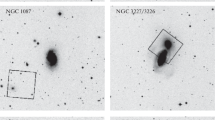
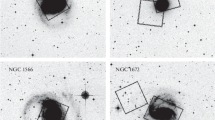
Abstract—We use the archival data obtained with the Hubble space telescope to measure distances by the tip of the red-giant branch (TRGB) method to SNIa parent galaxies. Our sample consists of four galaxies: NGC2841, NGC4496A, NGC4535, and NGC4527. For three of them, we were able to determine only the lower bounds of the distance. For the galaxy NGC4527, we estimated the TRGB distance modulus: (m − M)0 = 30m.56 ± 0m.09. Combining our measurements with the published data, we compared the supernova distance moduli using the MLCS2k2 method and the host galaxies with the TRGB method. SNIa distance moduli show systematically higher value at 0m.15–0m.18 relative to the scale of the TRGB distances. This corresponds to overestimation of the luminosity of supernovae with the MLCS2k2 method. We estimated the luminosity of supernovae at the brightness maximum as MV = −19m.33 ± 0m.03 which allows one to accept the following Hubble constant: H0 = 70.4 ± 1.0 km s−1 Mpc−1.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Antipova, D. Makarov, and L. Makarova, ASP Conf.Ser. 510, 203 (2017).
E. Aubourg, S. Bailey, J. E. Bautista, et al., Phys. Rev. D 92 (12), 123516 (2015).
C. L. Bennett, D. Larson, J. L. Weiland, et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 208, 20 (2013).
C. R. Burns, E. Parent, M. M. Phillips, et al., Astrophys. J. 869, 56 (2018).
A. E. Dolphin, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 112, 1383 (2000).
W. L. Freedman, B. F. Madore, D. Hatt, et al., Astrophys. J. 882 (1), 34 (2019).
W. L. Freedman, B. F. Madore, V. Scowcroft, et al., Astrophys. J. 758, 24 (2012).
J. Guy, P. Astier, S. Baumont, et al., Astron. and Astrophys. 466, 11 (2007).
E. M. L. Humphreys, M. J. Reid, J. M. Moran, et al., Astrophys. J. 775, 13 (2013).
B. A. Jacobs, L. Rizzi, R. B. Tully, et al., Astron. J. 138, 332 (2009).
I. S. Jang and M. G. Lee, Astrophys. J. 836, 74 (2017a).
I. S. Jang and M. G. Lee, Astrophys. J. 835, 28 (2017b).
S. Jha, A. G. Riess, and R. P. Kirshner, Astrophys. J.659, 122 (2007).
M. G. Lee, I. S. Jang, R. Beaton, et al., Astrophys. J. 835, L27 (2017).
D. Makarov, L. Makarova, L. Rizzi, et al., Astron. J. 132, 2729 (2006).
D. Makarov, P. Prugniel, N. Terekhova, et al., Astron. and Astrophys. 570, A13 (2014).
Planck Collaboration, et al., Astron. and Astrophys. 596, A107 (2016).
B. Reindl, G. A. Tammann, A. Sandage, and A. Saha, Astrophys. J. 624, 532 (2005).
A. G. Riess, L. Macri, S. Casertano, et al., Astrophys. J. 730, 119 (2011).
A. G. Riess, L. M. Macri, S. L. Hoffmann, et al., Astrophys. J. 826, 56 (2016).
L. Rizzi, R. B. Tully, D. Makarov, et al., Astrophys. J. 661, 815 (2007).
E. F. Schlafly and D. P. Finkbeiner, Astrophys. J. 737, 103 (2011).
J. M. Silverman, R. J. Foley, A. V. Filippenko, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 425, 1789 (2012).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to N.A. Tikhonov for critical comments and discussion of our work. In the paper, we used the TRGB distance moduli from the Extragalactic Distance Database (EDD) (Jacobs et al., 2009). We also made use of the HyperLeda database (Makarov et al., 2014). For the stellar photometry of galaxies, we used the data from the archive of the Hubble telescope (Hubble Legacy Archive, https://hla.stsci.edu/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Translated by N. Oborina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antipova, A.V., Makarov, D.I. & Makarova, L.N. Distance Measurements to Parent Galaxies of SNIa by the Tip of the Red-Giant Branch. Astrophys. Bull. 75, 93–102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341320020030
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341320020030