Abstract
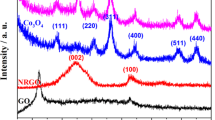
The present investigation deals with the synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/copper oxide (CuO)/silver (Ag) ternary nanocomposites (NCs) by hydrothermal method to improve the electrical behavior. In typical synthesis, ammonia was used as a reducing agent at room temperature. The powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) pattern revealed the existence of single-phase monoclinic structure and face-centered cubic (FCC) phase of CuO and Ag. Other phase impurities were also observed from the prepared rGO/CuO/Ag NCs. The surface morphology of rGO/CuO/Ag NCs was investigated by SEM and TEM analysis. The surface elemental composition of the prepared material was investigated by the EDAX analysis. The dielectric response of the materials was studied by dielectric constant, dielectric loss, and AC conductivity studies. The lesser amount of activation energy was attained from the synthesized rGO/CuO/Ag NCs, and it was proved that this type of material is the most emerging candidate for various opto-electronics application. The electrochemical behavior was studied by the cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge discharge (GCD), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements. From this study, ideal capacitance behavior with high capacitance of about 575 F/g was achieved respectively for rGO/CuO/Ag NCs at the current density of 1 Ag−1in 0.5 M K2SO4 electrolyte solution. These superior electrochemical features demonstrated that the prepared rGO/CuO/Ag NCs are a potential candidate for next-generation supercapacitor systems.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ates, M., Garip, A., Yörük, O., Bayrak, Y., Kuzgun, O., Yildirim, M.: Energy Technol. 168, 48 (2019)
Gopalakrishnan, A., Vishnu, N., Badhulika, S.: J. Electroanal. Chem. 187, 834 (2019)
Dubal, D.P., Chodankar, N.R., Gund, G.S., Holze, R., Lokhande, C.D., Romero, P.G.: Energy Technol. 168, 3 (2015)
Purushothaman, K.K., Saravanakumar, B., Babu, I.M., Sethuraman, B., Muralidharan, G.: RSC Adv. 23485, 4 (2014)
Yu, G., Xie, X., Pan, L., Bao, Z., Cui, Y.: Nano Energy. 213, 2 (2013)
Li, X., Wei, B.: Nano Energy. 159, 2 (2013)
Dubal, D.P., Kim, J.G., Kim, Y., Holze, R., Lokhande, C.D., Kim, W.B.: Energy Technol. 325, 2 (2014)
Vivek, C., Balraj, B., Thangavel, S.: J. Electron. Mater. 49, 1075–1070 (2020)
Dey, K.K., Kumar, A., Shanker, R., Dhawan, A., Wan, M., Yadav, R.R., Srivastava, A.K.: RSC Adv. 1387, 2 (2012)
Zhang, Y.X., Huang, M., Li, F., Wen, Z.Q.: Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8645, 8 (2013)
Sridevi, A., Siva, C., Balraj, B., Venkatesan, G.K.D.P.: J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 29, 535–540 (2019)
Pendashteha, A., Mousavia, M.F., Rahmanifa, M.S.: Electrochim. Acta. 347, 88 (2013)
Mai, Y.J., Wang, X.L., Xiang, J.Y., Qiao, Y.Q., Zhang, D., Gu, C.D., Tu, J.P.: Electrochim. Acta. 2306, 56 (2011)
Zhao, B., Liu, P., Zhuang, H., Jiao, Z., Fang, T., Xu, W., Lub, B., Jiang, Y.: J. Mater. Chem. A. 367, 1 (2013)
Bhargava, R., Khan, S.: Adv. Powder Technol. 2812, 28 (2017)
Shao, P.R., Deng, S.Z., Chen, J., Chen, J., Xu, N.S.: J. Appl. Phys. 023710, 109 (2011)
Jeong, Y.K., Choi, G.M.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 81, 57 (1996)
Pramothkumar, A., Senthilkumar, N., Malar, K.C.M.G., Meena, M., Potheher, I.V.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19043, 30 (2019)
Wang, Y., Guan, H., Dong, C., Xiao, X., Du, S., Wang, Y.: Ceram. Int. 936, 42 (2016)
Senthilkumar, N., Ganapathy, M., Arulraj, A., Meena, M., Vimalan, M., VethaPotheher, I.: J. Alloys Compd. 171, 750 (2018)
Ganapathy, M., Senthilkumar, N., Vimalan, M., Jeysekaran, R., Vetha Potheher, I.: Mater. Res. Express. 045020, 5 (2018)
Senthilkumar, N., Vivek, E., Shankar, M., Meena, M., Vimalan, M., Vetha Potheher, I.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2927, 29 (2018)
Viswanathan, A., Shetty, A.N.: Electrochim. Acta. 204, 289 (2018)
Viswanathan, A., Shetty, A.N.: Electrochim. Acta. 483, 257 (2017)
Xu, D., Zhu, C., Meng, X., Chen, Z., Li, Y., Zhang, D., Zhu, S.: Sensors Actuators. B435, 265 (2018)
Koops, C.G.: Phys. Rev. 121, 83 (1951)
Wagner, K.W.: Ann. Phys. 817, 626 (1913)
Xue, D., Kitamura, K.: Solid State Commun. 537, 122 (2002)
Singh, A.K.: Synthesis, Adv. Powder Technol. 609, 21 (2010)
Senthilkumar, N., Ganapathy, M., Sharmila, S., Shankar, M., Vimalan, M., Vetha Potheher, I.: J. Alloys Compd. 624, 703 (2017)
Jeyachitra, R., Senthilnathan, V., Senthil, T.S.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1189, 29 (2017)
Senthilkumar, N., Venkatachalam, V., Kandiban, M., Vigneshwaran, P., Jayavel, R., VethaPotheher, I.: Physica E. 121, 106 (2019)
Vigneshwaran, P., Kandiban, M., Senthilkumar, N., Venkatachalam, V., Jayavel, R., VethaPotheher, I.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 4653, 27 (2016)
Vijayabala, V., Senthilkumar, N., Nehru, K., Karvembu, R.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 323, 29 (2018)
Majumdar, D., Baugh, N., Bhattacharya, S.K.: Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 158, 512 (2017)
Bu, I.Y.Y., Huang, R.: Ceram. Int. 45, 43 (2017)
Park, H., Han, T.H.: Macromol. Res. 809, 22 (2014)
Rai, A.K., Anh, L.T., Gim, J., Mathew, V., Kang, J., Paul, P.J., Singh, N.K., Song, J., Kim, J.: J. Power Sources. 435, 244 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridevi, A., Balraj, B., Senthilkumar, N. et al. Synthesis of rGO/CuO/Ag Ternary Nanocomposites Via Hydrothermal Approach for Opto-electronics and Supercapacitor Applications. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 3501–3510 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05594-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05594-z