Abstract
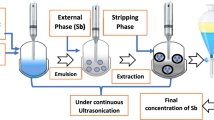
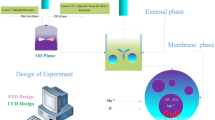
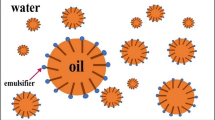
Hafnium metal is used in a wide range of industries such as microprocessor manufacturing, nuclear reactors and special alloys due to its physical, chemical and radiation properties. Emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) is an effective and efficient alternative for heavy metal separation compared to conventional methods due to high selectivity, energy-saving, high mass transfer and low operating capital. In this study, Cyanex 572 as a carrier, Span 85 as a surfactant, hydrochloric acid as an internal phase and kerosene as a diluent were used. In the first part of the study, the stability of the emulsions was investigated. The most stable emulsions were obtained by adding PIB polymer (3% w/v), Span 85 surfactant (3% w/v) and stirring for 15 min. In the second part, the separation of hafnium metal ions from aqueous solutions was investigated using ELM technique. The highest separation was obtained at 4% (v/v) as carrier concentration, 4% (w/v) as surfactant concentration, the membrane-to-feed volume ratio of 20/100 and W/O/W emulsion stirring rate and time equal to 400 rpm and 5 min, respectively. Moreover, to optimize the factors influencing the tests, the design of experiment (DOE) was performed using D-optimal method via Design Expert 10 software. Based on DOE results, the maximum extraction (> 99%) was achieved when the carrier concentration, the surfactant concentration, W/O/W emulsion stirring time, W/O/W emulsion stirring rate and emulsion volume/feed phase ratio were 4.49% v/v, 3.90% w/v, 11.49 min, 310.54 rpm and 2:1, respectively.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Fonseca Couto, L.C. Lange, M.C. Santos Amaral, A critical review on membrane separation processes applied to remove pharmaceutically active compounds from water and wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 26, 156–175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.10.010
T.C. Zhang, R.Y. Surampalli, S. Vigneswaran, R. Tyagi, S. Leong Ong, C. Kao, Membrane Technology and Environmental Applications (American Society of Civil Engineers, New York, 2012)
D. Nasirian, I. Salahshoori, M. Sadeghi, N. Rashidi, M. Hassanzadeganroudsari, Investigation of the gas permeability properties from polysulfone/polyethylene glycol composite membrane. Polym. Bull. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03031-3
I. Salahshoori, D. Nasirian, N. Rashidi, M.K. Hossain, A. Hatami, M. Hassanzadeganroudsari, The effect of silica nanoparticles on polysulfone–polyethylene glycol (PSF/PEG) composite membrane on gas separation and rheological properties of nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03255-8
A. Hatami, I. Salahshoori, N. Rashidi, D. Nasirian, The effect of ZIF-90 particle in Pebax/PSF composite membrane on the transport properties of CO2, CH4 and N2 gases by molecular dynamics simulation method. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.12.011
S. Mondal, M.K. Purkait, S. De, Emulsion liquid membrane, in Advances in Dye Removal Technologies, ed. by S. Mondal, M.K. Purkait, S. De (Springer, Singapore, 2018), pp. 313–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6293-3_10
A.L. Ahmad, A. Kusumastuti, C.J.C. Derek, B.S. Ooi, Emulsion liquid membrane for heavy metal removal: an overview on emulsion stabilization and destabilization. Chem. Eng. J. 171(3), 870–882 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.102
M.B. Rosly, N. Jusoh, N. Othman, H.A. Rahman, N.F.M. Noah, R.N.R. Sulaiman, Effect and optimization parameters of phenol removal in emulsion liquid membrane process via fractional-factorial design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 145, 268–278 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.03.007
P. Dzygiel, P. Wieczorek, Extraction of amino acids with emulsion liquid membranes using industrial surfactants and lecithin as stabilisers. J. Membr. Sci. 172(1), 223–232 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00330-6
N. Othman, H. Mat, M. Goto, Separation of silver from photographic wastes by emulsion liquid membrane system. J. Membr. Sci. 282(1), 171–177 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.05.020
A. Kargari, T. Kaghazchi, B. Mardangahi, M. Soleimani, Experimental and modeling of selective separation of gold(III) ions from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane system. J. Membr. Sci. 279(1), 389–393 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.027
H. Valdés, J. Romero, J. Sanchez, S. Bocquet, G.M. Rios, F. Valenzuela, Characterization of chemical kinetics in membrane-based liquid–liquid extraction of molybdenum(VI) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 151(1), 333–341 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.04.012
A. Srivastava, A. Bhagat, U. Sharma, R.K. Dohare, K. Singh, S. Upadhyaya, Comparative study of arsenic(V) removal from aqueous solution using Aliquat-336 and 2-ethyl hexanol through emulsion liquid membrane. J. Water Process Eng. 16, 64–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.12.007
K. Wongkaew, V. Mohdee, U. Pancharoen, A. Arpornwichanop, A.W. Lothongkum, Separation of platinum(IV) across hollow fiber supported liquid membrane using non-toxic diluents: mass transfer and thermodynamics. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 54, 278–289 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.06.002
F. Moyo, R. Tandlich, Daphnia pulex toxicity testing of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium salt dihydrate and the wastewater effluent from extraction of rhodium using emulsion liquid membranes. Int. J. Environ. Res. 8(4), 1019–1026 (2014)
A.L. Ahmad, M.M.H. Shah Buddin, B.S. Ooi, A. Kusumastuti, Utilization of environmentally benign emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) for cadmium extraction from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 15, 26–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.05.010
A. Hachemaoui, K. Belhamel, Simultaneous extraction and separation of cobalt and nickel from chloride solution through emulsion liquid membrane using Cyanex 301 as extractant. Int. J. Miner. Process. 161, 7–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2017.02.002
H. Ma, O. Kökkılıç, K.E. Waters, The use of the emulsion liquid membrane technique to remove copper ions from aqueous systems using statistical experimental design. Miner. Eng. 107, 88–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.10.014
M.D. Asl, I. Salahshoori, A. Seyfaee, A. Hatami, A.A. Golbarari, Experimental results and optimization via design of experiment (DOE) of the copper ion recovery from aqueous solutions using emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) method. Desalination and Water Treatment (in press) (2020)
S.S. Kulkarni, V.A. Juvekar, S. Mukhopadhyay, Intensification of emulsion liquid membrane extraction of uranium(VI) by replacing nitric acid with sodium nitrate solution. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intens. 125, 18–26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2017.12.021
N.F.M. Noah, N. Othman, N. Jusoh, Highly selective transport of palladium from electroplating wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 64, 134–141 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.047
A. Choudhury, S. Sengupta, C. Bhattacharjee, S. Datta, Extraction of hexavalent chromium from aqueous stream by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM). Sep. Sci. Technol. 45(2), 178–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390903409617
F. Valenzuela, J. Cabrera, C. Basualto, J. Sapag, J. Romero, J. Sánchez, G. Rios, Separation of zinc ions from an acidic mine drainage using a stirred transfer cell-type emulsion liquid membrane contactor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 42(2), 363–377 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390601069887
A. Yadollahi, M. Torab-Mostaedi, K. Saberyan, A. Charkhi, F. Zahakifar, Intensification of zirconium and hafnium separation through the hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane technique using synergistic mixture of TBP and Cyanex-272 as extractant. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 27(8), 1817–1827 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.12.018
P. Davoodi-Nasab, A. Rahbar-Kelishami, J. Safdari, H. Abolghasemi, Selective separation and enrichment of neodymium and gadolinium by emulsion liquid membrane using a novel extractant CYANEX® 572. Miner. Eng. 117, 63–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.11.008
M. Chakraborty, C. Bhattacharya, S. Datta, Emulsion liquid membranes: definitions and classification, theories, module design, applications, new directions and perspectives, in Liquid Membranes, vol. 4, ed. by V.S. Kislik (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2010), pp. 141–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53218-3.00004-0
O.I. Lee, The mineralogy of hafnium. Chem. Rev. 5(1), 17–37 (1928)
C.E. Curtis, Bibliography of hafnium oxide, hafnium silicate and hafnium carbide (Oak Ridge National Lab, Oak Ridge, 1952)
J. van Liempt, Hafnium oxide in tungsten filaments. Nature 115(2884), 194 (1925)
C.M. Swamidoss, D.D. Malkhede, A highly selective liquid–liquid extraction technique for the extraction and separation of hafnium(IV) with hexaacetato calix(6)arene. Orient. J. Chem. 26, 117–122 (2010)
K. Mimura, K. Matsumoto, M. Isshiki, Purification of hafnium by hydrogen plasma arc melting. Mater. Trans. 52(2), 159–165 (2011)
S. Shishkin, T. Shishkina, G. Buklanov, S. Dmitriev, G.Y. Starodub, Separation of carrier free 178 W from α-particle activated hafnium with TBP impregnated resin. Czech J. Phys. 53(1), A425–A427 (2003)
Z.-G. Xu, Y.-K. Wu, J.-D. Zhang, L. Zhang, L.-J. Wang, Equilibrium and kinetic data of adsorption and separation for zirconium and hafnium onto MIBK extraction resin. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 20(8), 1527–1533 (2010)
L. Beer, D. van der Westhuizen, H. Krieg, Solvent extraction and separation of hafnium from zirconium using Ionquest 801. J. South Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 116, 93–99 (2016). https://doi.org/10.17159/2411-9717/2016/v116n1a14
B. Nandi, N.R. Das, S.N. Bhattacharyya, Solvent extraction of zirconium and hafnium. Solv. Extr. Ion Exchange 1(1), 141–202 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1080/07366298308918397
M. Khan, A.A. Ali, Liquid–liquid extraction of Hf(IV) from nitric acid with dibutylsulfoxide in cyclohexane. Radiochim. Acta (2002). https://doi.org/10.1524/ract.2002.90.5_2002.297
A.A. Nayl, Y. El-Nadi, J. Daoud, Extraction and separation of Zr(IV) and Hf(IV) from nitrate medium by some CYANEX extractants. Sep. Sci. Technol. 44, 2956–2970 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390903014169
J. Amaral, C. Morais, Study of zirconium and hafnium separation by solvent extraction technique from nitric and hydrochloric solutions with acid, basic and neutral extractants. World J. Eng. Technol. 04, 138–150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2016.43D017
J. Zhao, T. Yang, H. Zhang, G. Sun, Y. Cui, Preferential extraction of hafnium over zirconium with D2EHPA through selective complexation of organic acids. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 321(1), 333–339 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06585-8
R. Banda, H.Y. Lee, M.S. Lee, Separation of Zr from Hf in hydrochloric acid solution using amine-based extractants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(28), 9652–9660 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie3008264
C. Tunsu, Hydrometallurgical recovery of rare earth elements from fluorescent lamp waste fractions. Department of chemistry and chemical engineering, Chalmers University of Technology Gutenburg, Sweden (2016)
Y. Wang, F. Li, Z. Zhao, Y. Dong, X. Sun, The novel extraction process based on CYANEX® 572 for separating heavy rare earths from ion-adsorbed deposit. Sep. Purif. Technol. 151, 303–308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.07.063
P.S. Kulkarni, V.V. Mahajani, Application of liquid emulsion membrane (LEM) process for enrichment of molybdenum from aqueous solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 201(1), 123–135 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(01)00720-7
K. Abbassian, A. Kargari, Effect of polymer addition to membrane phase to improve the stability of emulsion liquid membrane for phenol pertraction. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(7), 2942–2951 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.983981
Y.S. Ng, N.S. Jayakumar, M.A. Hashim, Performance evaluation of organic emulsion liquid membrane on phenol removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 184(1), 255–260 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.030
A. Barkat, B. Khan, A. Naveed, H. Muhammad, H.M.S. Khan, K. Waseem, T. Mahmood, A. Rasul, M. Iqbal, H. Khan, Basics of pharmaceutical emulsions: a review. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 525, 2715–2725 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPP11.698
A.L. Ahmad, A. Kusumastuti, C.J.C. Derek, O. Seng, Emulsion liquid membrane for heavy metal removal: an overview on emulsion stabilization and destabilization. Chem. Eng. J. Chem. Eng. J. 171, 870–882 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.102
S. Gupta, P.B. Khandale, M. Chakraborty, Application of emulsion liquid membrane for the extraction of diclofenac and relationship with the stability of water-in-oil emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2019.1579655
Y. Park, Development and optimization of novel emulsion liquid membranes stabilized by non-Newtonian conversion in Taylor-Couette flow for extraction of selected organic and metallic contaminants, Georgia Institute of Technology (2006)
J. Barad, M. Chakraborty, H.-J. Bart, Stability and performance study of water-in-oil-in-water emulsion: extraction of aromatic amines. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 5808–5815 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie901698u
Y. Park, L.J. Forney, J.H. Kim, A.H.P. Skelland, Optimum emulsion liquid membranes stabilized by non-Newtonian conversion in Taylor–Couette flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 59(24), 5725–5734 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.06.015
A.H.P. Skelland, X. Meng, A new solution to emulsion liquid membrane problems by non-Newtonian conversion. AIChE J. 42(2), 547–561 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690420224
B. Brugger, W. Richtering, Emulsions stabilized by stimuli-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-methacrylic acid polymers: microgels versus low molecular weight polymers. Langmuir ACS J. Surfaces Colloids 24(15), 7769–7777 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/la800522h
S.C. Lee, S.M. Yeo, Role of dilute polymer solution in penicillin G extraction by emulsion liquid membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 8(2), 114–119 (2002)
H.R. Mortaheb, M.H. Amini, F. Sadeghian, B. Mokhtarani, H. Daneshyar, Study on a new surfactant for removal of phenol from wastewater by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 160(2–3), 582–588 (2008)
H.R. Mortaheb, H. Kosuge, B. Mokhtarani, M.H. Amini, H.R. Banihashemi, Study on removal of cadmium from wastewater by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 165(1–3), 630–636 (2009)
A.H.P. Skelland, X. Meng, Non-Newtonian conversion solves problems of stability, permeability, and swelling in emulsion liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 158(1), 1–15 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(98)00332-9
F. Nakashio, M. Goto, M. Matsumoto, J. Irie, K. Kondo, Role of surfactants in the behavior of emulsion liquid membranes—development of new surfactants. J. Membr. Sci. 38(3), 249–260 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)82423-0
F. Goodarzi, S. Zendehboudi, A comprehensive review on emulsions and emulsion stability in chemical and energy industries. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 97(1), 281–309 (2019)
A. Dâas, O. Hamdaoui, Extraction of anionic dye from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 178(1–3), 973–981 (2010)
W. Yinhua, X. Zhang, Swelling determination of W/O/W emulsion liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 196, 185–201 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(01)00554-3
A. Dâas, O. Hamdaoui, Extraction of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 348(1), 360–368 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2009.11.026
A.L. Ahmad, M.M.H. Shah Buddin, B.S. Ooi, A. Kusumastuti, Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM): influence of emulsion formulation on cadmium removal and emulsion swelling. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(58), 28274–28283 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1179674
N. Jusoh, N. Othman, Stability of water-in-oil emulsion in liquid membrane prospect. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. (2017). https://doi.org/10.11113/mjfas.v12n3.429
A.L. Ahmad, A. Kusumastuti, C.J.C. Derek, B.S. Ooi, Emulsion liquid membrane for cadmium removal: studies on emulsion diameter and stability. Desalination 287, 30–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.002
S. Laki, A. Bbbbbb, S. Madaeni, M. Niroomanesh, Separation of manganese from aqueous solution using emulsion liquid membrane. RSC Adv. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08547K
Z.-Y. Ooi, N. Othman, C.-L. Choo, The role of internal droplet size on emulsion stability and the extraction performance of kraft lignin removal from pulping wastewater in emulsion liquid membrane process. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 37(4), 544–554 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2015.1050728
A. Dâas, O. Hamdaoui, Extraction of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 348(1–2), 360–368 (2010)
S.C. Lee, Effect of volume ratio of internal aqueous phase to organic membrane phase (w/o ratio) of water-in-oil emulsion on penicillin G extraction by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 163(2), 193–201 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00182-9
M. Hasan, Y. Selim, K. Mohamed, Removal of chromium from aqueous waste solution using liquid emulsion membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 168(2–3), 1537–1541 (2009)
P.S. Kankekar, S.J. Wagh, V.V. Mahajani, Process intensification in extraction by liquid emulsion membrane (LEM) process: a case study; enrichment of ruthenium from lean aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. Process. 49(4), 441–448 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2010.02.005
M.A. Malik, M.A. Hashim, F. Nabi, Extraction of metal ions by ELM separation technology. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 33(3), 346–356 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2011.567148
Y. Wang, F. Li, Z. Zhao, Y. Dong, X. Sun, The novel extraction process based on CYANEX® 572 for separating heavy rare earths from ion-adsorbed deposit. Sep. Purif. Technol. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.07.063
I. Bhatti, K. Qureshi, K.S.N. Kamarudin, A.A. Bazmi, A.W. Bhutto, F. Ahmad, M. Lee, Innovative method to prepare a stable emulsion liquid membrane for high CO2 absorption and its performance evaluation for a natural gas feed in a rotating disk contactor. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 34, 716–732 (2016)
I. Torotwa, C. Ji, A study of the mixing performance of different impeller designs in stirred vessels using computational fluid dynamics. Designs 2(1), 10 (2018)
B. Mokhtari, K. Pourabdollah, Inclusion separation of alkali metals in emulsion liquid membranes by nanobaskets of calix [4] crown-3. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 29(4), 783–793 (2012)
J. Yan, R. Pal, Isotonic swelling behavior of W/O/W emulsion liquid membranes under agitation conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 213, 1–12 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(02)00501-X
N. Noah, N.N. Othman, Emulsion stability of palladium extraction containing cyanex 302 as a mobile carrier in emulsion liquid membrane process. Chem. Eng. Trans. 56, 1069–1074 (2017)
L.M. Collins, J.J. Dziak, R. Li, Design of experiments with multiple independent variables: a resource management perspective on complete and reduced factorial designs. Psychol. Methods 14(3), 202 (2009)
J.R. Wagner, E.M. Mount, H.F. Giles, 25-Design of experiments, in Extrusion, 2nd edn., ed. by J.R. Wagner, E.M. Mount, H.F. Giles (William Andrew Publishing, Oxford, 2014), pp. 291–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4377-3481-2.00025-9
M.A. Bezerra, R.E. Santelli, E.P. Oliveira, L.S. Villar, L.A. Escaleira, Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76(5), 965–977 (2008)
S.C. Ferreira, R. Bruns, H. Ferreira, G. Matos, J. David, G. Brandao, E.P. da Silva, L. Portugal, P. Dos Reis, A. Souza, Box-Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 597(2), 179–186 (2007)
H. Ahn, Central composite design for the experiments with replicate runs at factorial and axial points, in Industrial Engineering, Management Science and Applications, ed. by M. Gen, K.J. Kim, X. Huang, Y. Hiroshi (Springer, Berlin, 2015), pp. 969–979
P.F. de Aguiar, B. Bourguignon, M.S. Khots, D.L. Massart, R. Phan-Than-Luu, D-optimal designs. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 30(2), 199–210 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-7439(94)00076-X
L. St, S. Wold, Analysis of variance (ANOVA). Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 6(4), 259–272 (1989)
J. Martin, D.D.R. De Adana, A.G. Asuero, Fitting models to data: residual analysis, a primer. Chapter 7, 133 (2017)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thanks the Science and Research Branch of the Islamic Azad University (Tehran SRBIAU) for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salahshoori, I., Hatami, A. & Seyfaee, A. Investigation of experimental results and D-optimal design of hafnium ion extraction from aqueous system using emulsion liquid membrane technique. J IRAN CHEM SOC 18, 87–107 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-020-02007-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-020-02007-9