coronary artery disease. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014;4:706–12.
Ghazouani L, Abboud N, Khalifa SBH, Added F, Khalfallah AB, Nsiri B, et al. 174G > C interleukin-6 gene polymorphism in Tunisian patients with coronary artery disease. Ann Saudi Med. 2011;31:40–4.
Masafi S, Saadat SH, Tehranchi K, Olya R, Heidari M, Malihialzackerini S, et al. Effect of stress, depression and type D personality on immune system in the incidence of coronary artery disease. Open Access Macedonian J Med Sci. 2018;6:1533.
Terry CF, Loukaci V, Green FR. Cooperative influence of genetic polymorphisms on interleukin 6 transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18138–44.
Karahan ZC, Deda G, Sipahi T, Elhan AH, Akar N. TNF-α − 308G/A and IL-6 − 174 G/C polymorphisms in the Turkish pediatric stroke patients. Thromb Res. 2005;115:393–8.
Kelberman D, Hawe E, Luong LA, Mohamed-Ali V, Lundman P, Tornvall P, et al. Effect of Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphisms in survivors of myocardial infarction and matched controls in the North and South of Europe. Thromb Haemost. 2004;92:1122–8.
Kou L, Yang N, Dong B, Li Y, Yang J, Qin Q. Interaction between SELP genetic polymorphisms with inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene variants on cardiovascular disease in Chinese Han population. Mamm Genome. 2017;28:436–42.
Lalouschek W, Schillinger M, Hsieh K, Endler G, Greisenegger S, Marculescu R, et al. Polymorphisms of the inflammatory system and risk of ischemic cerebrovascular events. Clin Chem Lab Med (CCLM). 2006;44:918–23.
Satti HS, Hussain S, Javed Q. Association of interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism with coronary artery disease in Pakistani families. Sci World J. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/538365.
Sekuri C, Cam FS, Sagcan A, Ercan E, Tengiz I, Alioglu E, et al. No association of interleukin-6 gene polymorphism (-174 G/C) with premature coronary artery disease in a Turkish cohort. Coron Artery Dis. 2007;18:333–7.
Sie MP, Sayed-Tabatabaei FA, Oei H-HS, Uitterlinden AG, Pols HA, Hofman A, et al. Interleukin 6–174 g/c promoter polymorphism and risk of coronary heart disease: results from the rotterdam study and a meta-analysis. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:212–7.
Song H, Zhou X, Guo L, Tian F, Guo X, Sun Y. Association of phosphodiesterase 4D gene and interleukin-6 receptor gene polymorphisms with ischemic stroke in a Chinese hypertensive population. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:19396–403.
Koch W, Tiroch K, von Beckerath N, Schömig A, Kastrati A. Tumor necrosis factor-α, lymphotoxin-α, and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms and restenosis after coronary artery stenting. Cytokine. 2003;24:161–71.
Allen R, Lee E, Roberts D, Park B, Pirmohamed M. Polymorphisms in the TNF-α and TNF-receptor genes in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2001;31:843–51.
Hou L, Huang J, Lu X, Wang L, Fan Z, Gu D. Polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene and coronary heart disease in a Chinese Han population: interaction with cigarette smoking. Thromb Res. 2009;123:822–6.
Allen RD. Polymorphism of the human TNF-α promoter—random variation or functional diversity? Mol Immunol. 1999;36:1017–27.
Wang XL, Oosterhof J. Tumour necrosis factor α G − 308 → A polymorphism and risk for coronary artery disease. Clin Sci. 2000;98:435–7.
Cheng Y, An B, Jiang M, Xin Y, Xuan S. Association of tumor necrosis factor-alpha polymorphisms and risk of coronary artery disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatitis Monthly. 2015;15(3):e26818.
Shih C-M, Lee Y-L, Chiou H-L, Chen W, Chang G-C, Chou M-C, et al. Association of TNF-α polymorphism with susceptibility to and severity of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2006;52:15–20.
Fan H-M, Wang Z, Feng F-M, Zhang K-L, Yuan J-X, Sui H, et al. Association of TNF-α-238G/A and 308 G/A gene polymorphisms with pulmonary tuberculosis among patients with coal worker’s pneumoconiosis. Biomed Environ Sci. 2010;23:137.
Jk Wang, Zw Feng, Yc Li, Qy Li, Xy Tao. Association of tumor necrosis factor-α gene promoter polymorphism at sites-308 and-238 with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:670–6.
Cui G, Wang H, Li R, Zhang L, Li Z, Wang Y, et al. Polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) gene promoter, circulating TNF-alpha level, and cardiovascular risk factor for ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflam. 2012;9:235.
Banerjee I, Pandey U, Hasan OM, Parihar R, Tripathi V, Ganesh S. Association between inflammatory gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in an Indian population. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009;27:88–94.
Herrmann S, Ricard S, Nicaud V, Mallet C, Arveiler D, Evans A, et al. Polymorphisms of the tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene, coronary heart disease and obesity. Eur J Clin Invest. 1998;28:59–66.
Cho H-C, Yu G, Lee M-Y, Kim H-S, Shin D-H, Kim Y-N. TNF-α polymorphisms and coronary artery disease: association study in the Korean population. Cytokine. 2013;62:104–9.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1.
Huedo-Medina TB, Sánchez-Meca J, Marín-Martínez F, Botella J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol Methods. 2006;11:193.
MartorellMarugan J, ToroDominguez D, AlarconRiquelme ME, CarmonaSaez PJBB. MetaGenyo: a web tool for meta-analysis of genetic association studies. BMC Bioinform. 2017;18:563.
Piira O-P, Miettinen JA, Hautala AJ, Huikuri HV, Tulppo MP. Physiological responses to emotional excitement in healthy subjects and patients with coronary artery disease. Autonomic Neurosci. 2013;177:280–5.
Mayyas FA, Al-Jarrah MI, Ibrahim KS, Alzoubi KH. Level and significance of plasma myeloperoxidase and the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with coronary artery disease. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8:1951–7.
Anderson DR, Poterucha JT, Mikuls TR, Duryee MJ, Garvin RP, Klassen LW, et al. IL-6 and its receptors in coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction. Cytokine. 2013;62:395–400.
Smith AJ, D’Aiuto F, Palmen J, Cooper JA, Samuel J, Thompson S, et al. Association of serum interleukin-6 concentration with a functional IL6− 6331T> C polymorphism. Clin Chem. 2008;54:841–50.
Yin Y-W, Li J-C, Zhang M, Wang J-Z, Li B-H, Liu Y, et al. Influence of interleukin-6 gene − 174G > C polymorphism on development of atherosclerosis: a meta-analysis of 50 studies involving 33,514 subjects. Gene. 2013;529:94–103.
Hou H, Wang C, Sun F, Zhao L, Dun A, Sun Z. Association of interleukin-6 gene polymorphism with coronary artery disease: an updated systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. Inflamm Res. 2015;64:707–20.
González-Castro TB, Hernández-Díaz Y, Pérez-Hernández N, Tovilla-Zárate CA, Juárez-Rojop IE, López-Narvaez ML, et al. Interleukin 6 (rs1800795) gene polymorphism is associated with cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of 74 studies with 86,229 subjects. EXCLI J. 2019;18:331.
Song C, Liu B, Yang D, Diao H, Zhao L, Lu Y, et al. Association between interleukin-6 gene − 572G > C polymorphism and coronary heart disease. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;71:359–65.
Asifa GZ, Liaquat A, Murtaza I, Kazmi SAR, Javed Q. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene promoter region polymorphism and the risk of coronary heart disease. Sci World J. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/203492.
Zhang H-F, Zhong B-L, Zhu W-L, Xie S-L, Qiu L-X, Zhu L-G, et al. CD14 C-260T gene polymorphism and ischemic heart disease susceptibility: a HuGE review and meta-analysis. Genet Med. 2009;11:403.
Pulido-Gómez K, Hernández-Díaz Y, Tovilla-Zárate CA, Juárez-Rojop IE, González-Castro TB, López-Narváez ML, et al. Association of G308A and G238A polymorphisms of the TNF-α gene with risk of coronary heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Med Res. 2016;47:557–72.
Georges J-L, Loukaci V, Poirier O, Evans A, Luc G, Arveiler D, et al. Interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to myocardial infarction: the ECTIM study. J Mol Med. 2001;79:300–5.
Humphries S, Luong L, Ogg M, Hawe E, Miller G. The interleukin-6 − 174 G/C promoter polymorphism is associated with risk of coronary heart disease and systolic blood pressure in healthy men. Eur Heart J. 2001;22:2243–52.
Basso F, Lowe GD, Rumley A, McMahon AD, Humphries SE. Interleukin-6 − 174G > C polymorphism and risk of coronary heart disease in West of Scotland coronary prevention study (WOSCOPS). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:599–604.
Bennet AM, Prince JA, Fei G-Z, Lyrenäs L, Huang Y, Wiman B, et al. Interleukin-6 serum levels and genotypes influence the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 2003;171:359–67.
Fu H, Li G, Li Y, Xu J, Zhang J. Interleukin-6-597G/A and-572C/G polymorphisms and risk of coronary heart disease. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2006;34:519–22.
Park S, Youn J-C, Shin D-J, Park C-M, Kim J-S, Ko Y-G, et al. Genetic polymorphism in the pregnancy-associated plasma protein—a associated with acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 2007;18:417–22.
Fan W, Liu D, Xiao L, Xie C, Sun S, Zhang J. Coronary heart disease and chronic periodontitis: is polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene the common risk factor in a Chinese population? Oral Dis. 2011;17:270–6.
Jia X, Tian Y, Wang Y, Deng X, Dong Z, Scafa N, et al. Association between the interleukin-6 gene-572G/C and-597G/A polymorphisms and coronary heart disease in the Han Chinese. Med Sci Mon. 2010;16:103–8.
Çoker A, Arman A, Soylu O, Tezel T, Yildirim A. Lack of association between IL-1 and IL-6 gene polymorphisms and myocardial infarction in Turkish population. Int J Immunogenet. 2011;38:201–8.
Li L, Li E, Zhang L, Jian L, Liu H, Wang T. IL-6-174G/C and IL-6-572C/G polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:8451–7.
Jabir NR, Firoz CK, Kamal MA, Damanhouri GA, Alama MN, Alzahrani AS, et al. Assessment of genetic diversity in IL-6 and RANTES promoters and their level in Saudi coronary artery disease patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 2017;31:e22092.
Mao L, Geng GY, Han WJ, Zhao MH, Wu L, Liu HL. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) -174G/C genomic polymorphism contribution to the risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. Genet Mol Res. 2016;196:15–43.
Mitrokhin V, Nikitin A, Brovkina O, Khodyrev D, Zotov A, Vachrushev N, et al. Association between interleukin-6/6R gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in Russian population: influence of interleukin-6/6R gene polymorphisms on inflammatory markers. J Inflamm Res. 2017;10:151.
Chen H, Ding S, Liu X, Wu Y, Wu X. Association of interleukin-6 genetic polymorphisms and environment factors interactions with coronary artery disease in a chinese han population. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018;40:514–7.
Nauck M, Winkelmann BR, Hoffmann MM, Böhm BO, Wieland H, März W. The interleukin-6 G (–174) C promoter polymorphism in the LURIC cohort: no association with plasma interleukin-6, coronary artery disease, and myocardial infarction. J Mol Med. 2002;80:507–13.
Licastro F, Chiappelli M, Caldarera CM, Tampieri C, Nanni S, Gallina M, et al. The concomitant presence of polymorphic alleles of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 and apolipoprotein E is associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction in elderly men: results from a pilot study. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004;125:575–9.
Lieb W, Pavlik R, Erdmann J, Mayer B, Holmer SR, Fischer M, et al. No association of interleukin-6 gene polymorphism (− 174 G/C) with myocardial infarction or traditional cardiovascular risk factors. Int J Cardiol. 2004;97:205–12.
Chiappelli M, Tampieri C, Tumini E, Porcellini E, Caldarera C, Nanni S, et al. Interleukin-6 gene polymorphism is an age-dependent risk factor for myocardial infarction in men. Int J Immunogenet. 2005;32:349–53.
Rosner SA, Ridker PM, Zee RY, Cook NR. Interaction between inflammation-related gene polymorphisms and cigarette smoking on the risk of myocardial infarction in the Physician’s Health Study. Hum Genet. 2005;118:287–94.
Mysliwska JW, Joanna W, Hak LS, Janusz S, Rogowski JS, Krzysztof S, Mysliwski A. Interleukin 6 polymorphism corresponds to the number of severely stenosed coronary arteries. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:181–8.
Tütün U, Aksöyek A, Ulus AT, Msrloglu M, Çiçekçioglu F, Özsk K, et al. Gene polymorphisms in patients below 35 years of age who underwent coronary artery bypass surgery. Coron Artery Dis. 2006;17:35–9.
Maitra A, Shanker J, Dash D, John S, Sannappa PR, Rao VS, et al. Polymorphisms in the IL6 gene in Asian Indian families with premature coronary artery disease–the Indian Atherosclerosis Research Study. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:944–50.
Sarecka B, Zak I, Krauze J. Synergistic effects of the polymorphisms in the PAI-1 and IL-6 genes with smoking in determining their associated risk with coronary artery disease. Clin Biochem. 2008;41:467–73.
Ghazouani L, Ben Hadj Khalifa S, Abboud N, BenHamda K, Ben Khalfallah A, Brahim N, Almawi WY, Mahjoub T. TNF-alpha-308G > A and IL-6-174G > C polymorphisms in Tunisian patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Biochem. 2010;43:1085–9.
Rios DL, Cerqueira CC, Bonfim-Silva R, Araújo LJ, Pereira JF, Gadelha SR, et al. Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 gene polymorphism associations with angiographically assessed coronary artery disease in Brazilians. Cytokine. 2010;50:292–6.
Bennermo M, Nordin M, Lundman P, Boqvist S, Held C, Samnegård A, et al. Genetic and environmental influences on the plasma interleukin-6 concentration in patients with a recent myocardial infarction: a case–control study. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31:259–64.
Vakili H, Ghaderian SMH, Najar RA, Panah AST, Azargashb E. Genetic polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene and susceptibility to acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 2011;22:299–305.
Phulukdaree A, Khan S, Ramkaran P, Govender R, Moodley D, Chuturgoon AA. The interleukin-6 − 147 G/C polymorphism is associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in young south african indian men. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2013;11:205–9.
Galimudi RK, Spurthi MK, Padala C, Kumar KG, Mudigonda S, Reddy SG, et al. Interleukin 6 (-174G/C) variant and its circulating levels in coronary artery disease patients and their first degree relatives. Inflammation. 2014;37:314–21.
Yang H, Wang S, Yan L, Qian P, Duan H. Association of interleukin gene polymorphisms with the risk of coronary artery disease. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:12489–96.
Toutouzas K, Klettas D, Anousakis-Vlachochristou N, Melidis K, Azilazian Z, Asimomiti M, et al. The-174 G > C interleukin-6 gene polymorphism is associated with angiographic progression of coronary artery disease over a 4-year period. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2017;58:80–6.
Shabana N, Ashiq S, Ijaz A, Khalid F, Ul Saadat I, Khan K, et al. Genetic risk score (GRS) constructed from polymorphisms in the PON1, IL-6, ITGB3, and ALDH2 genes is associated with the risk of coronary artery disease in Pakistani subjects. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17:224.
Szalai C, Füst G, Duba J, Kramer J, Romics L, Prohászka Z, et al. Association of polymorphisms and allelic combinations in the tumour necrosis factor-α-complement MHC region with coronary artery disease. J Med Genet. 2002;39:46–51.
Cheng Y, An B, Jiang M, Xin Y, Xuan S. Association of tumor necrosis factor-alpha polymorphisms and risk of coronary artery disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatitis Monthly. 2015;15:e26818.
Hussain S, Iqbal T, Javed Q. TNF-alpha-308G > A polymorphism and the risk of familial CAD in a Pakistani population. Hum Immunol. 2015;76:13–8.
Kumari R, Kumar S, Ahmad MK, Singh R, Kumar SK, Pradhan A, et al. Promoter variants of TNF-α rs1800629 and IL-10 rs1800871 are independently associated with the susceptibility of coronary artery disease in north Indian. Cytokine. 2018;110:131–6.
Georges J-L, Rupprecht HJ, Blankenberg S, Poirier O, Bickel C, Hafner G, et al. Impact of pathogen burden in patients with coronary artery disease in relation to systemic inflammation and variation in genes encoding cytokines. Am J Cardiol. 2003;92:515–21.
Ghazouani L, Abboud N, Addad F, Khalfallah AB, Brahim N, Mediouni M, et al. –308G > A and–1031T > C tumor necrosis factor gene polymorphisms in Tunisian patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47:1247–51.
Sobti RC, Kler R, Sharma YP, Talwar KK, Singh N. Risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes with tumor necrosis factor-α 308G/A gene polymorphism in metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease subjects. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;360:1–7.
Garg PR, Saraswathy KN, Kalla AK, Sinha E, Ghosh PK. Pro-inflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms and threat for coronary heart disease in a North Indian Agrawal population. Gene. 2013;514:69–74.
Chen W, Hua K, Gu H, Zhang J, Wang L. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C667T polymorphism is associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. Scand J Immunol. 2014;80:346–53.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful of Deputy of Research from Neyshabur University of Medical Science.
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST performed the statistical analysis and participated in manuscript drafting. MM performed the statistical analysis, involved in conception and design, and participated in manuscript drafting. SMT developed the main idea and participated in manuscript drafting. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors read the manuscript and consent for its publication.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabaei, S., Motallebnezhad, M. & Tabaee, S.S. Systematic review and meta-analysis of association of polymorphisms in inflammatory cytokine genes with coronary artery disease. Inflamm. Res. 69, 1001–1013 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01385-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01385-3