Abstract
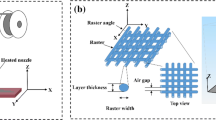
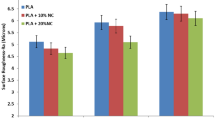
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) is a widely used additive manufacturing process. It utilizes a variety of homogeneous and heterogeneous materials for product development. A new manufacturing process termed as Hybrid Fused Deposition Modelling (HFDM) has been used for the manufacture of various copper metal mesh (99.99% pure)/PLA (polylactic acid or polylactide) plastic composites. These products have been subjected to standardized experimental testing for evaluating properties such as tear resistance, tensile strength, water absorption, hardness, and flexural strength. The tests have been conducted to analyse the effectiveness of the HFDM process in manufacturing stronger composites compared to commercially available PLA and copper-infused PLA. Microstructural characterization has also been carried out to analyse the bond between the plastic and metal mesh layers. The results have been promising and demonstrate the effectiveness of HFDM to produce Cu/PLA composites with superior mechanical properties compared to parent FDM-printed PLA plastic as well as copper-infused FDM-printed PLA. Multiple copper mesh layers have been placed strategically within the test specimens to study their effect on the composites made by HFDM. The experimental results show that the process is capable of manufacturing high-quality composites (Cu/PLA) with tailored properties for various engineering applications.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, X.; Chueh, Y.H.; Wei, C.; Sun, Z.; Yan, J.; Li, L.: Additive manufacturing of three-dimensional metal-glass functionally gradient material components by laser powder bed fusion with in situ powder mixing. Addit. Manuf. 2020(33), 101113 (2020)
Wu, H.; Fahy, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Zhao, N.; Pilato, L.; Kafi, A.; Bateman, S.; Koo, J.H.: Recent developments in polymers/polymer nanocomposites for additive manufacturing. Prog. Mater Sci. 1, 100638 (2010)
Butt, J.; Mebrahtu, H.; Shirvani, H.: Numerical and experimental analysis of product development by composite metal foil manufacturing. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 7(1), 59–82 (2018)
Butt, J.; Mebrahtu, H.; Shirvani, H.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar pure copper foil/1050 aluminium composites made with composite metal foil manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 238, 96–107 (2016)
Nieto, A.; Bisht, A.; Lahiri, D.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, A.: Graphene reinforced metal and ceramic matrix composites: a review. Int. Mater. Rev. 62(5), 241–302 (2017)
Singh, R.; Kumar, R.; Feo, L.; Fraternali, F.: Friction welding of dissimilar plastic/polymer materials with metal powder reinforcement for engineering applications. Compos. B Eng. 101, 77–86 (2016)
Duc, F.; Bourban, P.E.; Plummer, C.J.; Månson, J.A.: Damping of thermoset and thermoplastic flax fibre composites. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 64, 115–123 (2014)
Stavrov, D.; Bersee, H.E.: Resistance welding of thermoplastic composites-an overview. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 36(1), 39–54 (2005)
Biron, M.: Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Composites. William Andrew, Burlington (2018)
Butt, J.; Onimowo, D.A.; Gohrabian, M.; Sharma, T.; Shirvani, H.: A desktop 3D printer with dual extruders to produce customised electronic circuitry. Front. Mech. Eng. 13(4), 528–534 (2018)
Butt, J.; Mebrahtu, H.; Shirvani, H.: Production of multiple material parts using a desktop 3D printer. In: Advances in Manufacturing Technology XXXI: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Manufacturing Research, Incorporating the 32nd National Conference on Manufacturing Research, September 5–7, 2017, University of Greenwich, UK, vol. 6. IOS Press, pp. 148–153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-61499-792-4-148.
Butt, J.; Shirvani, H.: Additive, subtractive, and hybrid manufacturing processes. In: Advances in Manufacturing and Processing of Materials and Structures. CRC Press, pp. 187–218 (2018).
Butt, J.; Mebrahtu, H.; Shirvani, H.: Metal rapid prototyping technologies. In: Petrova, V.M. (ed.) Advances in Engineering Research, vol. 14, pp. 13–52. Nova Science Publishers, New York (2017)
Zhong, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Li, Z.: Short fiber reinforced composites for fused deposition modeling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 301(2), 125–130 (2001)
Shofner, M.L.; Lozano, K.; Rodríguez-Macías, F.J.; Barrera, E.V.: Nanofiber-reinforced polymers prepared by fused deposition modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89(11), 3081–3090 (2003)
Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Mankotia, K.: Development of ABS based wire as feedstock filament of FDM for industrial applications. Rapid Prototyp. J. 22(2), 300–310 (2016)
Gray IV, R.W.; Baird, D.G.; Helge, Bøhn J.: Effects of processing conditions on short TLCP fiber reinforced FDM parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 4(1), 14–25 (1998)
Li, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.: Rapid prototyping of continuous carbon fiber reinforced polylactic acid composites by 3D printing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 238, 218–225 (2016)
Van Der Klift, F.; Koga, Y.; Todoroki, A.; Ueda, M.; Hirano, Y.; Matsuzaki, R.: 3D printing of continuous carbon fibre reinforced thermo-plastic (CFRTP) tensile test specimens. Open J. Compos. Mater. 6(1), 18–27 (2016)
Lu, Y.; Poh, G.K.; Gleadall, A.; Zhao, L.; Han X.: Fabrication of the continuous carbon fiber reinforced plastic composites by additive manufacturing.
Butt, J.; Shirvani, H.: Experimental analysis of metal/plastic composites made by a new hybrid method. Addit. Manuf. 22, 216–222 (2018)
BS 2782-3: Method 360C: 1991: Methods of testing Plastics—Part 3: Mechanical properties—Method 360C: Determination of Tear Resistance of Plastics Film and Sheeting by the Initiation Method. London, UK, British Standard (2010)
BS EN ISO 527-2: Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics, p. 2012. British, European and International Standard, London, UK (2012)
BS EN ISO 62: Plastics—Determination of Water Absorption, p. 2008. British, European and International Standard, London (2008)
BS EN ISO 178: Plastics—Determination of Flexural Properties, p. 2011. British, European and International Standard, London, UK (2019)
BS EN ISO 2039-2: 2000 BS 2782-3: Method 365C:1992. Plastics—Determination of hardness—Part 2: Rockwell Hardness. British, European and International Standard: London, UK, 2000.
Torres, J.; Cotelo, J.; Karl, J.; Gordon, A.P.: Mechanical property optimization of FDM PLA in shear with multiple objectives. JOM 67(5), 1183–1193 (2015)
Ning, F.; Cong, W.; Qiu, J.; Wei, J.; Wang, S.: Additive manufacturing of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites using fused deposition modeling. Compos. B Eng. 80, 369–378 (2015)
Shaffer, S.; Yang, K.; Vargas, J.; Di Prima, M.A.; Voit, W.: On reducing anisotropy in 3D printed polymers via ionizing radiation. Polymer 55(23), 5969–5979 (2014)
Jansen, J.: Plastic failure through molecular degradation: multiple mechanisms can attack polymer chains—here’s what can go wrong. Plast. Eng. 71(1), 34–39 (2015)
Siparsky, G.L.; Voorhees, K.J.; Miao, F.: Hydrolysis of polylactic acid (PLA) and polycaprolactone (PCL) in aqueous acetonitrile solutions: autocatalysis. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 6(1), 31–41 (1998)
Ayrilmis, N.; Kariz, M.; Kwon, J.H.; Kuzman, M.K.: Effect of printing layer thickness on water absorption and mechanical properties of 3D-printed wood/PLA composite materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102(5–8), 2195–2200 (2019)
Yew, G.H.; Yusof, A.M.; Ishak, Z.M.; Ishiaku, U.S.: Water absorption and enzymatic degradation of poly (lactic acid)/rice starch composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 90(3), 488–500 (2005)
Liu, A.F.: Mechanics and mechanisms of fracture: an introduction. ASM International, Cleveland (2005)
Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Yee, K.; Lee, K.Y.; Tagarielli, V.L.: Measurements of the mechanical response of unidirectional 3D-printed PLA. Mater. Des. 123, 154–164 (2017)
Pei, E.; Lanzotti, A.; Grasso, M.; Staiano, G.; Martorelli, M.: The impact of process parameters on mechanical properties of parts fabricated in PLA with an open-source 3-D printer. Rapid Prototyp. J. 21, 1 (2015)
Zurita Hurtado, O.J.; Di Graci Tiralongo, V.C.; Aguirre, C.; Cristina, M.: Effect of surface hardness and roughness produced by turning on the torsion mechanical properties of annealed AISI 1020 steel. Revista Facultad de Ingeniería Universidad de Antioquia. 84, 55–59 (2017)
Lawn, B.R.; Howes, V.R.: Elastic recovery at hardness indentations. J. Mater. Sci. 16(10), 2745–2752 (1981)
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butt, J., Oxford, P., Sadeghi-Esfahlani, S. et al. Hybrid Manufacturing and Mechanical Characterization of Cu/PLA Composites. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 9339–9356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04778-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04778-y