Abstract
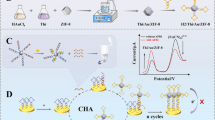
An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor was established based on the Zn-MOF/GO nanocomposite. Ag(I)-embedded DNA complexes were used as a signal amplification reagent. In this work, 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin (TCPP) and Zn2+ were integrated into a porphyrin paddlewheel framework (Zn-MOF) by a hydrothermal method. The synthesized Zn-MOF material has electrochemiluminescence property, and the luminescence intensity is improved after being composited with graphene oxide (GO). Based on the composite material, we constructed an ultrasensitive ECL biosensor for the p53 antibody detection. The composite material acted as an admirable substrate and then loaded plenty of p53 antigens to recognize the target (p53 antibody) accurately. Because of the bridging effect of streptavidin and biotin-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (bio-ab2), the rich-C DNA with positive correlation with the target was modified on the electrode and then captured the co-reactant accelerator Ag+ to amplify the signal. Therefore, the ECL biosensor response increases with increasing p53 antibody concentration. In the range 0.1 fg/mL–0.01 ng/mL, the response signal of the biosensor has a good linear relationship with the p53 antibody concentration. The detection limit is 0.03 fg/mL (S/N = 3). Impressively, the biosensor not only featured high sensitivity, good stability, and excellent specificity for the detection of p53 antibody, but also provides a new way for early detection of cancer.

Schematic representation of the electrochemiluminescence sensor based on a Zn-MOF/GO nanocomposite, which can be applied to the determination of p53 antibody.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108
Yeo JC, Park JY, Bae WJ, Lee YS, Kim BH (2009) Label-free electrochemical detection of the p53 core domain protein on its antibody immobilized electrode. Anal Chem 81:4770–4777
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ (2000) Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408:307–310
Yang LL, Tao YZ, Yue GY, Li RB, Qiu B, Guo LH, Lin ZY, Yang H (2016) Highly selective and sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for p53 DNA sequence based on nicking endonuclease assisted target recycling and hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Anal Chem 88:5097–5103
Lane DP (1992) Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 358:15–16
Schlichtholz B (1992) The immune response to p53 in breast cancer patients is directed against immunodominant epitopes unrelated to the mutational hot spot. Cancer Res 52:6380–6384
Winter SF (1992) Development of antibodies against p53 in lung cancer patients appears to be dependent on the type of p53 mutation. Cancer Res 52:4168–4174
Atta MM, El-Masry SA, Abdel-Hameed M, Baiomy HA, Ramadan NE (2008) Value of serum anti-p53 antibodies as a prognostic factor in Egyptian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Biochem 41:1131–1139
Anderson KS, Wong J, Vitonis A, Crum CP, Sluss PM, Labaer J, Cramer D (2010) P53 autoantibodies as potential detection and prognostic biomarkers in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 19:859–868
Lubin R, Zalcman G, Bouchet L, Tredanel J, Legros Y, Cazals D, Hirsch A, Soussi T (1995) Serum p53 antibodies as early markers of lung cancer. Nat Med 1:701–702
Mudenda B, Green JA, Green B, Jenkins JR, Robertson L, Tarunina M, Leinster SJ, The relationship between serum p53 autoantibodies and characteristics of human breast cancer (1994) Br J Cancer 69:1115–1119
Portefaix J, Fanutti C, Granier C, Crapez E, Perham R, Grenier J, Pau B, Del Rio M (2002) Detection of anti-p53 antibodies by ELISA using p53 synthetic or phage-displayed peptides. J Immunol Methods 259:65–75
Elshafey R, Siaj M, Tavares AC (2016) Au nanoparticle decorated graphene nanosheets for electrochemical immunosensing of p53 antibodies for cancer prognosis. Analyst 141:2733–2740
Ge JJ, Zhao Y, Gao XS, Li HK, Jie GF (2019) Versatile electrochemiluminescence and photoelectrochemical detection of glutathione using Mn2+ substitute target by DNA walker-induced allosteric switch and signal amplification. Anal Chem 91:14117–14124
Ge JJ, Zhao Y, Li CL, Jie GF (2019) Versatile electrochemiluminescence and electrochemical “on−off” assays of methyltransferases and aflatoxin B1 based on a novel multifunctional DNA nanotube. Anal Chem 91:3546–3554
Wang J, Zhuo Y, Zhou Y, Wang HJ, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2016) Ceria doped zinc oxide nanoflowers enhanced luminol-based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for amyloid-β detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:12968–12975
Ke H, Sha H, Wang Y, Guo W, Zhang X, Wang Z, Huang C, Jia N (2017) Electrochemiluminecence resonance energy transfer system between GNRs and Ru(bpy)32+: application in magnetic aptasensor for β-amyloid. Biosens Bioelectron 100:266–273
Wen W, Yan X, Zhu C, Du D, Lin Y (2017) Recent advances in electrochemical immunosensors. Anal Chem 89:138–156
Hu GB, Xiong CY, Liang WB, Zeng XS, Xu HL, Yang Y, Yao LY, Yuan R, Xiao DR (2018) Highly stable mesoporous luminescence-functionalized MOF with excellent electrochemiluminescence property for ultrasensitive immunosensor construction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:15913–15919
Cho KG, Lee JI, Lee S, Hong KY, Kang MS, Lee KH (2020) Light-emitting devices based on electrochemiluminescence gels. Adv Funct Mater 2020:1907936
Babamiri B, Bahari D, Salimi A (2020) Highly sensitive bioaffinity electrochemiluminescence sensors: recent advances and future directions. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111530
Valenti G, Rampazzo E, Kesarkar S, Genovese D, Fiorani A, Zanut A, Palomba F, Marcaccio M, Paolucci F, Prodi L (2018) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from metal complexes-based nanoparticles for highly sensitive sensors applications. Coord Chem Rev 367:65–81
Hou LL, Zhou BB (2019) Electrochemiluminescent biosensors for the detection of microRNAs: a review. Int J Electrochem Sci 14:2489–2508
Abednatanzi S, Derakhshandeh PG, Depauw H, Coudert FX, Vrielinck H, Voort PVD, Leus K (2019) Mixed-metal metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 48:2497–2658
Lin X, Jia JH, Zhao XB, Thomas KM, Blake AJ, Walker GS, Champness NR (2010) High H2 adsorption by coordination-framework materials. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 118:7518–7524
Li JR, Kuppler RJ, Zhou HC (2009) Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 38:1477–1504
Liu Q, Yang Y, Liu XP, Wei YP, Mao CJ, Chen JS, Niu HL, Song JM, Zhang SY, Jin BK, Jiang M (2016) A facile in situ synthesis of MIL-101-CdSe nanocomposites for ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:1073–1078
Murray LJ, Dinca M, Long JR (2009) Hydrogen storage in metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 38:1294–1314
Dong X, Zhao G, Liu L, Li X, Wei Q, Cao W (2018) Ultrasensitive competitive method-based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for diethylstilbestrol detection based on Ru(bpy)32+, as luminophor encapsulated in metal–organic frameworks UiO-67. Biosens Bioelectron 110:201–206
Zhao GH, Wang YG, Li XJ, Yue Q, Dong X, Du B, Cao W, Wei Q (2019) Dual-quenching electrochemiluminescence strategy based on three-dimensional metal−organic frameworks for ultrasensitive detection of amyloid-β. Anal Chem 91:1989–1996
Luo D, Huang B, Wang L, Idris AM, Wang SX, Lu XQ (2015) Cathodic electrochemiluminescence of meso-tetra(4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin/potassium peroxydisulfate system in aqueous media. Electrochim Acta 151:42–49
Zhao YM, Ling J, Li SG, Li M, Liu AR, Liu SQ (2018) Synthesis of porphyrin-based two-dimensional metal–organic framework nanodisk with small size and few layers. J Mater Chem A 6:2828–2833
Ge JJ, Li CL, Zhao Y, Yu XJ, Jie GF (2019) Versatile “on–off” biosensing of thrombin and miRNA based on Ag(I) ion-enhanced or Ag nanocluster-quenched electrochemiluminescence coupled with hybridization chain reaction amplification. Chem Commun 55:7350–7353
Ye L, Gao Y, Cao SY, Chen H, Yao YN, Hou JG, Sun LC (2018) Assembly of highly efficient photocatalytic CO2 conversion systems with ultrathin two-dimensional metal–organic framework nanosheets. Appl Catal B Environ 227:54–60
Jahan M, Bao QL, Loh KP (2012) Electrocatalytically active graphene–porphyrin MOF composite for oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc 134:6707–6713
Sadeghi N, Sharifnia S, Sheikh Arabi M (2016) A porphyrin-based metal organic framework for high rate photoreduction of CO2 to CH4 in gas phase J CO2 Util. 16: 450–457
Wang X, Wang QX, Wang QH, Gao F, Yang YZ, Guo HX (2014) Highly dispersible and stable copper terephthalate metal−organic framework−graphene oxide nanocomposite for an electrochemical sensing application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:11573–11580
Ang HX, Hong L (2017) Polycationic polymer-regulated assembling of 2D MOF nanosheets for high-performance nanofiltration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:28079–28088
Liu M, Xie K, Nothling MD, Gurr PA, Tan SSL, Fu Q, Webley PA, Qiao GG (2018) Ultrathin metal-organic framework nanosheets as a gutter layer for flexible composite gas separation membranes. ACS Nano 12:11591–11599
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21976001), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1808085QB53), and open fund for Discipline Construction of Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The protocol of this study was approved by the medical ethics committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. Human Serum Samples were also provided by The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The blood samples (2 mL) of the participants were collected after informed written consent was provided by the subjects.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3258 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Yp., Zhang, Yw., Chen, JS. et al. An electrochemiluminescence biosensor for p53 antibody based on Zn-MOF/GO nanocomposite and Ag+-DNA amplification. Microchim Acta 187, 455 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04425-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04425-1