Abstract
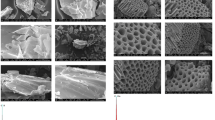
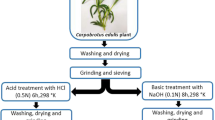
Wild carob (WC), an abundant and unused lignocellulosic waste in Algeria, has been used as an inexpensive biosorbent for the elimination of methylene blue (MB) from the aqueous solution and as a precursor for the preparation of a new activated carbon by chemical activation with ZnCl2 (ACWC). The adsorbent materials were characterized by N2 physisorption, SEM/EDX, FTIR spectroscopy and isoelectric point (pHpzc) measurements. The adsorption performance of WC and ACWC was estimated for MB at different adsorption variables, such as solution pH (2–11), MB initial concentrations (25–200 mg L−1), time (0–1500 min), adsorbent dose (0.25–2.00 g L−1), temperature (10–40 °C) and NaCl concentration (0.0–0.5 M). The obtained results indicate that WC has an acidic surface due to the presence of carboxyl and phenol groups that play an important role in the fixation of cationic dye molecules, obtaining a maximum monolayer adsorption capacity of 84 mg g−1 at natural pH (7.5) and 40 °C. However, this adsorption performance was much higher in the case of the ACWC sample (218 mg g−1). From the equilibrium data, the Freundlich, Langmuir, Sips and Redlich–Peterson isotherms parameters of both samples were calculated and compared. For WC, the experimental data fitted well with Redlich–Peterson, Langmuir and Sips isotherm models, while in the case of ACWC they were best represented by the Redlich–Peterson and Sips isotherms. The adsorption kinetics data were found to follow the pseudo-second-order model for WC and the pseudo-first-order model for ACWC. The thermodynamic parameters suggest that, for both materials, the process was endothermic and spontaneous in the range of temperatures studied.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lairini, S.; El Mahtal, K.; Miyah, Y.; Tanji, K.; Guissi, S.; Boumchita, S.; Zerrouq, F.: The adsorption of Crystal violet from aqueous solution by using potato peels (Solanum tuberosum): equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 8, 3252–3261 (2017)
Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, I.: Insight into adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of Malachite Green onto clayey soil of Indian origin. Chem. Eng. J. 165, 874–882 (2010)
Banerjee, S.; Sharma, G.C.; Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Sharma, Y.C.: Removal of Malachite Green, a hazardous dye from aqueous solutions using Avena sativa (oat) hull as a potential adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 213, 162–172 (2016)
Amode, J.O.; Santos, J.H.; Md. Alam, Z.; Mirza, A.H.; Mei, C.C.: Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution using untreated and treated (Metroxylon spp.) waste adsorbent: equilibrium and kinetics studies. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 7, 333–345 (2016)
Miyah, Y.; Lahrichi, A.; Idrissi, M.; Boujraf, S.; Taouda, H.; Zerrouq, F.: Assessment of adsorption kinetics for removal potential of Crystal Violet dye from aqueous solutions using Moroccan pyrophyllite. J. Assoc. Arab. Univ. Basic. Appl. Sci. 23, 20–28 (2017)
Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P.: Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 77, 247–255 (2001)
Güzel, F.; Sayǧili, H.; Sayǧili, G.A.; Koyuncu, F.: Decolorisation of aqueous crystal violet solution by a new nanoporous carbon: equilibrium and kinetic approach. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 3375–3386 (2014)
Khan, T.A.; Sharma, S.; Ali, I.; Khan, T.A.; Sharma, S.; Ali, I.: Adsorption of Rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution onto acid activated mango (Magnifera indica) leaf powder: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Sci. 3, 286–297 (2011)
Jain, S.; Jayaram, R.V.: Removal of basic dyes from aqueous solution by low-cost adsorbent: wood apple shell (Feronia acidissima). Desalination 250, 921–927 (2010)
Miyah, Y.; Idrissi, M.; Zerrouq, F.: Etude et Modélisation de la Cinétique d’Adsorption du Bleu de Méthylène sur les Adsorbants Argileux (Pyrophillite, Calcite) [Study and Modeling of the Kinetics Methylene blue Adsorption on the Clay Adsorbents (Pyrophillite, Calcite)]. J. Mater. Environ. Sc. 6, 699–712 (2015)
Mohammed, M.A.; Shitu, A.; Ibrahim, A.: Removal of methylene blue using low cost adsorbent: a review. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 4, 91–102 (2014)
Alizadeh, A.; Parizanganeh, A.; Yaftian, M.; Zamani, A.: Application of cellulosic biomass for removal of cationic dye rhodamine 6G from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Waste. Resour. 6, 256 (2016)
Mane, V.S.; Vijay Babu, P.V.: Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the removal of Congo red from aqueous solution using Eucalyptus wood (Eucalyptus globulus) sawdust. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 44, 81–88 (2013)
Ahmad, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Chuong, C.S.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumard, R.; Rafatullah, M.: Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv. 5, 30801–30818 (2015)
Ghaedi, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Kokhdan, S.N.: Multiwalled carbon nanotubes as adsorbents for the kinetic and equilibrium study of the removal of Alizarin red S and morin. J. Chem. Eng. Data 56, 2511–2520 (2011)
Shayesteh, H.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A.; Norouzbeigi, R.: Adsorption of malachite green and crystal violet cationic dyes from aqueous solution using pumice stone as a low-cost adsorbent: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 12822–12831 (2016)
Talarposhti, A.M.; Donnelly, T.; Anderson, G.K.: Colour removal from a simulated dye wastewater using a two-phase anaerobic packed bed reactor. Water Res. 35, 425–432 (2001)
Aydin, H.; Baysal, G.; Bulut, Y.: Utilization of walnut shells (Juglans regia) as an adsorbent for the removal of acid dyes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2, 141–150 (2009)
Priya, R.; Nithya, R.; Anuradha, R.; Kamachi, T.: Removal of colour from crystal violet dye using low cost adsorbents. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 6, 4346–4351 (2014)
Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M.: Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pine cone biomass of Pinus radiate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 218, 499–515 (2011)
Chowdhury, S.; Saha, P.: Sea shell powder as a new adsorbent to remove Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 164, 168–177 (2010)
Wang, B.E.; Hu, Y.Y.; Xie, L.; Peng, K.: Biosorption behavior of azo dye by inactive CMC immobilized Aspergillus fumigatus beads. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 794–800 (2008)
Saygili, H.; Güzel, F.; Önal, Y.: Conversion of grape industrial processing waste to activated carbon sorbent and its performance in cationic and anionic dyes adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 93, 84–93 (2015)
Liu, C.H.; Wu, J.S.; Chiu, H.C.; Suen, S.Y.; Chu, K.H.: Removal of anionic reactive dyes from water using anion exchange membranes as adsorbers. Water Res. 41, 1491–1500 (2007)
Gündüz, F.; Bayrak, B.: Biosorption of malachite green from an aqueous solution using pomegranate peel: equilibrium modelling, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 243, 790–798 (2017)
Nacke, H.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Coelho, G.F.; Schwantes, D.; Campagnolo, M.A.; Leismann, E.A.V.; Junior, E.C.; Miola, A.J.: Removal of Cd (II) from water using the waste of jatropha fruit (Jatropha curcas L.). Appl. Water Sci. 7, 3207–3222 (2017)
Bounaas, M.; Bouguettoucha, A.; Chebli, D.; Reffas, A.; Harizi, I.; Rouabah, F.; Amrane, A.: High efficiency of methylene blue removal using a novel low-cost acid treated forest wastes, Cupressus semperirens cones: experimental results and modeling. Part. Sci. Technol. 37, 500–509 (2019)
Reffas, A.; Bouguettoucha, A.; Chebli, D.; Amrane, A.: Adsorption of ethyl violet dye in aqueous solution by forest wastes, wild carob. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 9859–9870 (2016)
Grassi, P.; Reis, C.; Drumm, F.C.; Georgin, J.; Tonato, D.; Escudero, L.B.; Kuhn, R.; Jahn, S.L.; Dotto, G.L.: Biosorption of crystal violet dye using inactive biomass of the fungus Diaporthe schini. Water Sci. Technol. 79(4), 709–717 (2019)
Bounaas, M.; Bouguettoucha, A.; Chebli, D.; Reffas, A.; Gatica, J.M.; Amrane, A.: Batch adsorption of synthetic dye by Maclura Pomifera, a new eco-friendly waste biomass: experimental studies and modeling. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2018-0063
Sulaka, M.T.; Yatmaz, H.C.: Removal of textile dyes from aqueous solutions with eco-friendly biosorbent. Desalin. Water Treat. 37, 169–177 (2012)
Radhakrishnana, K.; Sethuramana, L.; Panjanathana, R.; Natarajana, A.; Solaiappan, V.; Thilagaraja, W.R.: Biosorption of heavy metals from actual electroplating wastewater using encapsulated Moringa oleifera beads in fixed bed column. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 3572–3587 (2014)
Haydar, S.; Ahmad, M.F.; Hussain, G.: Evaluation of new biosorbents prepared from immobilized biomass of Candida sp. for the removal of nickel ions. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(12), 5601–5613 (2015)
Sadaf, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nausheen, S.; Noreen, S.: Potential use of low-cost lignocellulosic waste for the removal of direct violet 51 from aqueous solution: equilibrium and breakthrough studies. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 66, 557–571 (2014)
Sadaf, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nausheen, S.; Amin, M.: Application of a novel lignocellulosic biomaterial for the removal of Direct Yellow 50 dye from aqueous solution: batch and column study. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 47, 160–170 (2015)
Alomaa, I.C.; Rodrıgueza, I.; Calerob, M.; Blazquezb, G.: Biosorption of Cr6 + from aqueous solution by sugarcane bagasse. Desalin. Water Treat. 59(31–33), 5912–5922 (2013)
Ferreira, R.M.; Oliveira, N.M.; Lima, L.L.S.; Campista, A.L.D.M.; Stapelfeldt, D.M.A.: Adsorption of indigo carmine on Pistia stratiotes dry biomass chemically modified. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26, 28614–28621 (2019)
Din, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Yasir, M.; Ashraf, A.: Direct dye biosorption by immobilized barley husk. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 9263–9271 (2016)
Zhanga, Y.Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Bian, W.; Li, Y.; Wanga, X.: Adsorption behavior of modified Iron stick yam skin with Polyethyleneimine as a potential biosorbent for the removal of anionic dyes in single and ternary systems at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 222, 285–293 (2016)
Yang, J.X.; Hong, G.B.: Adsorption behavior of modified Glossogyne tenuifolia leaves as a potential biosorbent for the removal of dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 252, 289–295 (2018)
Deng, H.; Yang, L.; Tao, G.; Dai, J.: Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from cotton stalk by microwave assisted chemical activation-Application in methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 1514–1521 (2009)
Msaada, A.; Belbahloula, M.; El Hajjajib, S.; Beakoua, B.H.; Houssainia, M.A.; Belhajjiaa, C.; Aassilac, H.; Zouhria, A.; Anouara, A.: Industrial wastewater decolorization by activated carbon from Ziziphus lotus. Desalin. Water Treat. 126, 296–305 (2018)
Senthilkumaar, S.; Varadarajan, P.R.; Porkodi, K.; Subbhuraam, C.V.: Adsorption of methylene blue onto jute fiber carbon: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 284, 78–82 (2005)
Amin, M.T.; Alazba, A.A.; Shafiq, M.: Comparative study for adsorption of methylene blue dye on biochar derived from orange peel and banana biomass in aqueous solutions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 191, 735 (2019)
Sun, Z.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Liang, J.; Duan, X.: Preparation and characterization of shiitake mushroom-based activated carbon with high adsorption capacity. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 5443–5456 (2019)
Bengoa, C.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J.; Stöber, F.: Reduction, Modification and Valorisation of Sludge (REMOVALS). IWA Publishing, London (2011)
Bandara, J.; Mielczarski, J.A.; Kiwi, J.: Molecular mechanism of surface recognition. Azo dyes degradation on Fe, Ti, and Al oxides through metal sulfonate complexes. Langmuir 15, 7670–7679 (1999)
Stavropoulos, G.G.: Precursor materials suitability for super activated carbons production. Fuel Process. Technol. 86, 1165–1173 (2005)
Budinova, T.K.; Petrov, N.V.; Minkova, V.N.; Gergova, K.M.: Removal of metal ions from aqueous solution by activated carbons obtained from different raw materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 60, 177–182 (1994)
Escudero, C.; Gabaldón, C.; Marzal, P.; Villaescusa, I.: Effect of EDTA on divalent metal adsorption onto grape stalk and exhausted coffee wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 152, 476–485 (2008)
Azouaou, N.; Sadaoui, Z.; Djaafri, A.; Mokaddem, H.: Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution onto untreated coffee grounds: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 184, 126–134 (2010)
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1403 (1918)
Freundlich, H.M.: Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 57, 385–470 (1906)
Dotto, G.L.; Vieira, M.L.G.; Esquerdo, V.M.; Pinto, L.A.A.: Equilibrium and thermodynamics of azo dyes biosorption onto Spirulina platensis. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 30, 13–21 (2013)
Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L.: A useful Adsorption Isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 63, 1024–1026 (1959)
Rouquerol, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.: Interpretation of physisorption isotherms at the gas-solid interface. In: Rouquerol, F., Rouquerol, J., Sing, K. (eds.) Adsorption by powders and porous solids, pp. 93–115. Academic Press, London (1999)
Stavropoulos, G.G.; Zabaniotou, A.A.: Production and characterization of activated carbons from olive-seed waste residue. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 82, 79–85 (2005)
Djilani, C.; Zaghdoudi, R.; Modarressi, A.; Rogalski, M.; Djazi, F.; Lallam, A.: Elimination of organic micropollutants by adsorption on activated carbon prepared from agricultural waste. Chem. Eng. J. 189, 203–212 (2012)
Ozdemir, I.; Şahin, M.; Orhan, R.; Erdem, M.: Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from grape stalk by zinc chloride activation. Fuel Process. Technol. 125, 200–206 (2014)
Marrakchi, F.; Ahmed, M.J.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H.: Mesoporous-activated carbon prepared from chitosan flakes via single-step sodium hydroxide activation for the adsorption of methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 98, 233–239 (2017)
Djilani, C.; Zaghdoudi, R.; Djazi, F.; Bouchekimad, B.; Lallame, A.; Modarressif, A.; Rogalski, M.: Adsorption of dyes on activated carbon prepared from apricot stones and commercial activated carbon. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 53, 112–121 (2015)
Liou, T.H.: Development of mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Chem. Eng. J. 158, 129–142 (2010)
Durán-Valle, C.J.; Gómez-Corzo, M.; Pastor-Villegas, J.; Gómez-Serrano, V.: Study of cherry stones as raw material in preparation of carbonaceous adsorbents. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 73, 59–67 (2005)
Liang, S.; Guo, X.; Feng, N.; Tian, Q.: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Cu2+ from aqueous solutions by Mg2+/K+ type orange peel adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 756–762 (2010)
Park, S.H.; McClain, S.; Tian, Z.R.; Suib, S.L.; Karwacki, C.: Surface and bulk measurements of metals deposited on activated carbon. Chem. Mater. 9, 176–183 (1997)
Njoku, V.O.; Hameed, B.H.: Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from corncob by chemical activation with H3PO4for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 173, 391–399 (2011)
Daoud, M.; Benturki, O.; Kecira, Z.; Girods, P.; Donnot, A.: Removal of reactive dye (BEZAKTIV Red S-MAX) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated carbons prepared from date palm rachis and jujube stones. J. Mol. Liq. 243, 799–809 (2017)
Zawadzki, J.: IR spectroscopic investigations of the mechanism of oxidation of carbonaceous films with HNO3 solution. Carbon 18, 281–285 (1980)
Socrates, G.: Infrared and raman characteristic group frequencies, 3rd edn. Chichester, New York (1994)
Moreno-Castilla, C.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Mueden, A.: The creation of acid carbon surfaces by treatment with (NH4)2S2O8. Carbon N. Y. 35, 1619–1626 (1997)
Ahmad, A.L.; Loh, M.M.; Aziz, J.A.: Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from oil palm wood and its evaluation on Methylene blue adsorption. Dye Pigment 75, 263–272 (2007)
Cengiz, G.; Aytar, P.; Şam, M.; Çabuk, A.: Removal of reactive dyes using magnetically separable trametes versicolor cells as a new composite biosorbent. Sep. Sci. Technol. 49, 1860–1871 (2014)
Albarelli, J.Q.; Rabelo, R.B.; Santos, D.T.; Beppu, M.M.; Meireles, M.A.A.: Effects of supercritical carbon dioxide on waste banana peels for heavy metal removal. J. Supercrit. Fluids 58(3), 343–351 (2011)
Khanday, W.A.; Marrakchi, F.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H.: Mesoporous zeolite–activated carbon composite from oil palm ash as an effective adsorbent for methylene blue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 70, 32–41 (2017)
Hameed, B.H.: Evaluation of papaya seeds as a novel non-conventional low-cost adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 162, 939–944 (2009)
Patil, A.K.; Shrivastava, V.S.: Alternanthera bettzichiana plant powder as low cost adsorbent for removal of congo red from aqueous solution. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2, 842–850 (2010)
Dahri, M.K.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, L.B.L.: Water remediation using low cost adsorbent walnut shell for removal of malachite green: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamic and regeneration studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2, 1434–1444 (2014)
Hu, Y.; Guo, T.; Ye, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.: Dye adsorption by resins: effect of ionic strength on hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 392–397 (2013)
Khattri, S.D.; Singh, M.K.: Removal of malachite green from dye wastewater using neem sawdust by adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 167, 1089–1094 (2009)
Cherifi, H.; Bentahar, F.; Hanini, S.: Kinetic studies on the adsorption of methylene blue onto vegetal fiber activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 282, 52–59 (2013)
Tan, I.A.W.; Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.L.: Equilibrium and kinetic studies on basic dye adsorption by oil palm fibre activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 127, 111–119 (2007)
Milonjić, S.K.: A consideration of the correct calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 72, 1363–1367 (2007)
Canzano, S.; Iovino, P.; Salvestrini, S.; Capasso, S.: Comment on “Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design”. Water Res. 46, 4314–4315 (2012)
Myers, D.: Surfaces, interfaces, and colloids: principles and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH, New York (1999)
Shermanhsu, C.P.: Infrared spectroscopy. Handbook of Instrumental Techniques for Analytical Chemistry. Prentice Hall, Frank Settle (1997)
Xiong, L.; Yang, Y.; Mai, J.X.; Sun, W.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wei, D.P.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J.R.: Adsorption behavior of methylene blue onto titanate nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 156, 313–320 (2010)
Ai, L.H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Liao, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Meng, L.Y.; Jiang, J.: Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with magnetite loaded multi-wall carbon nanotube: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 198, 282–290 (2011)
Aygün, A.; Yenisoy-Karakaş, S.; Duman, I.: Production of granular activated carbon from fruit stones and nutshells and evaluation of their physical, chemical and adsorption properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 66, 189–195 (2003)
Kavitha, D.; Namasivayam, C.: Experimental and kinetic studies on methylene blue adsorption by coir pith carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 14–21 (2007)
Aboua, K.N.; Yobouet, Y.A.; Yao, K.B.; Goné, D.L.; Trokourey, A.: Investigation of dye adsorption onto activated carbon from the shells of Macoré fruit. J. Environ. Manag. 156, 10–14 (2015)
Sharma, Y.C.; Uma, U.S.N.: Removal of a cationic dye from wastewaters by adsorption on activated carbon developed from coconut coir. Energy Fuels 23, 2983–2988 (2009)
Alaya, M.N.; Hourieh, M.A.; Youssef, A.M.; El-Sejariah, F.: Adsorption properties of activated carbons prepared from olive stones by chemical and physical activation. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 18, 27–42 (2000)
Fu, K.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.: Preparation, characterization and application of lignin-based activated carbon from black liquor lignin by steam activation. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 1074–1082 (2013)
Angin, D.; Altintig, E.; Köse, T.E.: Influence of process parameters on the surface and chemical properties of activated carbon obtained from biochar by chemical activation. Bioresour. Technol. 148, 542–549 (2013)
Bestani, B.; Benderdouche, N.; Benstaali, B.; Belhakem, M.; Addou, Z.: Methylene blue and iodine adsorption onto an activated desert plant. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 8441–8444 (2008)
Başar, C.A.: Applicability of the various adsorption models of three dyes adsorption onto activated carbon prepared waste apricot. J. Hazard. Mater. 135, 232–241 (2006)
Wenhong, L.; Qinyan, Y.; Peng, T.; Zuohao, M.; Baoyu, G.; Jinze, L.; Xing, X.: Adsorption characteristics of dyes in columns of activated carbon prepared from paper mill sewage sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 178, 197–203 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Directorate General for Scientific Research and Technological Development (DGRSDT) of Algeria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bounaas, M., Bouguettoucha, A., Chebli, D. et al. Role of the Wild Carob as Biosorbent and as Precursor of a New High-Surface-Area Activated Carbon for the Adsorption of Methylene Blue. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 325–341 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04739-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04739-5