Abstract
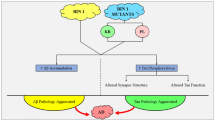
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia. The majority of AD cases are late-onset, multifactorial cases. Genome-wide association studies have identified more than 30 loci associated with sporadic AD (SAD), one of which is Bridging integrator 1 (BIN1). For the past few years, there has been a consensus that BIN1 is second only to APOE as the strongest genetic risk factor for SAD. Therefore, many researchers have put great effort into studying the mechanism by which BIN1 might be involved in the pathogenetic process of AD. To date, plenty of evidence has shown that BIN1 may participate in several pathways in AD, including tau and amyloid pathology. In addition, BIN1 has been indicated to take part in other relevant pathways such as inflammation, apoptosis, and calcium homeostasis. In this review, we systemically summarize the research progress on how BIN1 participates in the development of AD, with the expectation of providing promising perspectives for future research.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SL, Tilton K, Kozubek JA, Seshadri S, Delalle I (2016) Subcellular changes in bridging integrator 1 protein expression in the cerebral cortex during the progression of Alzheimer disease pathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75:779–790. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlw056
Andrew RJ et al (2019) Reduction of the expression of the late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk-factor BIN1 does not affect amyloid pathology in an AD mouse model. J Biol Chem 294:4477–4487. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.006379
Aoyagi A et al (2019) Abeta and tau prion-like activities decline with longevity in the Alzheimer’s disease human brain. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aat8462
Bamberger ME, Harris ME, McDonald DR, Husemann J, Landreth GE (2003) A cell surface receptor complex for fibrillar beta-amyloid mediates microglial activation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 23:2665–2674
Bhatia VK, Madsen KL, Bolinger PY, Kunding A, Hedegard P, Gether U, Stamou D (2009) Amphipathic motifs in BAR domains are essential for membrane curvature sensing. EMBO J 28:3303–3314. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.261
Cacace R, Sleegers K, Van Broeckhoven C (2016) Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimer’s & Dementia J Alzheimer’s Assoc 12:733–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.01.012
Cai Z, Xiao M (2016) Oligodendrocytes and Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neurosci 126:97–104. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2015.1025778
Calafate S, Flavin W, Verstreken P, Moechars D (2016) Loss of Bin1 promotes the propagation of Tau pathology. Cell Rep 17:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.063
Caldwell JL, Smith CE, Taylor RF, Kitmitto A, Eisner DA, Dibb KM, Trafford AW (2014) Dependence of cardiac transverse tubules on the BAR domain protein amphiphysin II (BIN-1). Circ Res 115:986–996. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.116.303448
Cassimere EK, Pyndiah S, Sakamuro D (2009) The c-MYC-interacting proapoptotic tumor suppressor BIN1 is a transcriptional target for E2F1 in response to DNA damage. Cell Death Differ 16:1641–1653. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.98
Cataldo AM, Peterhoff CM, Troncoso JC, Gomez-Isla T, Hyman BT, Nixon RA (2000) Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations. Am J Pathol 157:277–286
Chakroborty S, Stutzmann GE (2011) Early calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease: setting the stage for synaptic dysfunction. Sci China Life Sci 54:752–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-011-4205-7
Chang MY et al (2007) Bin1 ablation increases susceptibility to cancer during aging, particularly lung cancer. Cancer Res 67:7605–7612. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-1100
Chapuis J et al (2013) Increased expression of BIN1 mediates Alzheimer genetic risk by modulating tau pathology. Mol Psychiatry 18:1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.1
Chia PZ, Toh WH, Sharples R, Gasnereau I, Hill AF, Gleeson PA (2013) Intracellular itinerary of internalised beta-secretase, BACE1, and its potential impact on beta-amyloid peptide biogenesis. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 14:997–1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12088
Cirrito JR et al (2008) Endocytosis is required for synaptic activity-dependent release of amyloid-beta in vivo. Neuron 58:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.02.003
Crews L, Masliah E (2010) Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 19:R12–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq160
Crotti A et al (2019) BIN1 favors the spreading of Tau via extracellular vesicles. Sci Rep 9:9477. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45676-0
Das U, Scott DA, Ganguly A, Koo EH, Tang Y, Roy S (2013) Activity-induced convergence of APP and BACE-1 in acidic microdomains via an endocytosis-dependent pathway. Neuron 79:447–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.05.035
De Rossi P et al (2016) Predominant expression of Alzheimer’s disease-associated BIN1 in mature oligodendrocytes and localization to white matter tracts. Mol Neurodegener 11:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-016-0124-1
De Rossi P et al (2017) BIN1 localization is distinct from Tau tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Matters. https://doi.org/10.19185/matters.201611000018
De Rossi P et al (2019) Aberrant accrual of BIN1 near Alzheimer’s disease amyloid deposits in transgenic models. Brain Pathol (Zurich, Switzerland) 29:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12687
Du Yan S et al (1997) Amyloid-beta peptide-receptor for advanced glycation endproduct interaction elicits neuronal expression of macrophage-colony stimulating factor: a proinflammatory pathway in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5296–5301. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.10.5296
DuHadaway JB, Lynch FJ, Brisbay S, Bueso-Ramos C, Troncoso P, McDonnell T, Prendergast GC (2003) Immunohistochemical analysis of Bin1/Amphiphysin II in human tissues: diverse sites of nuclear expression and losses in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem 88:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.10380
Efthymiou AG, Goate AM (2017) Late onset Alzheimer’s disease genetics implicates microglial pathways in disease risk. Mol Neurodegener 12:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0184-x
El Khoury J, Hickman SE, Thomas CA, Cao L, Silverstein SC, Loike JD (1996) Scavenger receptor-mediated adhesion of microglia to beta-amyloid fibrils. Nature 382:716–719. https://doi.org/10.1038/382716a0
Elliott K et al (1999) Bin1 functionally interacts with Myc and inhibits cell proliferation via multiple mechanisms. Oncogene 18:3564–3573. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202670
Elliott K, Ge K, Du W, Prendergast GC (2000) The c-Myc-interacting adaptor protein Bin1 activates a caspase-independent cell death program. Oncogene 19:4669–4684. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203681
Esmailzadeh S, Huang Y, Su MW, Zhou Y, Jiang X (2015) BIN1 tumor suppressor regulates Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis through c-FLIP in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 29:1402–1413. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.9
Fassbender K et al (2004) The LPS receptor (CD14) links innate immunity with Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J Off Pub Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 18:203–205. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-0364fje
Franzmeier N, Rubinski A, Neitzel J, Ewers M (2019) The BIN1 rs744373 SNP is associated with increased tau-PET levels and impaired memory. Nat Commun 10:1766. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09564-5
Frost A, Unger VM, De Camilli P (2009) The BAR domain superfamily: membrane-molding macromolecules. Cell 137:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.010
Fugier C et al (2011) Misregulated alternative splicing of BIN1 is associated with T tubule alterations and muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy. Nat Med 17:720–725. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2374
Galderisi U et al (1999) Induction of apoptosis and differentiation in neuroblastoma and astrocytoma cells by the overexpression of Bin1, a novel Myc interacting protein. J Cell Biochem 74:313–322
Gatz M et al (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.2.168
Ge K, DuHadaway J, Du W, Herlyn M, Rodeck U, Prendergast GC (1999) Mechanism for elimination of a tumor suppressor: aberrant splicing of a brain-specific exon causes loss of function of Bin1 in melanoma. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96:9689–9694. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.17.9689
Ge K, Duhadaway J, Sakamuro D, Wechsler-Reya R, Reynolds C, Prendergast GC (2000) Losses of the tumor suppressor BIN1 in breast carcinoma are frequent and reflect deficits in programmed cell death capacity. Int J Cancer 85:376–383
Ghaneie A et al (2007) Bin1 attenuation in breast cancer is correlated to nodal metastasis and reduced survival. Cancer Biol Ther 6:192–194. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.6.2.3587
Glennon EB, Whitehouse IJ, Miners JS, Kehoe PG, Love S, Kellett KA, Hooper NM (2013) BIN1 is decreased in sporadic but not familial Alzheimer’s disease or in aging. PLoS ONE 8:e78806. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078806
Guimas Almeida C, Sadat Mirfakhar F, Perdigao C, Burrinha T (2018) Impact of late-onset Alzheimer’s genetic risk factors on beta-amyloid endocytic production. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:2577–2589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2825-9
Heppner FL, Ransohoff RM, Becher B (2015) Immune attack: the role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:358–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3880
Holler CJ, Davis PR, Beckett TL, Platt TL, Webb RL, Head E, Murphy MP (2014) Bridging integrator 1 (BIN1) protein expression increases in the Alzheimer’s disease brain and correlates with neurofibrillary tangle pathology. J Alzheimer’s Dis 42:1221–1227. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-132450
Hong TT et al (2010) BIN1 localizes the L-type calcium channel to cardiac T-tubules. PLoS Biol 8:e1000312. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000312
Hong T et al (2014) Cardiac BIN1 folds T-tubule membrane, controlling ion flux and limiting arrhythmia. Nat Med 20:624–632. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3543
Ishii A et al (2009) Human myelin proteome and comparative analysis with mouse myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14605–14610. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905936106
Jantaratnotai N, Ryu JK, Kim SU, McLarnon JG (2003) Amyloid beta peptide-induced corpus callosum damage and glial activation in vivo. NeuroReport 14:1429–1433. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200308060-00005
Karch CM, Jeng AT, Nowotny P, Cady J, Cruchaga C, Goate AM (2012) Expression of novel Alzheimer’s disease risk genes in control and Alzheimer’s disease brains. PLoS ONE 7:e50976. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050976
Kauwe JS et al (2011) Fine mapping of genetic variants in BIN1, CLU, CR1 and PICALM for association with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 6:e15918. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015918
Khachaturian ZS (1989) Calcium, membranes, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease. Introduction and overview. Ann NY Acad Sci 568:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb12485.x
Kinney EL, Tanida S, Rodrigue AA, Johnson JK, Tompkins VS, Sakamuro D (2008) Adenovirus E1A oncoprotein liberates c-Myc activity to promote cell proliferation through abating Bin1 expression via an Rb/E2F1-dependent mechanism. J Cell Physiol 216:621–631. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21437
Koenigsknecht J, Landreth G (2004) Microglial phagocytosis of fibrillar beta-amyloid through a beta1 integrin-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 24:9838–9846. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2557-04.2004
La Joie R et al (2018) Associations between [(18)F]AV1451 tau PET and CSF measures of tau pathology in a clinical sample. Neurology 90:e282–e290. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004860
Lambert JC et al (2011) Evidence of the association of BIN1 and PICALM with the AD risk in contrasting. Eur Popul Neurobiol Aging 32:756.e711–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.11.022
Lee E et al (2002) Amphiphysin 2 (Bin1) and T-tubule biogenesis in muscle. Science (New York, NY) 297:1193–1196. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071362
Leprince C, Le Scolan E, Meunier B, Fraisier V, Brandon N, De Gunzburg J, Camonis J (2003) Sorting nexin 4 and amphiphysin 2, a new partnership between endocytosis and intracellular trafficking. J Cell Sci 116:1937–1948. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00403
Loo DT, Copani A, Pike CJ, Whittemore ER, Walencewicz AJ, Cotman CW (1993) Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7951–7955. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.17.7951
Malki I, Cantrelle FX, Sottejeau Y, Lippens G, Lambert JC, Landrieu I (2017) Regulation of the interaction between the neuronal BIN1 isoform 1 and Tau proteins—role of the SH3 domain. FEBS J 284:3218–3229. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14185
Mattson MP (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1038/35040009
Mitew S, Kirkcaldie MT, Halliday GM, Shepherd CE, Vickers JC, Dickson TC (2010) Focal demyelination in Alzheimer’s disease and transgenic mouse models. Acta Neuropathol 119:567–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0657-2
Miyagawa T et al (2016) BIN1 regulates BACE1 intracellular trafficking and amyloid-beta production. Hum Mol Genet 25:2948–2958. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw146
Nakajo A et al (2016) EHBP1L1 coordinates Rab8 and Bin1 to regulate apical-directed transport in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 212:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201508086
Negorev D, Riethman H, Wechsler-Reya R, Sakamuro D, Prendergast GC, Simon D (1996) The Bin1 gene localizes to human chromosome 2q14 by pcr analysis of somatic cell hybrids and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics 33:329–331
Nicot AS et al (2007) Mutations in amphiphysin 2 (BIN1) disrupt interaction with dynamin 2 and cause autosomal recessive centronuclear myopathy. Nat Genet 39:1134–1139. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2086
Nishimura M, Tomimoto H, Suenaga T, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Akiguchi I, Kimura J (1995) Immunocytochemical characterization of glial fibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am J Pathol 146:1052–1058
Peter BJ, Kent HM, Mills IG, Vallis Y, Butler PJ, Evans PR, McMahon HT (2004) BAR domains as sensors of membrane curvature: the amphiphysin BAR structure. Science (New York, NY) 303:495–499. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092586
Piaceri I, Nacmias B, Sorbi S (2013) Genetics of familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Front Biosci (Elite edition) 5:167–177. https://doi.org/10.2741/e605
Prokic I, Cowling BS, Laporte J (2014) Amphiphysin 2 (BIN1) in physiology and diseases. J Mol Med (Berlin, Germany) 92:453–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1138-1
Prokop S, Miller KR, Heppner FL (2013) Microglia actions in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 126:461–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1182-x
Rajendran L, Annaert W (2012) Membrane trafficking pathways in Alzheimer’s disease. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 13:759–770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2012.01332.x
Ramjaun AR, McPherson PS (1998) Multiple amphiphysin II splice variants display differential clathrin binding: identification of two distinct clathrin-binding sites. J Neurochem 70:2369–2376. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70062369.x
Ramjaun AR, Micheva KD, Bouchelet I, McPherson PS (1997) Identification and characterization of a nerve terminal-enriched amphiphysin isoform. J Biol Chem 272:16700–16706. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.26.16700
Sakamuro D, Prendergast GC (1999) New Myc-interacting proteins: a second Myc network emerges. Oncogene 18:2942–2954. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202725
Sakamuro D, Elliott KJ, Wechsler-Reya R, Prendergast GC (1996) BIN1 is a novel MYC-interacting protein with features of a tumour suppressor. Nat Genet 14:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0996-69
Sartori M et al (2019) BIN1 recovers tauopathy-induced long-term memory deficits in mice and interacts with Tau through Thr(348) phosphorylation. Acta Neuropathol 138:631–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-02017-9
Sato C et al (2018) Tau kinetics in neurons and the human central nervous system. Neuron 98:861–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.04.035
Seshadri S et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 303:1832–1840. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.574
Sheedy FJ et al (2013) CD36 coordinates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by facilitating intracellular nucleation of soluble ligands into particulate ligands in sterile inflammation. Nat Immunol 14:812–820. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2639
Shupliakov O et al (1997) Synaptic vesicle endocytosis impaired by disruption of dynamin-SH3 domain interactions. Science (New York, NY) 276:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5310.259
Slepnev VI, De Camilli P (2000) Accessory factors in clathrin-dependent synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Nat Rev Neurosci 1:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/35044540
Sottejeau Y et al (2015) Tau phosphorylation regulates the interaction between BIN1’s SH3 domain and Tau’s proline-rich domain. Acta Neuropathol Commun 3:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-015-0237-8
Stoorvogel W, Oorschot V, Geuze HJ (1996) A novel class of clathrin-coated vesicles budding from endosomes. J Cell Biol 132:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.132.1.21
Sun L, Tan MS, Hu N, Yu JT, Tan L (2013) Exploring the value of plasma BIN1 as a potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 37:291–295. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-130392
Tajiri T et al (2003) Expression of a MYCN-interacting isoform of the tumor suppressor BIN1 is reduced in neuroblastomas with unfavorable biological features. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 9:3345–3355
Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2013) Bridging integrator 1 (BIN1): form, function, and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 19:594–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2013.06.004
Thinakaran G, Koo EH (2008) Amyloid precursor protein trafficking, processing, and function. J Biol Chem 283:29615–29619. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R800019200
Tjondrokoesoemo A et al (2011) Disrupted membrane structure and intracellular Ca2+ signaling in adult skeletal muscle with acute knockdown of Bin1. PLoS ONE 6:e25740. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025740
Ubelmann F, Burrinha T, Salavessa L, Gomes R, Ferreira C, Moreno N, Guimas Almeida C (2017) Bin1 and CD2AP polarise the endocytic generation of beta-amyloid. EMBO Rep 18:102–122. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201642738
Van Acker ZP, Bretou M, Annaert W (2019) Endo-lysosomal dysregulations and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: impact of genetic risk factors. Mol Neurodegener 14:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-019-0323-7
Wang HF et al (2016) Bridging integrator 1 (BIN1) genotypes mediate Alzheimer’s disease risk by altering neuronal degeneration. J Alzheimer’s Dis 52:179–190. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-150972
Wang Y et al (2017) The release and trans-synaptic transmission of Tau via exosomes. Mol Neurodegener 12:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-016-0143-y
Wechsler-Reya R, Sakamuro D, Zhang J, Duhadaway J, Prendergast GC (1997) Structural analysis of the human BIN1 gene. Evidence for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation and alternate RNA splicing. J Biol Chem 272:31453–31458. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.50.31453
Wigge P, Kohler K, Vallis Y, Doyle CA, Owen D, Hunt SP, McMahon HT (1997) Amphiphysin heterodimers: potential role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Mol Biol Cell 8:2003–2015. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.8.10.2003
Wixler V et al (1999) Identification of novel interaction partners for the conserved membrane proximal region of alpha-integrin cytoplasmic domains. FEBS Lett 445:351–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00151-9
Zhao Y, Keen JH (2008) Gyrating clathrin: highly dynamic clathrin structures involved in rapid receptor recycling. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 9:2253–2264. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00819.x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81500908).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors conceived the project. PG, LY and HC performed the material preparation and data collection. The first draft of the manuscript was written by PG. HL contributed to the final preparation of the manuscript and supervised the project. All authors contributed to the final draft of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, P., Ye, L., Cheng, H. et al. The Mechanistic Role of Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1) in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 1431–1440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00926-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00926-y