Abstract
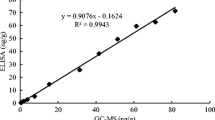
Bisphenol S (BPS) is a major alternative to Bisphenol A (BPA) newly applied in food packing material and disrupts reproductive and developmental endpoints through endocrine pathways. This study aimed to develop a rapid, sensitive, and accurate chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) for the detection of BPS in canned beverage. Anti-BPS monoclonal antibody (mAb) was generated by immunizing Balb/c mice with immunogen (BPS–BSA conjugation). CLIA assay conditions, including 3-[9-(((3-(N-succinimidyloxycarboxypropyl) [4-methxylphenyl] sulfonyl) amine) carboxyl]-10-acridiniumyl)-1-propanesulfonate inner salt (NSP-SA-NHS) labeling ratio (1:40), antigen concentration (1 μg mL−1) and antibody titer (1:8000; 125 ng mL−1 in PBS (0.01 M, pH 7.4)) were determined, respectively. The half inhibition concentration (IC50), detection limit (IC10), and working range of the CLIA in canned beverage were 0.04, 1.48, and 0.32–5 ng mL−1, respectively. Cross-reactivity with other bisphenols (4,4′-thiodiphenol, Bisphenol F, 4,4′- dihydroxy benzophenone, Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B) was less than 0.56%, and the recovery rates of BPS in canned beverage ranged from 80 to 109.2% (intra-assay) and from 82 to 108.4% (inter-assay). The results of CLIA were compared with high-performance liquid chromatography–UV (HPLC–UV) analysis, showing a good correlation of 0.956. After proper sample pre-treatment, this method allows relatively large amounts of sample analysis in a limited time period (30 min). Thus, it was deemed suitable and efficient for routine screening of BPS in canned beverage.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang W, Yin K, Chen L (2013) Bacteria-mediated bisphenol A degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(13):5681–5689
Liao C, Liu F, Kannan K (2012) Bisphenol S, a new bisphenol analogue, in paper products and currency bills and its association with bisphenol A residues. Environ Sci Technol 46(12):6515–6522
Russo G, Barbato F, Cardone E, Fattore M, Albrizio S, Grumetto L (2018) Bisphenol A and Bisphenol S release in milk under household conditions from baby bottles marketed in Italy. J Environ Sci Health Part B 53(2):116–120
Liao C, Liu F, Alomirah H, Loi VD, Mohd MA, Moon H-B, Nakata H, Kannan K (2012) Bisphenol S in urine from the United States and seven Asian countries: occurrence and human exposures. Environ Sci Technol 46(12):6860–6866
Xiao X, Zhang X, Zhang C, Li J, Zhao Y, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Zhou X (2019) Caenorhabditis elegansToxicity and multigenerational effects of bisphenol S exposure to on developmental, biochemical, reproductive and oxidative stress. Toxicol Res 8(5):630–640
Ullah H, Jahan S, Ain QU, Shaheen G, Ahsan N (2016) Effect of bisphenol S exposure on male reproductive system of rats: a histological and biochemical study. Chemosphere 152:383–391
Gallart-Ayala H, Moyano E, Galceran MT (2011) Analysis of bisphenols in soft drinks by on-line solid phase extraction fast liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 683(2):227–233
Mei SX, Hui SD, Shuang WB, Bei LB, Yuan HF (2014) Simultaneous determination of bisphenols and alkylphenols in water by solid phase extraction and ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Environ Sci 27(6):471–474
Xian Y, Wu Y, Dong H, Guo X, Wang B, Wang L (2017) Dispersive micro solid phase extraction (DMSPE) using polymer anion exchange (PAX) as the sorbent followed by UPLC–MS/MS for the rapid determination of four bisphenols in commercial edible oils. J Chromatogr A 1517:35–43
Wang C, Wu J, Zong C, Xu J, Hx JU (2012) Chemiluminescent immunoassay and its applications. Chin J Anal Chem 40(1):3–10
Li C, He J, Ren H, Zhang X, Du E, Li X (2016) Preparation of a chicken scFv to analyze gentamicin residue in animal derived food products. Anal Chem 88(7):4092–4098
Lin L, Wu X, Luo P, Song S, Kuang H (2019) IC-ELISA and immunochromatographic strip assay based monoclonal antibody for the rapid detection of bisphenol S. Food Agric Immunol 30(1):633–646
Detroit R&D, Inc. https://www.detroitrandd.com/sites/default/files/documents/bps_spec_sheet_103018b.pdf
Yin Y, Liu L, Song S, Hua K, Xu C (2015) Development of a highly sensitive icELISA to detect semicarbazide based on a monoclonal antibody. Food Agric Immunol 26(3):356–365
Zheng Q, Cao L, Zheng H, Lin H, Sui J (2016) Preparation and characterization of an immunoaffinity column for the selective extraction of neomycin. J Food Saf Qual 7(3):1037–1045
Diao CP, Yang X, Sun AL, Liu RM (2015) Vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction of bisphenol S prior to its determination by HPLC with UV detection. Microchim Acta 182(15–16):2593–2600
Jorge R, Thomas W (2015) Determination of bisphenols in beverages by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1422:230–238
Lu Y, Peterson JR, Gooding JJ, Lee NA (2012) Development of sensitive direct and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for monitoring bisphenol-A in canned foods and beverages. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(6):1607–1618
Lehmler H-J, Liu B (2018) Exposure to Bisphenol A, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol S in U.S. Adults and Children: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2014. ACS Omega 3 (6):6523–6532
Vázquez Loureiro P, Rodríguez-Bernaldo De Quirós A, Sendón R (2018) Determination of bisphenol S in food and drink take away packaging by LC-MS/MS. Int J Environ Anal Chem 98(15):1413–1422
Sosvorova LK, Chlupacova T, Vitku J, Vlk M, Heracek J, Starka L, Saman D, Simkova M, Hampl R (2017) Determination of selected bisphenols, parabens and estrogens in human plasma using LC-MS/MS. Talanta 174:21–28
Yang Y, Lu L, Zhang J, Yang Y, Wu Y, Shao B (2014) Simultaneous determination of seven bisphenols in environmental water and solid samples by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1328:26–34
Vela-Soria F, Ballesteros O, Zafra-Gómez A, Ballesteros L, Navalón A (2014) UHPLC–MS/MS method for the determination of bisphenol A and its chlorinated derivatives, bisphenol S, parabens, and benzophenones in human urine samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 406(15):3773–3785
Luo S, Wu Z, Shang G, Zhu H, Jiang H (2014) Determination of bisphenol S in food contact materials by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Food Saf Qual 5(11):3576–3579
Česen M, Lambropoulou D, Laimou-Geraniou M, Kosjek T, Uk B, Heath D, Heath E (2016) Determination of bisphenols and related compounds in honey and their migration from selected food contact materials. J Agric Food Chem 64(46):8866–8875
Chen K, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Huang L, Wang R, Yue X, Zhu W, Zhang D, Zhang X, Zhang Y (2018) Label-free fluorescence aptasensor for sensitive determination of bisphenol S by the salt-adjusted FRET between CQDs and MoS2. Sens Actuators B Chem 259:717–724
Wang T, Liang R, Yin T, Yao R, Qin W (2016) An all-solid-state imprinted polymer-based potentiometric sensor for determination of bisphenol S. RSC Adv 6(77):73308–73312
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 31572556; 31873006); the Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Project of Shaanxi Province (Grant Number 2017KW-ZD-10); the Incubation Project on State Key Laboratory of Biological Resources and Ecological Environment of Qinba Areas (Grant Number SLGPT2019KF04-04); and the FCT I.P, the Ministério da Ciência Tecnologia e Ensino Superior (MCTES), the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) (Grant Number POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007569).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ conceived and designed the study. FFY and LX conducted experiments, analyzed data and prepared the manuscript. CC and XL analyzed data. XZ and ACPD critically revised the manuscript. All authors discussed results, edited and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All animal experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shaanxi University of Technology for the use of Laboratory Animals (2019–008, Chinese-German Joint Laboratory for Natural Product Research).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Xu, L., Liu, X. et al. Chemiluminescence immunoassay approach to quantify Bisphenol S in canned beverage using a NSP-SA-labeled specific monoclonal antibody. Eur Food Res Technol 246, 1857–1865 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-020-03539-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-020-03539-3