Abstract
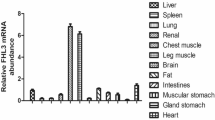
Immunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (Islr) contains an Ig-like domain, an LRR motif, and a transmembrane domain and is highly expressed in various chicken tissues. Although Islr has known roles in muscle regeneration, its role in the regulation of muscle atrophy has not been studied. In this study, we constructed Islr-silenced or Islr-overexpressed myoblasts to investigate its role during the differentiation of myoblasts into myotubes. The results showed that Islr was highly expressed in chicken skeletal muscle tissue and regulated myoblast differentiation, but not proliferation. Islr regulated the expression of atrophy-related genes including atrogin-1 and MuRF-1, and could rescue dexamethasone-induced atrophy in myoblasts and myotubes. Western blot analysis indicated that Islr participates in myoblast atrophy through IGF/PI3K/AKT-FOXO signaling. Meanwhile, the expression of caspase-8 and caspase-9 increased in Islr-silenced groups, indicating its role in cell viability. Taken together, these data suggested that Islr plays an important role in myoblasts differentiation, and which can alleviate skeletal muscle atrophy and prevents muscle cell apoptosis via IGF/PI3K/AKT-FOXO signaling pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK-M, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K (2001) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294(5547):1704–1708
Bulfield G, Siller W, Wight P, Moore KJ (1984) X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81(4):1189–1192
Chang NC, Chevalier FP, Rudnicki MA (2016) Satellite cells in muscular dystrophy–lost in polarity. Trends Mol Med 22(6):479–496
Charge SB, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84(1):209–238
Devol DL, Rotwein P, Sadow JL, Novakofski J, Bechtel PJ (1990) Activation of insulin-like growth factor gene expression during work-induced skeletal muscle growth. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 259(1):E89–E95
Fuster G, Busquets S, Almendro V, López-Soriano FJ, Argilés JM (2007) Antiproteolytic effects of plasma from hibernating bears: a new approach for muscle wasting therapy? Clin Nutr 26(5):658–661
Glass DJ (2005) Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy signaling pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(10):1974–1984
Glass DJ (2010) PI3 kinase regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. In: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in health and disease. Springer, pp 267-278
Goldspink DF, Garlick PJ, McNurlan M (1983) Protein turnover measured in vivo and in vitro in muscles undergoing compensatory growth and subsequent denervation atrophy. Biochem J 210(1):89–98
Gussoni E, Blau HM, Kunkel LM (1997) The fate of individual myoblasts after transplantation into muscles of DMD patients. Nat Med 3(9):970
Han S, Cui C, Wang Y, He H, Shen X, Chen Y, Liu Z, Zhu Q, Li D, Yin H (2019) FHL3 negatively regulates the differentiation of skeletal muscle satellite cells in chicken. 3. Biotech 9(6):206
Hasty P, Bradley A, Morris JH, Edmondson DG, Venuti JM, Olson EN, Klein WH (1993) Muscle deficiency and neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin gene. Nature 364(6437):501
Jagoe RT, Goldberg AL (2001) What do we really know about the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in muscle atrophy? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 4(3):183–190
Knapp JR, Davie JK, Myer A, Meadows E, Olson EN, Klein WH (2006) Loss of myogenin in postnatal life leads to normal skeletal muscle but reduced body size. Development 133(4):601–610
Kress JP, Hall JB (2014) ICU-acquired weakness and recovery from critical illness. N Engl J Med 370(17):1626–1635
Latres E, Amini AR, Amini AA, Griffiths J, Martin FJ, Wei Y, Lin HC, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2005) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) inversely regulates atrophy-induced genes via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) pathway. J Biol Chem 280(4):2737–2744
Li Z, Cai B, Abdalla BA, Zhu X, Zheng M, Han P, Nie Q, Zhang X (2019) LncIRS1 controls muscle atrophy via sponging miR-15 family to activate IGF1-PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 10(2):391–410
Liao R, Yan F, Zeng Z, Farhan M, Little P, Quirion R et al (2017) Amiodarone-induced retinal neuronal cell apoptosis attenuated by igf-1 via counter regulation of the pi3k/akt/foxO3a pathway. Mol Neurobiol 54(9):6931–6943
Liu XZ, Fan J, Qi K, Liu SP, Xu WD, Gao Y, Gu XD, Li J, Bai CG, Shi YQ (2017) Dishevelled2 promotes apoptosis and inhibits inflammatory cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through crosstalk with the NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget 8(8):12649
Luo W, Chen J, Li L, Ren X, Cheng T, Lu S, Lawal RA, Nie Q, Zhang X, Hanotte O (2019) c-Myc inhibits myoblast differentiation and promotes myoblast proliferation and muscle fibre hypertrophy by regulating the expression of its target genes, miRNAs and lincRNAs. Cell Death Differ 26(3):426
Maddock D, Burton M (1994) Some effects of starvation on the lipid and skeletal muscle layers of the winter flounder, Pleuronectes americanus. Can J Zool 72(9):1672–1679
Maeda K, Enomoto A, Hara A, Asai N, Kobayashi T, Horinouchi A, Maruyama S, Ishikawa Y, Nishiyama T, Kiyoi H (2016) Identification of Meflin as a potential marker for mesenchymal stromal cells. Sci Rep 6:22288
Meadows E, Cho J-H, Flynn JM, Klein WH (2008) Myogenin regulates a distinct genetic program in adult muscle stem cells. Dev Biol 322(2):406–414
Milan G, Romanello V, Pescatore F, Armani A, Paik J-H, Frasson L, Seydel A, Zhao J, Abraham R, Goldberg AL (2015) Regulation of autophagy and the ubiquitin–proteasome system by the FoxO transcriptional network during muscle atrophy. Nat Commun 6:6670
Nagasawa A, Kubota R, Imamura Y, Nagamine K, Wang Y, Asakawa S, Kudoh J, Minoshima S, Mashima Y, Oguchi Y (1997) Cloning of the cDNA for a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily (ISLR) containing leucine-rich repeat (LRR). Genomics 44(3):273–279
Nagasawa A, Kudoh J, Noda S, Mashima Y, Wright A, Oguchi Y, Shimizu N (1999) Human and mouse ISLR (immunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat) genes: genomic structure and tissue expression. Genomics 61(1):37–43
Pereira JASA, Wessels A, Nijtmans L, Moorman AF, Sargeant AJ (1995) New method for the accurate characterization of single human skeletal muscle fibres demonstrates a relation between mATPase and MyHC expression in pure and hybrid fibre types. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 16(1):21–34
Povsic TJ, Kohout TA, Lefkowitz RJ (2003) β-Arrestin1 mediates insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and anti-apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278(51):51334–51339
Powers SK, Morton AB, Ahn B, Smuder AJ (2016) Redox control of skeletal muscle atrophy. Free Radic Biol Med 98:208–217
Sacco A, Mourkioti F, Tran R, Choi J, Llewellyn M, Kraft P, Shkreli M, Delp S, Pomerantz JH, Artandi SE (2010) Short telomeres and stem cell exhaustion model Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mdx/mTR mice. Cell 143(7):1059–1071
Sacheck JM, Ohtsuka A, McLary SC, Goldberg AL (2004) IGF-I stimulates muscle growth by suppressing protein breakdown and expression of atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases, atrogin-1 and MuRF1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287(4):E591–E601
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C, Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH, Goldberg AL (2004) Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell 117(3):399–412
Sartorelli V, Fulco M (2004) Molecular and cellular determinants of skeletal muscle atrophy and hypertrophy. Sci STKE 2004(244):re11
Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, Panaro F, Timofeyva Y, Kline WO, Gonzalez M, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2004) The IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription factors. Mol Cell 14(3):395–403
Yablonka-Reuveni Z, Paterson BM (2001) MyoD and myogenin expression patterns in cultures of fetal and adult chicken myoblasts. J Histochem Cytochem 49(4):455–462
Zhang Y, Li W, Zhu M, Li Y, Xu Z, Zuo B (2016) FHL3 differentially regulates the expression of MyHC isoforms through interactions with MyoD and pCREB. Cell Signal 28(1):60–73
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Gu L, Lan M, Liu C, Wang M, Su Y, Ge M, Wang T, Yu Y (2018) Islr regulates canonical Wnt signaling-mediated skeletal muscle regeneration by stabilizing Dishevelled-2 and preventing autophagy. Nat Commun 9(1):5129
Zhao W, Pan J, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Bauman WA, Cardozo CP (2008) Testosterone protects against dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy, protein degradation and MAFbx upregulation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 110(1–2):125–129
Funding
This research was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2018JY0488) and the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-40-K06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, CC, SH, and HY; data curation, CC and SH; formal analysis, CC, SH, JZ, and DL; funding acquisition, QZ and HY; investigation, SH, CC, HH, XS, YW, and YC; project administration, YW and HY; resources, HY; supervision, HY; writing—original draft, SH and CC; writing—review and editing, HY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics statement
All experimental procedures in the present study complied with the recommendations of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University, and the study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University (Sichuan, China) under permit number: YCS-2018-10200601.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 21 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, C., Han, S., Shen, X. et al. ISLR regulates skeletal muscle atrophy via IGF1-PI3K/Akt-Foxo signaling pathway. Cell Tissue Res 381, 479–492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03251-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03251-4