Abstract
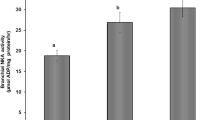
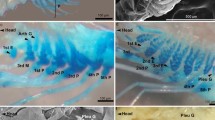
The obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus is a euryhaline fish species suitable for studying the molecular mechanism of osmoregulation. The distributional changes of branchial ionocytes were detected following the transfer from freshwater (FW) to seawater (SW) based on two main ion transporters, Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA) and Na+/K+/ 2Cl− cotransporter 1 (NKCC1). The mRNA and protein expression levels of NKA and NKCC1 in the gills all increased rapidly in the first four days after transfer to SW. Double immunofluorescence staining showed that NKCC1 and NKA were colocalized in the branchial ionocytes and the immunoreaction of NKCC1 was stronger after transfer. Moreover, following transfer to SW, the number of lamellar ionocytes in the gills is reduced and the number of filament ionocytes is increased significantly. Taken together, these findings indicated that SW transfer of obscure puffer promotes the changes of distribution, function and size of branchial ionocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen AK, Hiroi J, Schultz ET, McCormick SD (2012) Branchial ionocyte organization and ion-transport protein expression in juvenile alewives acclimated to freshwater or seawater. J Exp Biol 215:642–652
Choi JH, Lee KM, Inokuchi M, Kaneko T (2011) Morphofunctional modifications in gill mitochondria-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia transferred from freshwater to 70% seawater, detected by dual observations of whole-mount immunocytochemistry and scanning electron microscopy. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 158:132–142
Cutler CP, Cramb G (2002) Two isoforms of the Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter (NKCC1) are expressed in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Biochim Biophys Acta 1566:92–103
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
Gamba G (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol Rev 85:423–493
Giffard-Mena I, Lorin-Nebel C, Charmantier G, Castille R, Boulo V (2008) Adaptation of the sea-bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) to fresh water: role of aquaporins and Na+/K+-ATPases. Comp Biochem Physiol A 150:332–338
Henry RP, Lucu C, Onken H, Weihrauch D (2012) Multiple functions of the crustacean gill: osmotic/ionic regulation, acid-base balance, ammonia excretion, and bioaccumulation of toxic metals. Front Physiol 3:431
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2007) Variation in salinity tolerance, gill Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter and mitochondria-rich cell distribution in three salmonids Salvelinus namaycush, Salvelinus fontinalis and Salmo salar. J Exp Biol 210:1015–1024
Hiroi J, Yasumasu S, McCormick SD, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2008) Evidence for an apical Na-Cl cotransporter involved in ion uptake in a teleost fish. J Exp Biol 211:2584–2599
Hiroi J, Mccormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:257–268
Hoffmann EK, Dunham PB (1995) Membrane mechanisms and intracellular signalling in cell volume regulation. Int Rev Cytol 161:173–262
Hwang PP, Fang MJ, Tsai JC, Huang CJ, Chen ST (1998) Expression of mRNA and protein of Na+-K+ ATPase α subunit in gills of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Fish Physiol Biochem 18:363–373
Hwang PP, Lee TH (2007) New insights into fish ion regulation and mitochondrion-rich cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:479–497
Inokuchi M, Nakamura M, Miyanishi H, Hiroi J, Kaneko T (2017) Functional classification of gill ionocytes and spatiotemporal changes in their distribution after transfer from seawater to freshwater in Japanese seabass. J Exp Biol 220:4720–4732
Jeong SY, Kim JH, Lee WO, Dahms HU, Han KN (2013) Salinity changes in the anadromous river pufferfish, Takifugu obscurus, mediate gene regulation. Fish Physiol Biochem 40:205–219
Kammerer BD, Kultz D (2009) Prolonged apoptosis in mitochondria-rich cells of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) exposed to elevated salinity. J Comp Physiol B 179:535–542
Kang CK, Tsai SC, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2008) Differential expression of branchial Na+/K+-ATPase of two medaka species, Oryzias latipes and Oryzias dancena, with different salinity tolerances acclimated to fresh water, brackish water and seawater. Comp Biochem Physiol 151:566–575
Kang CK, Tsai HJ, Liu CC, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2010) Salinity-dependent expression of a Na+, K+, 2Cl- cotransporter in gills of the brackish medaka Oryzias dancena: a molecular correlate for hyposmoregulatory endurance. Comp Biochem Physiol A 157:7–18
Kato A, Doi H, Nakada T, Sakai H, Hirose S (2005) Takifugu obscurus is a euryhaline fugu species very close to Takifugu rubripes and suitable for studying osmoregulation. BMC Physiol 5:18
Kato A, Muro T, Kimura Y, Li S, Hirose S (2011) Differential expression of Na+-Cl- cotransporter and Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter 2 in the distal nephrons of euryhaline and seawater pufferfishes. Am J Physiol 300:R284–297
Kumai Y, Perry SF (2012) Mechanisms and regulation of Na+ uptake by freshwater fish. Respir Physiol Neuro 184:249–256
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kurita Y, Nakada T, Kato A, Doi H, Hirose S (2008) Identification of intestinal bicarbonate transporters involved in formation of carbonate precipitates to stimulate water absorption in marine teleost fish. Am J Physiol 294: R1402-1412.
Liang F, Li L, Zhang G, Yin S, Wang X, Li P, Jia Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Wang X (2017) Na+/K+-ATPase response to salinity change and its correlation with FXYD11 expression in Anguilla marmorata. J Comp Physiol B 187(7):973–984
Li JJ, Wang L, Yang Y, Chen YF, Yang Z (2014a) Changes in plasma osmolality and Na+/K+ ATPase activity of juvenile obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus following salinity challenge. Biochem Syst Ecol 56:111–117
Li Z, Lui EY, Wilson JM, Ip YK, Lin Q, Lam TJ, Lam SH (2014b) Expression of key ion transporters in the gill and esophageal-gastrointestinal tract of euryhaline Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus acclimated to fresh water, seawater and hypersaline water. PLoS One 9:e87591
Lin YM, Chen CN, Yoshinaga T, Tsai SC, Shen ID, Lee TH (2006) Short-term effects of hyposmotic shock on Na+/K+-ATPase expression in gills of the euryhaline milkfish, Chanos chanos. Comp Biochem Physiol A 143:406–415
Lorin-Nebel C, Boulo V, Bodinier C, Charmantier G (2007) The Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter in the sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax during ontogeny: Involvement in osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 209:4908–4922
Lytle C, Xu JC, Biemesderfer D, Forbush B (1995) Distribution and diversity of Na-K-Cl cotransport proteins: a study with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Physiol 269:C1496–1505
McCormick SD (2003) Influence of salinity on the localization of Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter (NKCC) and CFTR anion channel in chloride cells of the Hawaiian goby (Stenogobius hawaiiensis). J Exp Biol 206:4575–4583
Ouattara N, Bodinier C, Negre-Sadargues G, D'Cotta H, Messad S, Charmantier G, Panfili J, Baroiller JF (2009) Changes in gill ionocyte morphology and function following transfer from fresh to hypersaline waters in the tilapia Sarotherodon melanotheron. Aquaculture 290:155–164
Scott GR, Richards JG, Forbush B, Isenring P, Schulte PM (2004) Changes in gene expression in gills of the euryhaline killifish Fundulus heteroclitus after abrupt salinity transfer. Am J Physiol 287:C300–309
Seo MY, Mekuchi M, Teranishi K, Kaneko T (2013) Expression of ion transporters in gill mitochondrion-rich cells in Japanese eel acclimated to a wide range of environmental salinity. Comp Biochem Physiol A 166:323–332
Shen ID, Chiu YH, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2007) Localization of chloride transporters in gill epithelia of the grass pufferfish, Takifugu niphobles. J Fish Soc Taiwan 34:87–100
Shi Y, Zhang G, Zhu Y, Liu J (2010) Effects of photoperiod, temperature, and salinity on growth and survival of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus larvae. Aquaculture 309:103–108
Takeyasu K, Tamkun MM, Renaud KJ, Fambrough DM (1988) Ouabain-sensitive (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the alpha-subunit of an avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem 263:4347
Tang CH, Hwang LY, Shen ID, Chiu YH, Lee TH (2011) Immunolocalization of chloride transporters to gill epithelia of euryhaline teleosts with opposite salinity-induced Na+/K+-ATPase responses. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:709–724
Tang CH, Lee TH (2007) The effect of environmental salinity on the protein expression of Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, anion exchanger 1, and chloride channel 3 in gills of a euryhaline teleost, Tetraodon nigroviridis. Comp Biochem Physiol A 147:521–528
Tipsmark CK, Madsen SS, Seidelin M, Christensen AS, Cutler CP, Cramb G (2002) Dynamics of Na+, K+,2Cl− cotransporter and Na+, K+-ATPase expression in the branchial epithelium of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J Exp Zool 293:106–118
Tse WKF, Au DWT, Wong CKC (2006) Characterization of ion channel and transporter mRNA expressions in isolated gill chloride and pavement cells of seawater acclimating eels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:1181–1190
Wu YC, Lin LY, Lee TH (2003) Na+,K+,2Cl−-cotransporter: a novel marker for identifying freshwater-and seawater-type mitochondria-rich cells in gills of the euryhaline tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Zool Stud 42:186–192
Yancey PH (2005) Organic osmolytes as compatible, metabolic, and counteracting cytoprotectants in high osmolarity and other stresses. J Exp Biol 208:2819–2830
Yang WK, Kang CK, Chen TY, Chang WB, Lee TH (2011) Salinity-dependent expression of the branchial Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter and Na+/K+-ATPase in the sailfin molly correlates with hypoosmoregulatory endurance. J Comp Physiol B 181:953–964
Yang Z, Chen Y (2006) Salinity tolerance of embryos of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus. Aquaculture 253:393–397
Yang Z, Chen Y (2003) Length-weight relationship of obscure puffer (Takifugu obscurus) during spawning migration in the Yangtze River, China. J Freshwat Ecol 18:349–352
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0900200), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180502), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2017B04214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study conception was designed by Yan Shi. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Tie Ding, Wen Duan, and Sufei Hu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Tie Ding. The manuscript was revised by Zhe Zhao and all authors commented on the early versions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Consent for publication
All authors read the manuscript and approved the publication.
Additional information
Communicated by Bernd Pelster.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, T., Shi, Y., Duan, W. et al. Immunohistochemical characterization and change in location of branchial ionocytes after transfer from freshwater to seawater in the euryhaline obscure puffer, Takifugu obscurus. J Comp Physiol B 190, 585–596 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-020-01298-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-020-01298-x