Abstract
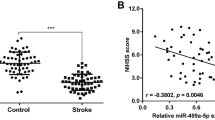
Ischemic stroke is characterized by loss of brain function because of cerebral ischemia. Evidence has been shown that miR-217-5p is significantly downregulated in infarcted brain areas following focal cerebral ischemia. However, the role of miR-217-5p in ischemic stroke is still unclear. To mimic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury conditions in vitro, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R). Our data found that PTEN was the directly target of miR-217-5p in SH-SY5Y cells. The level of miR-217-5p was significantly decreased, while the level of PTEN was notably increased in SH-SY5Y cells following OGD/R treatment. Overexpression of miR-217-5p markedly promoted the proliferation and cell cycle progression, and inhibited apoptosis in OGD/R-treated SH-SY5Y cells. In addition, overexpression of miR-217-5p significantly decreased the expressions of PTEN and FOXO1, but increased the expression of p-Akt in OGD/R-treated SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, methylation specific PCR (MSP) results indicated the CpG islands in the promoter region of miR-217-5p were hypermethylated in SH-SY5Y cells under OGD/R. Meanwhile, the DNA methylation of miR-217-5p promoter region decreased expression of miR-217-5p. Our data indicated that miR-217-5p could attenuate ischemic injury by inhibiting PTEN. In addition, DNA methylation-mediated silencing of miR-217-5p may serve as a promising therapeutic target of ischemic stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han B, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Chen X, Huang R, et al. Novel insight into circular RNA HECTD1 in astrocyte activation via autophagy by targeting MIR142-TIPARP: implications for cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy. 2018;14(7):1164–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1458173.
Jiang D, Sun X, Wang S, Man H. Upregulation of miR-874-3p decreases cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by directly targeting BMF and BCL2L13. Biomed Pharmacother (Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie). 2019;117:108941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108941.
Du K, Zhao C, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhang K-Z, Shen X-Y, et al. MiR-191 inhibit angiogenesis after acute ischemic stroke targeting VEZF1. Aging. 2019;11(9):2762–86. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101948.
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DWJ, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet (London, England). 2016;387(10029):1723–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X.
Xing B, Chen H, Zhang M, Zhao D, Jiang R, Liu X, et al. Ischemic postconditioning inhibits apoptosis after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Stroke. 2008;39(8):2362–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.507939.
Zhao H, Han Z, Ji X, Luo Y. Epigenetic regulation of oxidative stress in ischemic stroke. Aging Dis. 2016;7(3):295–306. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2015.1009.
Jhelum P, Karisetty BC, Kumar A, Chakravarty S. Implications of epigenetic mechanisms and their targets in cerebral ischemia models. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(6):815–30. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X14666161213143907.
Portela A, Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(10):1057–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1685.
Shivakumar M, Lee Y, Bang L, Garg T, Sohn K-A, Kim D. Identification of epigenetic interactions between miRNA and DNA methylation associated with gene expression as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer. BMC Med Genom. 2017;10(Suppl 1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-017-0269-y.
Oltra SS, Peña-Chilet M, Vidal-Tomas V, Flower K, Martinez MT, Alonso E, et al. Methylation deregulation of miRNA promoters identifies miR124-2 as a survival biomarker in breast cancer in very young women. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32393-3.
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C. Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol. 2018;9:402. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00402.
Ge X-L, Wang J-L, Liu X, Zhang J, Liu C, Guo L. Inhibition of miR-19a protects neurons against ischemic stroke through modulating glucose metabolism and neuronal apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0160-2.
Huang L, Ma Q, Li Y, Li B, Zhang L. Inhibition of microRNA-210 suppresses pro-inflammatory response and reduces acute brain injury of ischemic stroke in mice. Exp Neurol. 2018;300:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.10.024.
Xu W, Gao L, Zheng J, Li T, Shao A, Reis C, et al. The roles of MicroRNAs in stroke: possible therapeutic targets. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(12):1778–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689718773361.
Li B, Huang Z, Meng J, Yu W, Yang H. MiR-202-5p attenuates neurological deficits and neuronal injury in MCAO model rats and OGD-induced injury in Neuro-2a cells by targeting eIF4E-mediated induction of autophagy and inhibition of Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Mol Cell Probes. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101497.
Zhou J, Chen L, Chen B, Huang S, Zeng C, Wu H, et al. Increased serum exosomal miR-134 expression in the acute ischemic stroke patients. BMC Neurol. 2018;18(1):198. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1196-z.
Duan X, Gan J, Peng D-Y, Bao Q, Xiao L, Wei L, et al. Identification and functional analysis of microRNAs in rats following focal cerebral ischemia injury. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):4175–84. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10073.
Meller R, Pearson A, Simon RP. Dynamic changes in DNA methylation in ischemic tolerance. Front Neurol. 2015;6:102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00102.
Giordano M, Ciarambino T, D'Amico M, Trotta MC, Di Sette AM, Marfella R, et al. Circulating MiRNA-195-5p and -451a in transient and acute ischemic stroke patients in an emergency department. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020130.
Eyileten CA-O, Wicik ZA-O, De Rosa SA-OX, Mirowska-Guzel D, Soplinska AA-O, Indolfi C, et al. MicroRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in ischemic stroke—a comprehensive review and bioinformatic analysis. Cells. 2018;7(12):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120249.
Wang R, Bao H, Zhang S, Li R, Chen L, Zhu Y. miR-186-5p Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting IGF-1 in SH-SY5Y OGD/R Model. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(13):1791–9. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.25352.
Bai M, Zhang M, Long F, Yu N, Zeng A, Wang X. MiR-217 promotes cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting PTRF. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(2):647–55.
Dai Z, Jin Y, Zheng J, Liu K, Zhao J, Zhang S, et al. MiR-217 promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by targeting DKK1 in steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1112–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.166.
Flum M, Kleemann M, Schneider H, Weis B, Fischer S, Handrick R, et al. miR-217-5p induces apoptosis by directly targeting PRKCI, BAG3, ITGAV and MAPK1 in colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018;12(2):451–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-017-0410-x.
Gao Y, Wang B, Luo H, Zhang Q, Xu M. miR-217 represses TGF-β1-induced airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through targeting ZEB1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.030.
Li W, Gao YQ. MiR-217 is involved in the carcinogenesis of gastric cancer by down-regulating CDH1 expression. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2018;34(7):377–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2018.02.003.
Chai C, Song LJ, Han SY, Li XQ, Li M. MicroRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24(5):369–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12785.
Zheng T, Shi Y, Zhang J, Peng J, Zhang X, Chen K, et al. MiR-130a exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemic stroke through PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109117.
Fu Z, Tindall DJ. FOXOs, cancer and regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 2008;27(16):2312–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.24.
Eijkelenboom A, Burgering BM. FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(2):83–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3507.
Sun K, Huang R, Yan L, Li DT, Liu YY, Wei XH, et al. Schisandrin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by regulating TLR-4 and Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathways. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1104. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01104.
Halder B, Das Gupta S, Gomes A. Black tea polyphenols induce human leukemic cell cycle arrest by inhibiting Akt signaling: possible involvement of Hsp90, Wnt/β-catenin signaling and FOXO1. FEBS J. 2012;279(16):2876–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08668.x.
Li Z, Zhang G, Li D, Jie Z, Chen H, Xiong J, et al. Methylation-associated silencing of miR-495 inhibit the migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PRL-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456(1):344–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.11.083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Z., Shi, Y., Zhao, P. et al. Overexpression of miR-217-5p protects against oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced neuronal injury via inhibition of PTEN. Human Cell 33, 1026–1035 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00396-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00396-w