No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Bounding Selmer Groups for the Rankin–Selberg Convolution of Coleman Families
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 July 2020
Abstract
Let f and g be two cuspidal modular forms and let 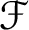 ${\mathcal {F}}$
be a Coleman family passing through f, defined over an open affinoid subdomain V of weight space
${\mathcal {F}}$
be a Coleman family passing through f, defined over an open affinoid subdomain V of weight space 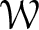 $\mathcal {W}$
. Using ideas of Pottharst, under certain hypotheses on f and
$\mathcal {W}$
. Using ideas of Pottharst, under certain hypotheses on f and 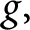 $g,$
we construct a coherent sheaf over
$g,$
we construct a coherent sheaf over  $V \times \mathcal {W}$
that interpolates the Bloch–Kato Selmer group of the Rankin–Selberg convolution of two modular forms in the critical range (i.e, the range where the p-adic L-function
$V \times \mathcal {W}$
that interpolates the Bloch–Kato Selmer group of the Rankin–Selberg convolution of two modular forms in the critical range (i.e, the range where the p-adic L-function 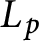 $L_p$
interpolates critical values of the global L-function). We show that the support of this sheaf is contained in the vanishing locus of
$L_p$
interpolates critical values of the global L-function). We show that the support of this sheaf is contained in the vanishing locus of 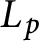 $L_p$
.
$L_p$
.
MSC classification
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Canadian Mathematical Society 2020
Footnotes
The Winter School was supported by NSF grant DMS-1504537 and by the Clay Mathematics Institute. AG was supported by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council [EP/L015234/1], the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Geometry and Number Theory (The London School of Geometry and Number Theory), University College London and Imperial College London. DG was supported in part by Royal Society grant RP∖EA∖180020. YX was supported by Harvard University scholarships.





