Abstract
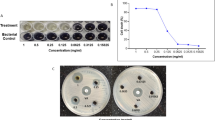
The present study was aimed to extract tannins from methanolic extracts of Salix alba and determination of their antimicrobial potential. Antibacterial activity of tannins extracted from S. alba leaves and stem bark methanolic extracts was determined by using agar well diffusion assay against seven Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains including Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus (1), S. aureus (2), Shigella sonnei, Escherichia coli (1), E. coli (2), and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and zone of inhibition was measured in terms of millimeter. The highest inhibition zone was recorded at 17.33 ± 1.15 by using bark tannins (100 mg/ml) against S. aureus (2) after an incubation period of 48 h while no activity was reported against S. sonnei by using leaves tannins. It was observed that the tannins from the bark of the S. alba were more effective to kill all bacterial pathogens and the inhibition percentage increased with increasing the concentration of the tannins. Major classes of secondary metabolites were determined qualitatively and quantitatively. Leaves fraction of S. alba methanolic extract was enriched with Tannins, Quinones, Steroids, Resins, and Phenols while stem bark extracts were embellished with Flavonoids, Tannins, Quinones, and Phenols. Findings from this study will help to develop formulation from S. alba tannins and endorse the ethnopharmacological utilization of the evaluated plant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan M, Bibi R, Azizullah A, Andaleeb R, Mussarat S, Tariq A, Ullah R, AbdElsalam NM, Khan AL, Begum S (2015) Ethnomedicinal plants used against common digestive problems. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 12(5):99–117
Alamgeer Uttra AM, Ahsan H, Hasan UH, Chaudhary MA (2018) Traditional medicines of plant origin used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders in Pakistan: a review. J Tradit Chin Med 38(4):636–656
Bhuyan DJ, Vuong QV, Chalmers AC, van Altena IA, Bowyer MC, Scarlett CJ (2017) Phytochemical, antibacterial and antifungal properties of an aqueous extract of Eucalyptus microcorys leaves. S Afr J Bot 112:180–185
Burčová Z, Kreps F, Greifová M, Jablonský M, Ház A, Schmidt Š, Šurina I (2018) Antibacterial and antifungal activity of phytosterols and methyl dehydroabietate of Norway spruce bark extracts. J Biotechnol 282:18–24
Carvalho RS, Carollo CA, de Magalhães JC, Palumbo JMC, Boaretto AG, Nunes e Sá IC, Ferraz FC, Lima WG, de Siqueira JM, Ferreira JMS (2018) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of phenolic compound-enriched ethyl acetate fraction from Cochlospermum regium (mart. Et. Schr.) Pilger roots: mechanisms of action and synergism with tannin and gallic acid. S Afr J Bot 114:181–187
Cuellar JE, Martínez J, Rojano B, Gil JH, Durango D (2018) Chemical composition and antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Platymiscium gracile Benth.: a species threatened by extinction. J King Saud Univ 1(2):702–708
Dafallah Bilal MA, Hossain MA (2019) Antibacterial activity of different crude extracts of Suaeda maritima used traditionally for the treatment of hepatitis. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 22:101383
Desam NR, Al-Rajab AJ, Sharma M, Mylabathula MM, Gowkanapalli RR, Albratty M (2017) Chemical constituents, in vitro antibacterial and antifungal activity of Mentha × Piperita L. (peppermint) essential oils. J King Saud Univ Sci 1(2):528–533
dos Reis CM, da Rosa BV, da Rosa GP, do Carmo G, Morandini LMB, Ugalde GA, Kuhn KR, Morel AF, Jahn SL, Kuhn RC (2019) Antifungal and antibacterial activity of extracts produced from Diaporthe schini. J Biotechnol 294:30–37
El Moussaoui A, Zahra Jawhari F, Almehdi AM, Elmsellem H, Fikri Benbrahim K, Bousta D, Bari A (2019) Antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant activity of total polyphenols of Withania frutescens L. Bioorg Chem 103337:1–18
Fortini P, Di Marzio P, Guarrera PM, Iorizzi M (2016) Ethnobotanical study on the medicinal plants in the Mainarde Mountains (central-southern Apennine, Italy). J Ethnopharmacol 184:208–218
Gligorić E, Igić R, Suvajdžić L, Grujić-Letić N (2019) Species of the genus Salix L.: Biochemical screening and molecular docking approach to potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Appl Sci 9(9):1–14
Hossain MA, Nagooru MR (2011) Biochemical profiling and total flavonoids contents of leaves crude extract of endemic medicinal plant Corydyline terminalis L. Kunth. Pharmacogn J 3(24):25–30
Jalalvand AR, Zhaleh M, Goorani S, Zangeneh MM, Seydi N, Zangeneh A, Moradi R (2019) Chemical characterization and antioxidant, cytotoxic, antibacterial, and antifungal properties of ethanolic extract of Allium Saralicum R.M. Fritsch leaves rich in linolenic acid, methyl ester. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 192:103–112
Khanbabaee K, van Ree T (2001) Tannins: classification and definition. Nat Prod Rep 18(6):641–649
Khunoana ET, Madikizela B, Erhabor JO, Nkadimeng SM, Arnot LF, Van Wyk I, McGaw LJ (2019) A survey of plants used to treat livestock diseases in the Mnisi community, Mpumalanga, South Africa, and investigation of their antimicrobial activity. S Afr J Bot 126:21–29
Kutluk I, Aslan M, Orhan IE, Özçelik B (2018) Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral bioactivities of selected Helichrysum species. S Afr J Bot 119:252–257
Mativandlela SPN, Lall N, Meyer JJM (2006) Antibacterial, antifungal and antitubercular activity of (the roots of) Pelargonium reniforme (CURT) and Pelargonium sidoides (DC) (Geraniaceae) root extracts. S Afr J Bot 72(2):232–237
Mogashoa MM, Masoko P, Eloff JN (2019) Different Combretum molle (Combretaceae) leaf extracts contain several different antifungal and antibacterial compounds. S Afr J Bot 126:322–327
Okuda T (2005) Systematics and health effects of chemically distinct tannins in medicinal plants. Phytochemistry 66:2012–2031
Putra MY, Hadi TA, Murniasih T (2016) In vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities of twelve sponges collected from the Anambas Islands, Indonesia. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 6(9):732–735
Qureshi MN, Numonov S, Aisa HA (2019) Total polyphenolic compounds, total flavonoids, GC-MS analysis of volatile constituents, evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Prunus dulcis nuts. Pak J Pharm Sci 32(4):1461–1466
Robbins CT, Mole S, Hagerman AE, Hanley TA (1987) Role of Tannins in defending plants against ruminants: reduction in dry matter. Ecol Soc Am 68(6):1606–1615
Sati P, Dhyani P, Bhatt ID, Pandey A (2019) Ginkgo biloba flavonoid glycosides in antimicrobial perspective with reference to extraction method. J Tradit Complement Med 9(1):15–23
Scalbert A (1991) Antimicrobial properties of tannins. Phytochem 30(12):3875–3883
Shah MD, Hossain MA (2014) Total flavonoids content and biochemical screening of the leaves of tropical endemic medicinal plant Merremia borneensis. Arab J Chem 7(6):1034–1038
Shai LJ, McGaw LJ, Masoko P, Eloff JN (2008) Antifungal and antibacterial activity of seven traditionally used South African plant species active against Candida albicans. S Afr J Bot 74(4):677–684
Sulima P, Przyborowski JA (2019) Purple willow (Salix purpurea L.) and its potential uses for the treatment of arthritis and rheumatism. Bioact. Food as Diet. Interv. Arthritis Relat. Inflamm. Dis. (Elsevier), pp 535–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, B., Nawaz, K. & Munazir, M. Phytochemical Analysis and Antibacterial Activity of Tannins Extracted from Salix alba L. Against Different Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Strains. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 44, 1303–1314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00937-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00937-w