Abstract
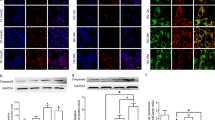
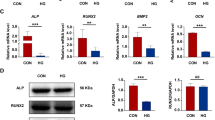
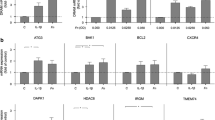
Impaired periodontal healing is a common complication of diabetes mellitus (DM), frequently related to hyperglycemia. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 have been studied as biomarkers for inflammatory diseases, including diabetes, but their role in the periodontal ligament (PL) is unknown. The effects of high glucose on human PL cells death were studied, as well as the expression of microRNA-221 and microRNA-222, potentially modulated by DM. Cells were obtained from the premolar teeth of young humans and cultured for 7 days under different glucose concentrations (5 or 30 mM). MicroRNAs-221/222 expressions were evaluated by real-time RT-PCR and apoptosis by TUNEL assays. Caspase-3 expression was studied by western blotting and immunocytochemistry. High glucose increased apoptosis and caspase-3 protein expression by about 3×. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 expressions decreased by nearly 40% under high glucose. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 inhibition using antagomiRs increased apoptosis by 2–3×, while the expression of caspase-3, a validated target for these microRNAs, was increased by 50%. The overexpression of both microRNAs using miR mimics in high glucose cells did no effect on apoptosis but increased caspase-3 expression by 30%. In conclusion, high glucose induces apoptosis of human PL cells potentially through a reduction of microRNA-221 and microRNA-222 expression and elevation of caspase-3.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2016). Global report on diabetes. World Health Organization Press, Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.who.int.
Brownlee, M. (2001). Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature, 144, 813–820.
Tsai, C., Hayes, C., & Taylor, G. W. (2002). Glycemic control of type 2 diabetes and severe periodontal disease in the US adult population. Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, 30, 182–192.
Chavarry, N. G. M., Vettore, M. V., Sansone, C., & Sheiham, A. (2009). The relationship between diabetes mellitus and destructive periodontal disease: a meta-analysis. Oral Health & Preventive Dentistry, 7, 107–127.
Sanz, M., Ceriello, A., Buysschaert, M., Chapple, I., Demmer, R. T., Graziani, F., Herrera, D., Jepsen, S., Lione, L., & Madianos, P., et al. (2018). Scientific evidence on the links between periodontal diseases and diabetes: Consensus report and guidelines of the joint workshop on periodontal diseases and diabetes by the International Diabetes Federation and the European Federation of Periodontology. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(2), 138–149.
Rohani, B. (2019). Oral manifestations in patients with diabetes mellitus. World Journal of Diabetes, 10(9), 485–489.
Villard, A., Marchand, L., Thivolet, C., & Rome, S. (2015). Diagnostic value of cell-free circulating microRNAs for obesity and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Journal of Molecular Biomarkers & Diagnosis, 6(6), 251.
Li M. Y., Pan S. R., Qiu A. Y. (2016). Roles of microRNA-221/222 in type 2 diabetic patients with post-menopausal breast cancer. Genetics and Molecular Research, 15(2), https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15027259.
Coleman, C. B., Lightell, Jr, D. J., Moss, S. C., Bates, M., Parrino, P. E., & Woods, T. C. (2013). Elevation of miR-221 and -222 in the internal mammary arteries of diabetic subjects and normalization with metformin. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 374(1-2), 125–129.
Li, Y., Song, Y. H., Li, F., Yang, T., Lu, Y. W., & Geng, Y. J. (2009). MicroRNA-221 regulates high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 381(1), 81–83.
Fornari, F., Pollutri, D., Patrizi, C., La Bella, T., Marinelli, S., Casadei Gardini, A., Marisi, G., Baron Toaldo, M., Baglioni, M., & Salvatore, V., et al. (2017). Hepatocellular carcinoma miR-221 modulates Sorafenib resistance through Inhibition of caspase-3-mediated apoptosis. Clinical Cancer Research, 23(14), 3953–3965.
Jin, X., Cai, L., Wang, C., Deng, X., Yi, S., Lei, Z., Xiao, Q., Xu, H., Luo, H., & Sun, J. (2018). CASC2/miR-24/miR-221 modulates the TRAIL resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cell through caspase-8/caspase-3. Cell Death & Disease, 9(3), 318.
Tonetti, M. S., Greenwell, H., & Kornman, K. S. (2018). Staging and grading of periodontitis: framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. Journal of Periodontology, 89(1 Suppl), S159–S172.
Beertsen, W., Mcculloch, C. A. G., & Sodek, J. (1997). The periodontal ligament: a unique, multifunctional connective tissue. Periodontology, 13, 20–40. 2000.
Grzesik, W. J., & Narayanan, A. S. (2002). Cementum and periodontal wound healing and regeneration. Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine, 13, 474–484.
Liu, J., Jiang, Y., Mao, J., Gu, B., Liu, H., & Fang, B. (2013). High levels of glucose induce a dose-dependent apoptosis in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts by activating caspase-3 signaling pathway. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 170(6), 1458–1471.
Liu, J., Wu, Y., Wang, B., Yuan, X., & Fang, B. (2013). High levels of glucose induced the caspase-3/PARP signaling pathway, leading to apoptosis in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 66(2), 229–237.
Li, D. X., Deng, T. Z., Lv, J., & Ke, J. (2014). Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and their receptor (RAGE) induce apoptosis of periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 47(12), 1036–1043.
You, L., Gu, W., Chen, L., Pan, L., Chen, J., & Peng, Y. (2014). MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 7(10), 7249–7261.
O’Brien, J., Hayder, H., Zayed, Y., & Peng, C. (2018). Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 9, 402.
Gebert, L. F. R., & MacRae, I. J. (2019). Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 20(1), 21–37.
Zhou, L., Jiang, F., Chen, X., Liu, Z., Ouyang, Y., Zhao, W., & Yu, D. (2016). Downregulation of miR-221/222 by a microRNA sponge promotes apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through upregulation of PTEN. Oncology Letters, 12(6), 4419–4426.
Brognara, E., Fabbri, E., Montagner, G., Gasparello, J., Manicardi, A., Corradini, R., Bianchi, N., Finotti, A., Breveglieri, G., & Borgatti, M., et al. (2016). High levels of apoptosis are induced in human glioma cell lines by co-administration of peptide nucleic acids targeting miR-221 and miR-222. International Journal of Oncology, 48(3), 1029–1038.
Milani, R., Brognara, E., Fabbri, E., Manicardi, A., Corradini, R., Finotti, A., Gasparello, J., Borgatti, M., Cosenza, L. C., & Lampronti, I., et al. (2019). Targeting miR-155-5p and miR-221-3p by peptide nucleic acids induces caspase-3 activation and apoptosis in temozolomide-resistant T98G glioma cells. International Journal of Oncology, 55(1), 59–68.
Yang, X., Yang, Y., Gan, R., Zhao, L., Li, W., Zhou, H., Wang, X., Lu, J., & Meng, Q. H. (2014). Down-regulation of mir-221 and mir-222 restrain prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration that is partly mediated by activation of SIRT1. PLoS ONE, 9(6), e98833.
Wang, L., Liu, C., Li, C., Xue, J., Zhao, S., Zhan, P., Lin, Y., Zhang, P., Jiang, A., & Chen, W. (2015). Effects of microRNA-221/222 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Gene, 572(2), 252–258.
Qin, B., Cao, Y., Yang, H., Xiao, B., & Lu, Z. (2015). MicroRNA-221/222 regulate ox-LDL-induced endothelial apoptosis via Ets-1/p21 inhibition. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 405(1-2), 115–124.
Liu, Z., Wang, C., Jiao, X., Zhao, S., Liu, X., Wang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2016). miR-221 promotes growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by constitutive activation of NFκB. American Journal of Translational Research, 8(11), 4764–4777.
Lima, C. R., Geraldo, M. V., Fuziwara, C. S., Kimura, E. T., & Santos, M. F. (2016). MiRNA-146b-5p upregulates migration and invasion of different Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer, 16, 108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2146-z.
Caton, J. G., Armitage, G., Berglundh, T., Chapple, I. L. C., Jepsen, S., Kornman, K. S., Mealey, B. L., Papapanou, P. N., Sanz, M., & Tonetti, M. S. (2018). A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions - Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(20 Suppl), S1–S8.
Radović, N., Nikolić Jakoba, N., Petrović, N., Milosavljević, A., Brković, B., & Roganović, J. (2018). MicroRNA-146a and microRNA-155 as novel crevicular fluid biomarkers for periodontitis in non-diabetic and type 2 diabetic patients. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(6), 663–671. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12888.
Song, J., Ouyang, Y., Che, J., Li, X., Zhao, Y., Yang, K., Zhao, X., Chen, Y., Fan, C., & Yuan, W. (2017). Potential value of miR-221/222 as diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic biomarkers for diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 56.
Van Vliet, E., Melis, M., Foidart, J. M., & Van Ewijk, W. (1986). Reticular fibroblasts in peripheral lymphoid organs identified by a monoclonal antibody. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 34, 883–890.
Costantino, S., Paneni, F., Lüscher, T. F., & Cosentino, F. (2016). MicroRNA profiling unveils hyperglycaemic memory in the diabetic heart. European Heart Journal, 37(6), 572–576.
Fiorentino, L., Cavalera, M., Mavilio, M., Conserva, F., Menghini, R., Gesualdo, L., & Federici, M. (2013). Regulation of TIMP3 in diabetic nephropathy: a role for microRNAs. Acta Diabetologica, 50(6), 965–969.
Ortega, F. J., Mercader, J. M., Moreno-Navarrete, J. M., Rovira, O., Guerra, E., Esteve, E., Xifra, G., Martínez, C., Ricart, W., & Rieusset, J., et al. (2014). Profiling of circulating microRNAs reveals common microRNAs linked to type 2 diabetes that change with insulin sensitization. Diabetes Care, 37(5), 1375–1383.
Herrera, B. M., Lockstone, H. E., Taylor, J. M., Ria, M., Barrett, A., Collins, S., Kaisaki, P., Argoud, K., Fernandez, C., & Travers, M. E., et al. (2010). Global microRNA expression profiles in insulin target tissues in a spontaneous rat model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia, 53(6), 1099–1109.
Chan, J. A., Krichevsky, A. M., & Kosik, K. S. (2005). MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Research, 65, 6029–6033.
Cheng, A. M., Byrom, M. W., Shelton, J., & Ford, L. P. (2005). Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, 1290–1297.
Ergun, S., Arman, K., Temiz, E., Bozgeyik, I., Yumrutaş, Ö., Safdar, M., Dağlı, H., Arslan, A., & Oztuzcu, S. (2014). Expression patterns of miR-221 and its target Caspase-3 in different cancer cell lines. Molecular Biology Reports, 41(9), 5877–5881.
Liu, Z., Sun, J., Liu, B., Zhao, M., Xing, E., & Dang, C. (2018). miRNA-222 promotes liver cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion and inhibits apoptosis by targeting BBC3. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 42(1), 141–148.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FAPESP (Grant awards 2015/19645-7, 2012/03990-9, 2012/24508-0, and 2011/18936-7), CNPq (Grant awards 310714/2018-4, 310440/2015-7, and 448052/2014-8), CAPES and Universidade de Sao Paulo (NAPMiR-USP). We also thank the excellent technical assistance from Gabriella Malheiros and Centro de Facilidades de Apoio a Pesquisa da Universidade de Sao Paulo (CEFAP-USP) for the research support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteiro, M.M., Lima, C.R., Gomes, C.C. et al. Lowered Expression of MicroRNAs 221 and 222 Mediate Apoptosis Induced by High Glucose in Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 78, 391–398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-020-00932-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-020-00932-3