Abstract
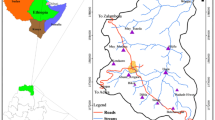
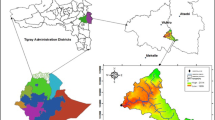
Saïss plain contains an important aquifer. This complex groundwater system plays an important socio-economic role. Managing the groundwater resources requests a good understanding of resources availability and human needs satisfaction. These two components are estimated to get annual water balance of Saïss aquifer. Resources availability depends on meteorological parameters (rainfall, wind speed, temperature, etc.), soil types, topography, water table, and land use. Previous studies do not consider all of these parameters in assessing the water resources availability in this region. In this study, we have identified the relationship between all Saïss hydro-meteorological parameters and we have organized all data in Geographic Information System (GIS) to assess inputs of the water balance. Meteorological and hydrological data and landuse/landcover maps obtained from Landsat imageries classification were used in Wet-Spass (water and energy transfer between soil, plants, and atmosphere under quasi-steady state) model and Soil Conservation Service Curve Number (CN-SCS) method to assess annual runoff, potential evapotranspiration, interception, actual evapotranspiration, and natural recharge of shallow aquifer of Saïss plain. The results of the water balance calculation indicate significant fluctuations in the aquifer recharge: 280 Mm3 (1987) and 418 Mm3 (2018). The annual direct runoff increased from 344 Mm3 (1987) to 638 Mm3 (2018).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABHS (Agence du Bassin Hydraulique du Sebou) (2006) Plan directeur d’aménagement intégré des ressources en eau (Mission 1). Rapport technique.
Amraoui F (2005) L’aquifère karstique du Moyen Atlas tabulaire: problème de la turbidité affectant les sources du complexe Ribâa-Bittit (Maroc). Sciences et techniques de l'environnement, Mémoire hors-série:5–8
Bargach K, Ruano P, Chabli A, Galindo-Zaldívar J, Chalouan A, Jabaloy A, M. Akil, Ahmamou M, Sanzde C, Galdeano and Benmakhlouf M (2004) Recent tectonic deformations and stresses in the frontal part of the Rif Cordillera and the Saïss Basin (Fes and Rabat Regions, Morocco), J Pure Appl Geophys https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-003-2461-6, 161, 521, 540
Bateelan O, De Smeedt F (2007) GIS-based recharge estimation by coupling surface–subsurface water balances. J Hydrol 337:337–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.02.001
Belhassan K (2011) Piezometric variations of Mikkes groundwater basin (Morocco). Res J Earth Sci 3(2):45–49
Benaabidate L, Cholli M (2011) Groundwater stress and vulnerability to pollution of Saïss Basin shallow aquifer (Morocco). In: Fifteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC-15. Alexandria, p 1–7.
Bolstad P, Lillesand TM (1991) Rapid maximum likelihood classification. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 57(1):67–74
Boumediene S, Gil-Rodriguez M, Juana L (2016) Development of one-dimensional solutions for water infiltration analysis and parameters estimation. J Hydrol 535:226–234
Carucci V, Petitta M, Aravena R (2012) Interaction between shallow and deep aquifers in the Tivoli Plain (Central Italy) enhanced by groundwater extraction: A multi-isotope approach and geochemical modeling. Appl Geochem 27(1):266–280
Chalouan A., Gil J-A., Galindo-Zaldívar J., Ahmamou M., Ruano P., DE Lacy M-C., and others (2014) Active faulting in the Frontal Rif Cordillera (Fes Region, Morocco): constraints from GPS data. J Geodyn https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2014.01.002, 77, 110, 122
Chamayou J, Combe M, Genetier B, Leclerc C (1975) Plaines et basins du Maroc atlantique. Le bassin de Fès-Meknès. Notes et mémoires du service géologique 231(2):38–92
Davis TJ (1994) The Ramsar Convention manual: a guide to the convention on wetlands of international importance especially as waterfowl habitat. Bureau, Gland (Switzerland) Ramsar Convention
Dauteuil O, Moreau F, Qarqori K (2016) Structural pattern of the Saïss basin and Tabular Middle Atlas in northern Morocco: hydrological implications. J Afr Earth Sci 119:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.04.001
Deshmukh DS, Hailu AE, Gdeta AD, Kassa MT, Chaube CU (2013) Estimation and comparison of curve numbers based on dynamic land use land cover change, observed rainfall-runoff data and land slope. J Hydrol 492:89–101
EL Ibrahimi A, Baali A, Couscous A, EL Kamel T (2015) Etude de l’impact des variations pluviométriques sur les fluctuations piézométriques des nappes phréatiques superficielles en zone semi-aride (cas de la plaine de Saïss, nord du Maroc). Eur Sci J 11(27):1–17
El Garouani A, Mulla DJ, El Garouani S, Knight J (2017) Analysis of urban growth and sprawl from remote sensing data: Case of Fez, Morocco. Int J Sustain Built Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsbe.2017.02.003
El Garouani A., Tribak A. & Abahrour M (2010) Assessment the effects of land use-cover changes on regional soil loss susceptibility using RUSLE model and remote sensing data. Red Books, International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication, 340 : 343-349
Essahlaoui A (2000) Contribution à la reconnaissance des formations aquifères dans le Bassin de Meknès-Fès (Maroc), Prospection géo électrique, étude hydrogéologique et inventaire des ressources en eau. These Uni. Mohammed VI, Rabat, Maroc. 258p.
Essahlaoui A, El Ouali A (2003) Determination of the geological structure of the southern part of the Saïss Plain (Meknes-Fes Basin, Morocco) using geo-electric techniques. Bull Eng Geol Environ 62:155–166
Essahlaoui A, Sahbi H, Bahi L, and EL-Yamine N (2001) Preliminary survey of the structure and hydrogeology of the Western Sais Basin, Morocco, Using Electrical Resistivity. J Afr Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-5362(02)00054-4, 32, 777, 789
El Ouali A, Sefrioui S, Mudry J. Fihri OF, Essahlaoui A, et Marah H (2011) Apport des isotopes de la molécule d'eau à la détermination de l'altitude de recharge des principales sources du Moyen Atlas calcaire (Maroc). In. H2 Karst-9thConference on Limestone Hydrogeology. 145-148.
Fofack R, Kuper M, Petit O (2015) Hybridation Des Règles D’accès À L’eau Souterraine Dans Le Saïss (Maroc). Entre Anarchie et Léviathan. Etudes Rurales 196:127–149
Goldstein M, Howard JV (1991) A likelihood paradox. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 53:619–628
Hubert-Moy L, Cotonnec A, Le Du L, Chardin A, Pérez P (2001) A comparison of parametric classification procedures of remotely sensed data applied on different landscape units. Remote Sens Environ 75(2):174–187
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
Mac Donald et al (1990) Etablissement et mise au point du modèle de gestion des nappes du bassin de Fès-Meknès. Département de coopération technique pour le développement. Nations Unis. Rapport DRPE (inédit).
Mac Donald AM, Bonsor CH, Dochartaigh BEO, Taylor RG (2012) Quantitative maps of groundwater resources in Africa. Environ Res Lett http://stacks.iop.org/1748-9326/7/i=2/a=024009
Martin ME, Newman SD, Aber JD, Congalton RG (1998) Determining forest species composition using high spectral resolution remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 65(3):249–254
Meiresonne L, Sampson DA, Kowalski AS, Janssens IA, Nadezhdin N, Cerma´k J, Van Slycken J, Ceulemans R (2003) Water flux estimates from a Belgian Scots pine stand: a comparison of different approaches. J Hydrol, 270 (3–4):230–252.
Priyantha RS, So K, Masaki S (2006) Effects of climate and land use changes on groundwater resources. J Environ Manag 80:25–35
Richards JA (1984) Thematic mapping from multi temporal image data using the principal components transformation. Remote Sens Environ 16(1):35–46
Sendide O (2000) Étude qualitative des eaux de la nappe phréatique du bassin de Fès-Meknès : caractérisation évolution, modélisation mathématique, et moyen de protection. Thèse Doctorat, École Nationale d’Ingénieurs de Sfax
Vandewiele GL, Xu CY, Ni-Lar-Win (1991) Methodology for constructing monthly water balance models on basin scale, vol 20. VUB-Hydrologie. Vrije University de Brussels’, Brussels
Wada Y, Van Beek LPH, Bierkens MFP (2011) Modeling global water stress of the recent past: on the relative importance of trends in water demand and climate variability. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-3785-2011
Xu CY (1992) Monthly water balance models in different climatic regions. PhD thesis, Laboratory of Hydrology. Vrije Universiteit Brussels, Brussels.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Garouani, A., Aharik, K. & El Garouani, S. Water balance assessment using remote sensing, Wet-Spass model, CN-SCS, and GIS for water resources management in Saïss Plain (Morocco). Arab J Geosci 13, 738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05730-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05730-y