Abstract
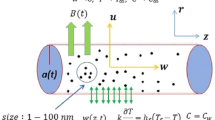
The Buongiorno nanofluid model is utilized to scrutinize the impacts of important slip mechanisms, i.e., thermophoresis diffusion and Brownian momentum on the Darcy–Forchheimer three-dimensional stagnation point flow of viscous fluid towards a flat surface with multi slips (velocity, temperature, concentration). The thermo-physical and experimental correlations for the thermal conductivity, density and dynamic viscosity of nanoliquid are implemented in the governing expressions. Nanoliquids are mostly utilized in the continuous phase liquid to enhance their thermal characteristics as coolants in transport equipment, i.e., electronic cooling system, heat exchangers and radiators. Heat transport subject to flat plate has been examined by numerous analyst. Appropriate similarity transformations which is derived from Lie point symmetry is incorporated to alter the system of governing equation into ordinary one. The transformed system is solved numerically through bvp4v (built-in-shooting) technique. The influences of important flow parameters on the dimensionless temperature, velocity, Nusselt number, concentration, wall shear stress and Sherwood number are plotted graphically and tabular form.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas SZ, Khan WA, Kadry S, Khan MI, Waqas M, Khan MI (2020a) Entropy optimized Darcy–Forchheimer nanofluid (silicon dioxide, molybdenum disulfide) subject to temperature dependent viscosity. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 190:105363
Abbas SZ, Khan MI, Kadry S, Khan WA, Israr-Ur-Rehman M, Waqas M (2020b) Fully developed entropy optimized second order velocity slip MHD nanofluid flow with activation energy. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 190:105362
Abbas T, Rehman S, Shah RA, Idrees M, Qayyum M (2020c) Analysis of MHD Carreau fluid flow over a stretching permeable sheet with variable viscosity and thermal conductivity. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 551:124225
Acharya N, Das K, Kundu PK (2018) Rotating flow of carbon nanotube over a stretching surface in the presence of magnetic field: a comparative study. Appl Nanosci 8:369–378
Ahmadi M, Willing G (2018) Heat transfer measurement in water based nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 118:40–47
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: Proceedings of the 1995, ASME international mechanical engineering congress and exposition, FED 231/MD 66, pp 99–105
Gireesha BJ, Umeshaiah M, Prasannakumara BC, Shashikumar NS, Archana M (2020) Impact of nonlinear thermal radiation on magnetohydrodynamic three dimensional boundary layer flow of Jeffrey nanofluid over a nonlinearly permeable stretching sheet. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 549:124051
Hamid A, Khan M, Hafeez A (2018) Unsteady stagnation-point flow of Williamson fluid generated by stretching/shrinking sheet with Ohmic heating. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:933–940
Hayat T, Khan MI, Farooq M, Alsaedi A, Waqas M, Yasmeen T (2016) Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in flow of variable thermal conductivity fluid over a variable thicked surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 99:702–710
Hayat T, Khan MI, Alsaedi A, Khan MI (2017) Joule heating and viscous dissipation in flow of nanomaterial by a rotating disk. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 89:190–197
Hayat T, Ahmad S, Khan MI, Alsaedi A (2018) Modeling and analyzing flow of third grade nanofluid due to rotating stretchable disk with chemical reaction and heat source. Phys B 537:116–126
Hayat T, Haider F, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A (2020) Darcy–Forchheimer flow by rotating disk with partial slip. Appl Math Mech (Engl Ed) 41:741–752
Hina S, Shafique A, Mustafa M (2020) Numerical simulations of heat transfer around a circular cylinder immersed in a shear-thinning fluid obeying cross model. Phys A 540:123184
Hwang KS, Lee JH, Jang SP (2007) Buoyancy-driven heat transfer of water-based Al2O3 nanofluids in a rectangular cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:4003–4010
Jamshed W, Aziz A (2018) Cattaneo–Christov based study of TiO2–CuO/EG Casson hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching surface with entropy generation. Appl Nanosci 8:685–698
Khan MI, Waqas M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017a) A comparative study of Casson fluid with homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. J Colloid Interface Sci 498:85–90
Khan MI, Qayyum S, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017b) Entropy generation minimization and statistical declaration with probable error for skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number. Chin J Phys 56:1525–1546
Khan I, Lan J, Gao M, Huang S, Wu C (2020) Electron beam-induced changes in tips of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with/without Au nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 10:1521–1534
Muhammad R, Khan MI, Khan NB, Jameel M (2020a) Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) radiated nanomaterial viscous material flow by a curved surface with second order slip and entropy generation. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 189:105294
Muhammad R, Khan MI, Jameel M, Khan NB (2020b) Fully developed Darcy–Forchheimer mixed convective flow over a curved surface with activation energy and entropy generation. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 188:105298
Nasir S, Islam S, Gul T, Shah Z, Khan MA, Khan W, Khan AZ, Khan S (2018) Three-dimensional rotating flow of MHD single wall carbon nanotubes over a stretching sheet in presence of thermal radiation. Appl Nanosci 8:1361–1378
Prakash J, Tripathi D, Bég OA (2020) Comparative study of hybrid nanofluids in microchannel slip flow induced by electroosmosis and peristalsis. Appl Nanosci 10:1693–1706
Turkyilmazoglu M (2014) Nanofluid flow and heat transfer due to a rotating disk. Comput Fluids 94:139–146
Ullah Z, Zaman G, Ishak A (2020) Magnetohydrodynamic tangent hyperbolic fluid flow past a stretching sheet. Chin J Phys 66:258–268
Waini I, Ishak A, Pop I (2020) Transpiration effects on hybrid nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform shear flow. Alex Eng J 59:91–99
Wang Y, Su GH (2016) Experimental investigation on nanofluid flow boiling heat transfer in a vertical tube under different pressure conditions. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 77:116–123
Wang J, Muhammad R, Khan MI, Khan WA, Abbas SZ (2020) Entropy optimized MHD nanomaterial flow subject to variable thicked surface. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 189:105311
Yin C, Zheng L, Zhang C, Zhang X (2017) Flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a rotating disk with uniform stretching rate in the radial direction. Propul Power Res 6(1):25–30
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 11971142, 11871202, 61673169, 11701176, 11626101, 11601485).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.I., Khan, W.A., Waqas, M. et al. Numerical simulation for MHD Darcy–Forchheimer three-dimensional stagnation point flow by a rotating disk with activation energy and partial slip. Appl Nanosci 10, 5469–5477 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01517-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01517-5