Abstract
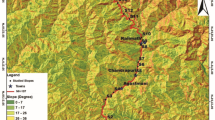
The Himalayan ranges are well known for active and incessant slope failures. The network of highways and local roads in the region is under sustained threat of potential fatal landslides. Urban sprawl and increased human intervention increased the vulnerability and probability of sliding to manifolds. Tampering the fragile conditions of the sensitive Himalayan orogen may generate new avenues of slope failures. Road widening and development projects have a close association with slope failures. However, such landslides can be coped with proper geotechnical planning and execution. The slopes along national highway-58 (NH-58) are being excavated for road widening. Large numbers of steep and unstable cut sections were visible soon after the excavation along the highway. The geotechnical assessment has been undertaken to determine stable slope geometry. The profile of existing slopes is modified by creating benches, and safety factor was determined at different overall angle. The optimization of slope geometry suggests that most of the unstable slope may have safety factor of 1.5, by creating benches of 10 m (height), 5 m (span), at an angle of 65°. It can also be inferred from the analysis that the safety factor may be improved from 11.5 to 32.2% for each 5° reduction in the overall slope angle. Certain adverse impacts and future projections of inadequately performed road widening were also discussed in the paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandis, S.C., Lumsden, A.C., Barton, N.R. (1983) Fundamentals of rock joint deformation. Internat. Jour. Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstract, v.20(6), pp.249–268.
Bartarya, S.K. and Valdiya, K.S. (1989) Landslide and erosion in the catchment of the Gaula River, Kumaun Lesser Himalaya, India. Mountain Research and Development, v.9(4), pp.405–419.
Barton, N.R. (1972) A model study of rock-joint deformation. Internat. Jour. Rock Mechanics and Mining Sci., v.9, pp.579–602.
Frank, F., McArdell, B.W., Huggel, C., Vieli, A. (2015) The importance of entrainment and bulking on debris flow runout modeling: examples from the Swiss Alps. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sci., v.15, pp.2569–2583.
Hoek, E. and Diederichs, M.S. (2006) Empirical estimation of rock mass modulus. Internat. Jour. Rock Mechanics and Mining Sci., v.43, pp.203–215.
Jiang, G., Blick, N.C., Kaufman, A.J., Banerjee, D.M., Rai, V. (2003) Carbonate platform growth and cyclicity at a terminal Proterozoic passive margin, Infra Krol Formation and Krol Group, Lesser Himalaya, India. Sedimentology, v.50, pp.921–952.
Katz, O., Reches, Z., Roegiers, J.C. (2000) Evaluation of mechanical rock properties using a Schmidt Hammer. Internat. Jour. Rock Mechanics Mining Sci., v.37, pp.723–728.
Kumar, G. and Dhaundiyal, J.N. (1979) Stratigraphy and structure of “Garhwal Synform” Garhwal and Tehri Garhwal Districts, Uttar Pradesh. A reappraisal. Himalayan Geol., v.9(1), pp.18–41.
Kumar, G. and Dhaundiyal, J.N. (1980) On the stratigraphic position of the Tal formation, Garhwal Synform, Garhwal and Tehri Garhwal Districts, Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Paleontol. Soc. India, v.23–24, pp.58–66.
Mondal, M.E.A., Siddique, T., Mondal, B., Alam, M.M. (2016) SMR Geomechanics and kinematic analysis near Rasulpur, Fatehpur Sikri, Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.87(5), pp.623–627.
Pain, A., Kanungo, D.P., Sarkar, S. (2014) Rock slope stability assessment using finite element based modelling-examples from the Indian Himalayas. Geomechanics and Geoengineering, v.9(3), pp.2015–230.
Pradhan, S.P. and Siddique, T. (2019) Stability assessment of landslide-prone road cut rock slopes in Himalayan terrain: A finite element method based approach. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.12.018.
Sarkar, S., Kanungo, D.P., Sharma, S. (2015) Landslide hazard assessment in the upper Alaknanda valley of Indian Himalayas. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, v.6(4), pp.308–325.
Sarkar, S., Pandit, K., Shamra, M., Pippal, A. (2018) Risk assessment and stability analysis of a recent landslide at Vishnuprayag on the Rishikesh-Badrinath highway, Uttarakhand, India. Curr. Sci., v.114(7), pp.1527–1533.
Sati, S.P., Sunderiyal, Y.P., Rana, N., Dangwal, S. (2011) Recent landslides in Uttarakhand: nature’s furry or human folly. Curr. Sci., v.100(11), pp.1617–1620.
Sazid, M. (2019) Analysis of rockfall hazards along NH 15: a case study of Al Hada road. Internat. Jour. Geo-Engineering, v.10(1), pp.1–13.
Scaringi, G., Fan, X., Xu, Q., Liu, C., Ouyang, C., Domenech, G., Yang, F., Dai, L. (2018) Some considerations on the use of numerical methods to simulate past landslides and possible new failures: the case of the recent Xinmo landslide (Sichuan, China). Landslides, v.15(7), pp.1359–1375.
Siddique, T., Alam, M.M., Mondal, M.E.A., Vishal, V. (2015) Slope Mass Rating and Kinematic analysis of slopes along National Highway-58, near Jonk, Rishikesh, India. Jour. Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engg., v.7(5), pp.600–606.
Siddique, T., Pradhan, S.P., Vishal, V., Mondal, M.E.A., Singh, T.N. (2017) Stability assessment of Himalayan road cut slopes along National Highway 58, India. Environ. Earth Sci., v.76, pp.759.
Singh, B. and Goel, R.K. (2002) Software for engineering control of landslide and tunnelling hazards. Rotterdam, the Netherlands: A.A. Balkema.
Singh, P.K., Wasnik, A.B., Kainthola, A., Sazid, M., Singh, T.N. (2013) The stability of road cut cliff face along SH-121: a case study. Natural Hazards, v.68, pp.497–507.
Sonmez, H. and Ulusay, R. (2002) A discussion on the Hoek-Brown failure criterion and suggested modification to the criterion verified by slope stability case studies. Yerbilimleri, v.26, pp.77–99.
Sundriyal, Y.P., Shukla, A.D., Rana, N., Jayangondaperumal, R., Srivastava, P., Chamyal, L.S., Sati, S.P., Juyal, N. (2015) Terrain response to the extreme rainfall event of June 2013: Evidence from Alaknanda and Mandakini valleys, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Episodes, v.38(3), pp.179–188.
Vishal, V., Siddique, T., Purohit, R., Phophliya, M.K., Pradhan, S.P. (2017) Hazard assessment in rockfall-prone Himalayan slopes National Highway-58, India: rating and simulation. Natural Hazards. v.85(1), pp.487–503.
Valdiya, K.S. (1980) Geology of Kumaun Lesser Himalaya. Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehradun, India. 291p.
Vásárhelyi, B. and Kovács, D. (2017) Empirical methods of calculating the mechanical parameters of the rock mass. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engg., v.61(1), pp.39–50.
Yagiz, S. (2009) Predicting uniaxial compressive strength, modulus of elasticity and index properties of rocks using the Schmidt hammer. Bull. Engg. Geol. Environ., v.68, pp.55–63.
You, G., Mandalawi, M.A., Soliman, A., Dowling, K., Dahlhaus, P. (2018) Finite element analysis of rock slope stability using shear strength reduction method. In: Frikha et al. (Eds.), Soil Testing, Soil Stability and Ground Improvement. GeoMEast, Sustainable Civil Infrastructures. Springer, Cham.
Acknowledgements
Authors express their thanks to Head of the Department, Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, India for providing necessary facilities to conduct field surveys.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddique, T., Pradhan, S.P., Das, N. et al. Stabilization of Cut Slopes along the Highway by Optimizing Geometry, NH-58, Lesser Himalaya. J Geol Soc India 96, 79–86 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1507-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1507-z