Abstract
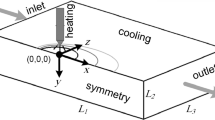
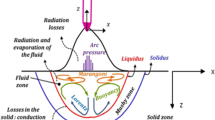
In order to improve our understanding of the PAMCHR process applied to the processing of Ti alloys, a 3D numerical simulation of the thermal and hydrodynamic behavior of the metal flowing in the refining hearth has been set up, based on Ansys-Fluent CFD software. The solid and liquid phases are governed by a set of transport equations expressing the conservation of mass, momentum, heat, and solutes. The turbulence of the liquid flow is modeled through the standard k–ε model. Heat input and tangential shear stress caused by the plasma jet originating from the torches, as well as the themocapillary effect, are accounted for as boundary conditions. Their effects on the turbulent liquid metal flow have been modeled together with the displacement of the torches. Simulation results are presented for a pilot furnace and representative operating conditions. Turbulent fluid flow in the Ti64 molten pool is analyzed in detail and the role of each momentum source is examined. Comparison between the measured and calculated pool profiles is also reported and reveals a satisfactory agreement.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C p :
-
Specific heat (J/kg/K)
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- D t :
-
Turbulent diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m2/s)
- g l :
-
Liquid fraction
- h wall :
-
Heat-transfer coefficient at the crucible walls (W/m2)
- k :
-
Coefficient of mass transfer (m/s)
- K :
-
Permeability of the mushy zone (m2)
- K 0 :
-
Permeability constant of the Kozeny-Carman law (m2)
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- P i :
-
Saturating vapor pressure of the element i
- r :
-
Distance from the plasma torch center (m)
- R :
-
Ideal gas constant (J/mol/K)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- v :
-
Velocity of the fluid (m/s)
- x i :
-
Mole fraction of the element i
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- β T :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (K−1)
- γ i :
-
activity coefficient of the element i
- ∆Hf :
-
Latent heat of melting (J/kg)
- ε :
-
Thermal emissivity
- φ torch :
-
Heat flux density of the plasma jet (W/m2)
- φ wall :
-
Heat flux density on the walls (W/m2)
- \( \varphi_{\text{i}}^{\text{eq}} \) :
-
Flux density of heat volatilization of the element i (kg/m2/s)
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/m/K)
- λ t :
-
Turbulent thermal conductivity (W/m/K)
- σ s :
-
Stefan constant (W/m2/K4)
- τ m :
-
Marangoni shear stress (Pa)
- τ max :
-
Maximum value of shear stress due to the plasma impact (Pa)
- τ s :
-
Shear stress due to the plasma impact (Pa)
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg/m/s)
- µ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity (kg/m/s)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- ρ 0 :
-
Density value at a temperature T0 (kg/m3)
- ω i :
-
Weight fraction of the element i
References
C.E. Schamblen: Technical Information Series Report No. R89AERB141, GEAE, OH, 1989.
Y. Honnorat: La Revue de Métallurgie-CIT, 1996, pp. 1029–41.
J.P. Bellot, B. Foster, S. Hans, E. Hess, D. Ablitzer and A. Mitchell: Metall. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 1001-1010
J.P. Bellot, E. Hess and D. Ablitzer: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 845-854
[5] M.J. Blackburn and D.R. Malley: Materials & Design, 1993, vol.14 pp. 19-27
C. Reimer, J. Jourdan and J.P. Bellot: Calphad, vol. 58, 2017, pp. 122-127.
X. Huang, J.S. Chou, D. Tilly, K.O. Yu: In Proceeding of the Int Conf. on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe (NM, USA), 1997, pp. 179–203.
R.M. Lothian and M. Mclean: In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe (NM, USA), 1997, pp. 133–44.
X. Huang, J.S. Chou, and Y. Pang: 1999. In Proceeding of the Int Conf. on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Santa Fe (NM, USA), 1999, pp. 224–43.
S.C. Chu and S.S. Lian: Computational Materials Science, 2004, vol. 30, pp. 441–447
X. Xu, H. Chang, H. Kou, Z.Yang, and J. Li: Int. J. Innovative Technol. Explor. Eng.(IJITEE), 2013, vol. 2, pp. 1123-1133
S. Ji, J. Duan, L. Yao, D.M. Maijer, S.L. Cockcroft, D. Fiore and D. W. Tripp: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, vol.119, pp. 271–281
L. Yao, D.M. Maijer, S. L. Cockcroft, D. Fiore and D.W. Tripp: Int J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2018, vol.126, pp. 1123-1133
L. Décultot, A. Jardy, S.Hans, E. Doridot, J. Delfosse, F. Ruby-Meyer and J.P. Bellot: In Proceeding of the Int Conf. on Titanium, Nantes, (France), 2019, USB key.
[15] B.E. Launder and D.B. Spalding: Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Eng., 1974, vol.3, pp. 269-289
R.Rai, P.Burgardt, J.O. Milewski, T.J. Lienert and T.DebRoy: J. Phys. D.: Appl. Phys., 2009, vol.42, pp. 1-12
W. Choi, J.Jourdan, A.Matveichev, A.Jardy and J.P.Bellot: High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2017, vol. 36, pp. 815-823
F. Qian, B. Farouk and R. Mutharasan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1995, vol. 26B, pp. 1057–67.
E. Hess: Ph.D. Thesis, 1997, Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine.
Y. Pang, S. Srivatsa, and K.-O. Yu: Modeling for Casting and Solidification Processing, Marcel Dekker, New York, 2002, Ch. 8, pp. 621–26.
P.A. Kobryn and S.L. Semiatin: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 685–95.
Zhao X., Reilly C., Yao L., Maijer D.M., Cockcroft S.L., Zhu J.: Applied Mathematical Modelling,2014, vol.38, pp. 3607-3623
P.G. Clites and R.A. Beall: Report No. 7035, United States Bureau of Mines, Albany, OR, 1967.
G.A. Khasin, V.Z. Bigashev, and N.A. Ermanovich: Steel USSR, 1973, vol. 3, pp. 383–85.
M. Boivineau, C. Cagran, D. Doytier, V. Eyraud, M. Nadal, B. Wilthan, B. and G. Pottlacher: In Proceedings of the International Journal of Thermophysics, 2006, vol. 27, pp. 507–29.
ANSYS Fluent-Solver Theory Guide, Released 17.1, ANSYS INC PA, 2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted January 16, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellot, JP., Décultot, L., Jardy, A. et al. Numerical Simulation of the Plasma Arc Melting Cold Hearth Refining Process (PAMCHR). Metall Mater Trans B 51, 1329–1338 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01866-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01866-0