Abstract
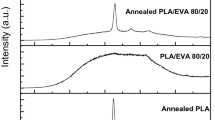
As far as we know, to enhance the toughness of poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) without compromising its inherent biodegradability, melt blending PLLA with flexible biodegradable polymers is the most effective and universal method. However, most of research results show a slight improvement in impact toughness due to the amorphous PLLA matrix. In other words, effective impact toughness can be achieved only if PLLA blend is in a highly crystalline state. In this work, blend of PLLA with 20 wt% PCL was prepared and then samples made by injection molding were applied to thermal annealing at different temperatures for 2 h to increase the crystallinity of PLLA matrix. The results show that the crystallinity of PLLA/PCL blend annealing at 80 °C is exceeding 40% and impact strength of the samples increases from 5.92 KJ/m2 of unannealed neat PLLA to 26.81 KJ/m2. At the same time, the thermal properties are also improved by a large margin.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garlotta D (2001) A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J Polym Environ 9(2):63–84
Anders S, Mikael S (2002) Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog Polym Sci 27(6):1123–1163
Lim LT, Auras R, Rubino M (2008) Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog Polym Sci 33(8):820–852
Baimark Y, Pasee S, Rungseesantivanon W, Prakymoramas N (2019) Flexible and high heat-resistant stereocomplex PLLA-PEG-PLLA/PDLA blends prepared by melt process: effect of chain extension. J Polym Res 26(9):218
Dorgan JR, Williams JS, Lewis DN (1999) Melt rheology of poly(lactic acid): entanglement and chain architecture effects. J Rheol 43(5):1141–1155
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2010) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35(3):338–356
Auras R, Harte B, Selke S (2004) An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol Biosci 4(9):835–864
Drumright RE, Gruber PR, Henton DE (2000) Polylactic acid technology. Adv Mater 12(23):1841–1846
Li H, Michel AH (2007) Effect of nucleation and plasticization on the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 48(23):6855–6866
Menczel JD, Prime RB (2009) Thermal analysis of polymers: fundamentals and applications. Macromol Chem Phys 12(6):131–142
Zhang J, Tashiro K, Tsuji H, Domb AJ (2008) Disorder-to-order phase transition and multiple melting behavior of poly(l-lactide) investigated by simultaneous measurements of WAXD and DSC. Macromolecules 41(4):1352–1357
Jose-Ramon Sarasua PHR-E, Muriel W et al (1998) Crystallization and melting behavior of Polylactides. Macromolecules 31(12):3895–3905
Martin O, Avérous L (2001) Poly(lactic acid): plasticization and properties of biodegradable multiphase systems. Polymer 42(14):6209–6219
Deng L, Xu C, Wang X, Wang Z (2017) Supertoughened Polylactide binary blend with high heat deflection temperature achieved by thermal annealing above the glass transition temperature. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(1):480–490
Oyama HT (2009) Super-tough poly(lactic acid) materials: reactive blending with ethylene copolymer. Polymer 50(3):747–751
Sang ZH, Xie X-L, Zhou S-Y, Li Y, Yan Z, Xu L, Zhong G-J, Li Z-M (2017) Gradient structure of crystalline morphology in injection-molded Polylactide parts tuned by oscillation shear flow and its influence on Thermomechanical performance. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(21):6295–6306
Zhang J, Zhu J, Lei Y, Zeng T, Shen K, Fu Q (2008) Mechanical property, thermal property and crystal structure of isotactic polypropylene samples prepared by vibration injection molding. Polym Bull 59(6):855–864
Zheng L, Geng Z, Zhen W (2019) Preparation, characterization, and reaction kinetics of poly (lactic acid)/amidated graphene oxide nanocomposites based on reactive extrusion process. J Polym Res 26(3):78
Broz ME, VanderHart DL, Washburn NR (2003) Structure and mechanical properties of poly(D,L-lactic acid)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) blends. Biomaterials 24(23):4181–4190
Takayama T, Mitsugu T, Hideto T (2011) Effect of annealing on the mechanical properties of PLA/PCL and PLA/PCL/LTI polymer blends. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4(3):255–260
Takeshi S, Kazuo K, Umaru Semo I, Hiroyuki H (2010) The effect of crosslinking on the mechanical properties of polylactic acid/polycaprolactone blends. J Appl Polym Sci 101(3):1816–1825
Nagarajan V, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2016) Perspective on Polylactic acid (PLA) based sustainable materials for durable applications: focus on toughness and heat resistance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(6):2899–2916
Chen Y, Fan Q, Yang S, Zhang Q, Li Z (2018) Greatly improved toughness of isotactic polypropylene blends with traces of carbon nanotubes. Polym Eng Sci 59(4):757–764
Pan Y, Liu X, Shi S, Liu C, Dai K, Yin R, Schubert DW, Zheng G, Shen C (2016) Annealing induced mechanical reinforcement of injection molded iPP parts. Macromol Mater Eng 301(12):1468–1472
Nagarajan V, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2016) Crystallization behavior and morphology of polylactic acid (PLA) with aromatic sulfonate derivative. J Appl Polym Sci 133(28):43673
Wang F, Xia C, Jin M, Du H, Zhang J (2015) Influences of nucleating agent TMB-5 on crystallization properties of poly(lactic-acid). China Synthetic Resin Plastics 32(6):4–7
Mi D, Liu H, Zhang L, Wang T, Zhang X, Zhang J (2015) The changes of microstructure and physical properties of isotactic polypropylene/β nucleation agent/polyolefin elastomer induced by annealing following processing. J Macromolec Sci Part B 54(11):1376–1390
Yanhui C, Zhiqiang W, Qian F, Song Y, Erchao S, Qiuyu Z (2018) Great toughness reinforcement of isotactic polypropylene/elastomer blends with quasi-cocontinuous phase morphology by traces of β-nucleating agents and carbon nanotubes. Compos Sci Technol 167:277–284
Liu Z, Zheng G, Dai K, Liu C, Shen C (2019) Simultaneously improving tensile strength and toughness of melt-spun -nucleated isotactic polypropylene fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 133(21):43454
Battegazzore D, Bocchini S, Frache A (2011) Crystallization kinetics of poly(lactic acid)-talc composites. Express Polym Lett 5(10):849–858
Liang JZ, Zhou L, Tang CY, Tsui CP (2013) Crystalline properties of poly(L-lactic acid) composites filled with nanometer calcium carbonate. Compos Pt B-Eng 45(1):1646–1650
Liang JZ, Duan DR, Tang CY, Tsui CP, Chen DZ, Zhang SD (2015) Mechanical properties and morphology of poly(l-lactic acid)/Nano-CaCO3Composites. J Polym Environ 23(1):21–29
Frone AN, Berlioz S, Chailan J-F (2013) O.; Panaitescu, D. M., morphology and thermal properties of PLA–cellulose nanofibers composites. Carbohydr Polym 91(1):377–384
Kowalczyk M, Piorkowska E, Kulpinski P, Pracella M (2011) Mechanical and thermal properties of PLA composites with cellulose nanofibers and standard size fibers. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manufact 42(10):1509–1514
Suchaiya V, Aht-Ong D (2013) Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties of MCC/PLA composite Compatibilized with modified cellulose. Adv Mater Res 747:698–702
Bai HW, Zhang WY, Deng H, Zhang Q, Fu QA (2011) Control of crystal morphology in poly(L-lactide) by adding nucleating agent. Macromolecules 44(6):1233–1237
Simmons H, Tiwary P, Colwell JE, Kontopoulou M (2019) Improvements in the crystallinity and mechanical properties of PLA by nucleation and annealing. Polym Degrad Stab 166:248–257
Cocca M, Di Lorenzo ML, Mario M, Vincenzo F (2011) Influence of crystal polymorphism on mechanical and barrier properties of poly(l-lactic acid). Eur Polym J 47(5):1073–1080
Gu X, Zhou M, Wang Y, Zhang J (2019) Influence of annealing on the morphology and mechanical properties of iPP/HDPE blend with tailored oriented crystalline structures. J Polym Res 26(8):194
Eling B, Gogolewski S, Pennings AJ (1982) Biodegradable materials of poly(l-lactic acid): 1. Melt-spun and solution-spun fibres. Polymer 23(11):1587–1593
Liu M, Hong R, Gu X, Fu Q, Zhang J (2019) Remarkably improved impact fracture toughness of isotactic polypropylene via combining the effects of shear layer-Spherulites layer alternated structure and thermal annealing. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(32):15069–15078
Puiggali J, Ikada Y, Tsuji H, Cartier L, Okihara T, Lotz B (2000) The frustrated structure of poly(L-lactide). Polymer 41(25):8921–8930
Mi D, Hou F, Zhou M, Zhang J (2018) Improving the mechanical and thermal properties of shish-kebab via partial melting and re-crystallization. Eur Polym J 101:1–11
Bai H, Xiu H, Gao J, Deng H, Zhang Q, Yang M, Fu Q (2012) Tailoring impact toughness of poly(L-lactide)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PLLA/PCL) blends by controlling crystallization of PLLA matrix. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(2):897–905
Liu H, Chen F, Liu B, Estep G, Zhang J (2010) Super toughened poly(lactic acid) ternary blends by simultaneous dynamic vulcanization and interfacial Compatibilization. Macromolecules 43(14):6058–6066
Pan P, Kai W, Zhu B, Dong T, Inoue YY (2007) Polymorphous crystallization and multiple melting behavior of poly(l-lactide): molecular weight dependence. Macromolecules 40(19):6898–6905
Jalali A, Shahbikian S, Huneault MA, Elkoun S d (2017) Effect of molecular weight on the shear-induced crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Polymer 112:393–401
Nagarajan V, Zhang K, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2015) Overcoming the fundamental challenges in improving the impact strength and Crystallinity of PLA biocomposites: influence of nucleating agent and Mold temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(21):11203–11214
Sakai F, Nishikawa K, Inoue Y, Yazawa K (2009) Nucleation enhancement effect in poly(L-lactide) (PLLA)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) blend induced by locally activated chain mobility resulting from limited miscibility. Macromolecules 42(21):8335–8342
Lauritzen JI (1973) Extension of theory of growth of chain-folded polymer crystals to large undercoolings. J Appl Phys 44(10):4340–4352
Bai H, Huang C, Xiu H, Gao Y, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2013) Toughening of poly(l-lactide) with poly(ε-caprolactone): combined effects of matrix crystallization and impact modifier particle size. Polymer 54(19):5257–5266
Zhang X, Meng L, Li G, Liang N, Rui W (2016) Effect of nucleating agents on the crystallization behavior and heat resistance of poly(L-lactide). J Appl Polym Sci 133(8):42999
Ran XH, Jia ZY, Yang YM, Dong LS (2010) Flexible plasticized PLA with high crystallinity obtained by controlling the annealing temperature. e-Polymers 10(1):7
Acknowledgments
The authors genuinely appreciate the financial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21627804) and State Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials Engineering (No. sklpme2019-2-18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Deng, C., Hong, R. et al. Effect of thermal annealing on crystal structure and properties of PLLA/PCL blend. J Polym Res 27, 221 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02206-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02206-1