Abstract
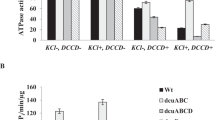
During fermentation Escherichia coli transport succinate mainly via Dcu family carriers. Current paper describes the role of externally added succinate on N’N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) sensitive ATPase activity and H+ flux depending on potassium ions. At pH 7.5 in wild type membrane vesicles DCCD-sensitive ATPase activity was the same as in dcuACBD quadruple mutant. In dcuACB it was increased ~ 3.3 fold while in dcuD DCCD-sensitive ATPase activity was absent. The DCCD-sensitive H+ efflux was fully dependent on FOF1 only in dcuACB mutant. This activity depended on potassium ions and only in dcuACBD mutant DCCD-sensitive ATPase activity was stimulated ~ 3 fold. At pH 5.5 DCCD-sensitive ATPase activities were determined in dcuACB or dcuD mutants but not in wild type. Interestingly, addition of potassium ions enhanced DCCD-sensitive ATPase activity in dcuD mutant ~ 3-fold compared to wild type. In dcuD mutant ~ 3-fold higher H+ uptake was registered, compared to wild type. Taken together it can be concluded that at pH 7.5 the FOF1-activity depends on DcuACB. Moreover, DcuACB but not DcuD are working towards H+ uptake direction. DcuD contributes to H+ efflux at pH 7.5 while at pH 5.5 it affects H+ influx when external succinate is present.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler LW, Rosen BP (1977) Functional mosaicism of membrane proteins in vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 129:959–966
Akopyan K, Trchounian A (2006) Escherichia coli membrane proton conductance and proton fluxes depends on growth pH and are sensitive to osmotic shock. Cell Biochem Biophys 46:201–206
Axe DD, Bailey JE (1995) Transport of lactate and acetate through the energized cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:8–19
Baba T, Ara T, Hasegawa M et al (2006) Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in‐frame, single‐gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol Syst Biol 2
Bagramyan K, Mnatsakanyan N, Poladian A, Vassilian A, Trchounia A (2002) The roles of hydrogenases 3 and 4, and the FOF1-ATPase, in H2 production by Escherichia coli at alkaline and acidic pH. FEBS Lett 516:172–178
Bagramyan K, Mnatsakanyan N, Trchounian A (2003) Formate increases the FOF1-ATPase activity in Escherichia coli growing on glucose under anaerobic conditions at slightly alkaline pH. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 306:361–365
Blbulyan S, Trchounian A (2015) Impact of membrane-associated hydrogenases on the FOF1-ATPase in Escherichia coli during glycerol and mixed carbon fermentation: ATPase activity and its inhibition by N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in the mutants lacking hydrogenases. Arch Biochem Biophys 579:67–72
Boyer PD (1997) The ATP synthase—a splendid molecular machine. Ann Rev Biochem 66(1):717–749
Clark DP (1989) The fermentation pathways of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev 5:223–234
Deckers-Hebestreit G, Greie JC, Stalz WD, Altendorf K (2000) The ATP synthase of Escherichia coli: structure and function of F0 subunits. BBA-Bioenerg 1458:364–373
Fillingame RH, Steed PR (2014) Half channels mediating H+ transport and the mechanism of gating in the FO sector of Escherichia coli F1FO ATP synthase. BBA Bioenerg 1837:1063–1068
Futai M (2006) Our research on proton pumping ATPases over three decades: their biochemistry, molecular biology and cell biology. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 82:416–438
Gevorgyan H, Trchounian A, Trchounian K (2020) Formate and potassium ions affect Escherichia coli proton ATPase activity at low pH during mixed carbon fermentation. IUBMB Life 72:915–921
Gonzalez JE, Long CP, Antoniewicz MR (2017) Comprehensive analysis of glucose and xylose metabolism in Escherichia coli under aerobic and anaerobic conditions by 13C metabolic flux analysis. Metabol Eng 39:9–18
Hong S, Pedersen PL (2008) ATP synthase and the actions of inhibitors utilized to study its roles in human health, disease, and other scientific areas. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72:590–641
Janausch IG, Unden G (1999) The dcuD (former yhcL) gene product of Escherichia coli as a member of the DcuC family of C4-dicarboxylate carriers: lack of evident expression. Arch Microbiol 172:219–226
Janausch IG, Zientz E, Tran QH, Kröger A, Unden G (2002) C4-dicarboxylate carriers and sensors in bacteria. BBA Bioenerg 1553:39–56
Junge W, Sielaff H, Engelbrecht S (2009) Torque generation and elastic power transmission in the rotary FOF1-ATPase. Nature 459:364
Karapetyan L, Valle A, Bolivar J, Trchounian A. Trchounian K (2019) Evidence for Escherichia coli DcuD carrier dependent FOF1-ATPase activity during fermentation of glycerol. Sci Rep 9:1–7
Karapetyan L, Pinske C, Sawers G, Trchounian A, Trchounian K (2020) Influence of C4-Dcu transporters on hydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase activities in stationary phase‐grown fermenting Escherichia coli. IUBMB Life Epub 11 Apr; https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2290
Konings WN, Kaback HR (1973) Anaerobic transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3376–3381
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mnatsakanyan N, Bagramyan K, Vassilian A, Nakamoto RK, Trchounian A (2002) FO Cysteine, bCys21, in the Escherichia coli ATP synthase is involved in regulation of potassium uptake and molecular hydrogen production in anaerobic conditions. Biosci Rep 22:421–430
Nakanishi-Matsui M, Sekiya M, Nakamoto RK, Futai M (2010) The mechanism of rotating proton pumping ATPases. BBA Bioenerg 1797:1343–1352
Otto RO, Lageveen RG, Veldkamp HA, Konings WN (1982) Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol 149:733–738
Riondet C, Cachon R, Waché Y, Alcaraz G, Diviès C (1999) Changes in the proton-motive force in Escherichia coli in response to external oxidoreduction potential. Eur J Biochem 262:595–599
Riondet C, Cachon R, Waché Y, Alcaraz G, Diviès C (2000) Extracellular oxidoreduction potential modifies carbon and electron flow in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182:620–626
Sá-Pessoa J, Paiva S, Ribas D, Silva IJ, Viegas SC, Arraiano CM, Casal M (2013) SATP (YaaH), a succinate–acetate transporter protein in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 454:585–595
Sobti M, Smits C, Wong AS, Ishmukhametov R, Stock D, Sandin S, Stewart AG (2016) Cryo-EM structures of the autoinhibited E. coli ATP synthase in three rotational states. Elife 5:e21598
Sobti M, Ishmukhametov R, Bouwer JC, Ayer A, Suarna C, Smith NJ, Christie M, Stocker R, Duncan TM, Stewart AG (2019) Cryo-EM reveals distinct conformations of E. coli ATP synthase on exposure to ATP. Elife 8:e43864
Trchounian A (2004) Escherichia coli proton-translocating FOF1-ATP synthase and its association with solute secondary transporters and/or enzymes of anaerobic oxidation–reduction under fermentation. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 315:1051–1057
Trchounian A, Sawers RG (2014) Novel insights into the bioenergetics of mixed-acid fermentation: can hydrogen and proton cycles combine to help maintain a proton motive force? IUBMB Life 66:1–7
Trchounian A, Trchounian K (2019) Fermentation revisited: how do microorganisms survive under energy-limited conditions? Trends Biochem Sci 44:391–400
Trchounian K, Poladyan A, Trchounian A (2009) Relation of potassium uptake to proton transport and activity of hydrogenases in Escherichia coli grown at low pH. Biochemistry 3:144–150
Trchounian K, Poladyan A, Vassilian A, Trchounian A (2012) Multiple and reversible hydrogenases for hydrogen production by Escherichia coli: dependence on fermentation substrate, pH and the FOF1-ATPase. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 47:236–249
Trchounian K, Blbulyan S, Trchounian A (2013) Hydrogenase activity and proton-motive force generation by Escherichia coli during glycerol fermentation. J Bioenerg Biomembr 45:253–260
Valle A, Cabrera G, Muhamadali H, Trivedi DK, Ratray NJ, Goodacre R, Cantero D, Bolivar J (2015) A systematic analysis of TCA Escherichia coli mutants reveals suitable genetic backgrounds for enhanced hydrogen and ethanol production using glycerol as main carbon source. Biotech J 10:1750–1761
Vik SB, Ishmukhametov RR (2005) Structure and function of subunit a of the ATP synthase of Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr 37:445–459
Weber J, Senior AE (2003) ATP synthesis driven by proton transport in F1F0-ATP synthase. FEBS Lett 545:61–70
Zakharyan E, Trchounian A (2001) K+ influx by Kup in Escherichia coli is accompanied by a decrease in H+ efflux. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:61–64
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Grant from State Committee of Science, Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sport of Armenia, to AT (18T-1F045) and KT (19YR-1F013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikoyan, G., Karapetyan, L., Vassilian, A. et al. External succinate and potassium ions influence Dcu dependent FOF1-ATPase activity and H+ flux of Escherichia coli at different pHs. J Bioenerg Biomembr 52, 377–382 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09847-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09847-3