Abstract
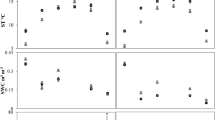
The melting of permafrost and the degradation of alpine meadow ecosystems caused by climate warming and high-intensity human activities have imposed serious threats to local and global ecological security. In order to estimate the effects of climate warming and grazing interference on the photosynthesis and respiration of alpine meadow plant community in permafrost regions, warming – infrared radiator is applied to simulate the climate warming (increasing temperature by +2°С). The winter grazing level is simulated by mowing the aboveground biomass of all plants. The responses of permafrost meadow community in terms of photosynthesis, respiration, surface soil temperature and moisture, as well as the carbon balance to simulated different climate warming and grazing level were analyzed and discussed. The results showed that: (1) the surface soil temperature in climate warming and grazing plots is significantly higher than in Ck plots (P < 0.01); (2) warming and warming + grazing plots enhanced community photosynthesis and respiration (P < 0.01); (3) warming and warming + grazing treatments increased community aboveground biomass (P < 0.05); (4) the photosynthetic rate increased in the second year, then decreased in the third year when both temperature and grazing level increased during the growing season. However, the ecosystem respiration increasingly increased year by year; (5) compared with the control groups, warming and grazing treatments resulted in an increase in carbon sequestration of the permafrost meadow community during the growing season.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Chapin, F.S., Matson, P.A., and Mooney, H.A., Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2002, pp. 83–144.
Han, H.Q., Zhang, J.Y., Ma, G., Zhang, X.D., and Bai, Y.M., Advances on impact of climate change on ecosystem service, J. Nanjing For. Univ.,Nat. Sci. Ed., 2018, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 184–190.
Yan, L.J., Yang, W.K., Lin, G.J., and Dong, P., Impact of global warming on forest ecosystems, Trop. Geogr., 2013, vol. 33, no. 05, pp. 621–627.
Martin, J., Markus, R., Christopher, R.S., Chris, H., Stephen, S., Anders, A., Almut, A., Gustau, C., Philippe, C., Pierre, F., Fabian, G., Kazuhito, I., Atul, K.J., Etsushi, K., Dario, P., et al., Nature, 2017, vol. 541, pp. 516–520.
Christian, B., Markus, R., and Enrico, T., Terrestrial gross carbon dioxide uptake: Global distribution and covariation with climate, Science, 2010, vol. 329, pp. 834–838.
Liu, L.X., Dong, Y.S., and Qi, Y.C., The development on the soil respiration of grassland ecosystem, Progr. Geogr., 2004, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 35–42.
Smith, S.D., Huxman. T.E., Zitzer. S.F., Charlet. T.N., Housman. D.C., Coleman. J.S., Fenstermaker. L.K., Seemann. J.R., and Nowak. R.S., Elevated CO2 increases productivity and invasive species success in an arid ecosystem, Nature, 2000, vol. 408, pp. 79–81.
Chang, X.F., Wang, S.P., Luo, C.Y., Zhang, Z.H., Duan, J.C., Zhu, X.X., Lin, Q.Y., and Xu, B., Responses of soil microbial respiration to thermal stress in alpine steppe on the Tibetan Plateau, Eur. J. Soil Sci., 2012, vol. 63, pp. 325–331.
Zhou, H.K., Zhou, X.M., and Zhao, X.Q., A preliminary study of the influence of simulated greenhouse effect on a Kobresia humilis meadow, Chin. J. Plant Ecol., 2000, no. 5, pp. 547–553.
Zhang, L.L., Wang, X.A., Zhu, Z.H., and Li, Y.N., The effects of simulated grazing intensity and fertilizing on the community characteristics and diversity in alpine meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Ecol.Environ. Sci., 2018, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 406–415.
Xu, M.H., Liu, M., Xue, X., Zhai, D.T., Peng, F., You, Q.G., and Liu, Z.Q., Effects of warming and clipping on vegetation species diversity and belowground biomass in an alpine meadow, Chin. J. Ecol., 2015, vol. 34, no. 9, pp. 2432–2439.
Li, Y.T., Yi, S.H., Hou, F.J., Chang, S.H., Wang, Z.F., Qin, Y., and Chen, J.J., Response of CO2 exchanges to short-term grazing by Euler’s sheep in an alpine meadow in the peak of the growing season, Acta Pratacult. Sinica, 2017, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 24–32.
Chen, X., Peng, F., You, Q.G., Wang, T., and Xue, X., Response of vegetation characteristics in the alpine meadow ecosystem to simulated temperature enhancement: A case study of permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China, Pratacult. Sci., 2018, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 825–834.
Niu, Y.J., Yang, S.W., Wang, G.Z., Liu, L., Du, G.Z., and Hua, L.M., Effects of grazing disturbance on soil properties and plant functional groups and their relationships in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau, China, Acta Ecol. Sinica, 2018, vol. 38, no. 14, pp. 5006–5016.
Niu, Y.J., Yang, S.W., Wang, G.Z., Liu, L., Du, G.Z., and Hua, L.M., Relationship between plant species, life form, functional group diversity, and biomass under grazing disturbance for four years on an alpine meadow, Acta Ecol. Sinica, 2018, vol. 38, no. 13, pp. 4733–4743.
Ganjurjav, H., Gao, Q., and Schwartz, M.W., Complex responses of spring vegetation growth to climate in a moisture-limited alpine meadow, Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6, no. 1, Article no. 23356.
Peng, F., Xue, X., and You, Q.G., Research advances in ecosystem carbon cycling response to experimental warming, J. Desert Res., 2014, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 1285–1292.
Zhu, L.L., Rong, Y.P., Wang, W.G., and Ma, L., Effects of grazing on the net ecosystem exchange of carbon dioxide in grassland ecosystems, Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 3–10.
Li, J.X., Zeng, H., Zhu, J.T., Zhang, Y.J., Chen, N., and Liu, Y.J., Responses of different experimental warming on ecosystem respiration in Tibetan alpine meadow, Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2016, vol. 25, no. 10, pp. 1612–1620.
Qi, W.W., Niu, H.S., Wang, S.P., Liu, Y.J., and Zhang, L.R., Simulation of effects of warming on carbon budget in alpine meadow ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau, Acta Ecol. Sinica, 2012, vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 1713–1722.
Li, Y., Hasbagan Ganjurjav, Hu, G.Z., Wan, Y.F., Li, Y.E., Danjiu, l.B., and Baima, Y.Z., Effects of warming on carbon exchange in an alpine steppe in the Tibetan Plateau, Acta Ecol. Sinica, 2019, vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 2004–2012.
Wang, H.B., Ma, M.G., Wang, X.F., Tan, J.L., Di, L.Y., Yu, W.P., and Jia, S.Z., Carbon flux variation characteristics and its influencing factors in an alpine meadow ecosystem on eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, J. Arid Land Resourc.Environ., 2014, vol. 28, no. 6, pp. 50–56.
Li, J.R. and Liu, Z.H., High-cold meadow plants respond to long-term warming, Qinghai Pratacult., 2017, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 13–18, 24.
Yan, W.C., Sun, G., Zhang, C.B., He, J., and Zhang, N.N., Impacts of experimental warming and moderate grazing on ecosystem carbon exchange and its compositions in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2018, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 132–139.
Xu, X.M., Wu, Q.B., and Zhang, Z.Q., Responses of active layer thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau to climate change, J. Glaciol. Geocryol., 2017, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 1–8.
Mu, C.C., Zhang, T.J., Zhao, Q., Su, H., Wang, S.F., Cao, B., Peng, X.Q., Wu, Q.B., and Wu, X.D., Permafrost affects carbon exchange and its response to experimental warming on the northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Agric. For. Meteorol., 2017, vol. 247, pp. 252–259.
Zhang, Z.Y., Wang, Y.R., and Zhao, L.J., Effect of soil moisture on physiological index of turf-grass, J. Anhui Agric. Sci., 2007, vol. 25, pp. 7779–7780, 7791.
Fan, A.W., Liu, W., and Liu, B.C., Effect of soil temperature on the growth of plant and an analysis of its mechanism, J. Eng. Thermophys., 2004, no. 1, pp. 124–126.
Xu, M.H., Liu, M., Xue, X., and Zhai, D.T., Warming effects on plant biomass allocation and correlations with the soil environment in an alpine meadow, J. Arid Land, 2016, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 773–786.
Xu, M.H., Liu, M., Zhai, D.T., Xue, X., Peng, F., and You, Q.G., Dynamic changes in biomass and its relationship with environmental factors in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, based on simulated warming experiments, Acta Ecol. Sinica, 2016, vol. 36, no. 18, pp. 5759–5767.
Yang, Y.J., Zhou, H.K., Yao, B.Q., Wang, W.Y., Dong, S.K., Yu, X.C., Zhao, X.Q., and Zhang, H., Effects of long-term simulated warming on soil physicochemical properties and plant chemical components of Kobresia humilis meadow, Chin. J. Ecol., 2015, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 781–789.
Qi, Y.C., Dong, Y.S., Geng, Y.B., Yang, X.H., and Geng, H.L., The progress in the carbon cycle researches in grassland ecosystem in China, Progr. Geogr., 2003, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 342–352.
Cao, G.M., Tang, Y.H., Mo, W.H., Mo, W.H., Wang, Y.S., Li, Y.N., and Zhao, X.Q., Grazing intensity alters soil respiration in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan plateau, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2003, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 237–243.
Ganjurjav, H., Gao, Q.Z., Zhang, W.N., Liang, Y., Li, Y.W., Cao, X.J., Wan, Y.F., Li, Y., and Danjiu, L.B., Effects of warming on CO2 fluxes in an alpine meadow ecosystem on the central Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 7, e0132044.
Emmett, B.A., Beier, C., Estiarte, M., Tietema, A., Kristensen, H.L., Williams, D., Peñuelas, J., Schmidt, I., and Sowerby, A., The response of soil processes to climate change: Results from manipulation studies of shrublands across an environmental gradient, Ecosystems, 2004, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 625–637.
Luo, C.Y., Xu, G.P., Chao, Z.G., Wang, S.P., Lin, X.W., Hu, Y.G., and Zhang, Z.H., Effect of warming and grazing on litter mass loss and temperature sensitivity of litter and dung mass loss on the Tibetan Plateau, Global Change Biol., 2010, vol. 16, pp. 1606–1617.
Yang, S.H., Li, Y.N., Pu, J.Y., Ma, Y.S., Zhao, L., Zhou, H.K., and Wang, C.T., Investigation of the plant community and soil environmental factors of three alpine vegetation types, Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2006, no. 1, pp. 77–83.
Chen, X., Peng, F., You, Q.G., Wang, T., and Xue, X., Response of vegetation characteristics in the alpine meadow ecosystem to simulated temperature enhancement: A case study of permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China, Pratacult. Sci., 2016, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 825–834.
Carlyle, C.N., Fraser, L.H., and Turkington, R., Response of grassland biomass production to simulated climate change and clipping along an elevation gradient, Oecologia, 2014, vol. 174, pp. 1065–1073.
Bai, W., Xi, J.Y., and Wang, G.X., Effects of short-term warming and nitrogen addition on CO2 emission during growing season in an alpine swamp meadow ecosystem of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Chin. J. Ecol., 2019, vol. 38, no. 4, pp. 927–936.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors express their sincere appreciation to the reviewers and editors for their time and effort.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was supported by the national natural science fund project (31560151, 31560668, 31460151), science and technology plan projects in Qinghai province (2017-ZJ-728), the department of applied basic research project in Qinghai province (2014-ZJ-779), the Qinghai province department project (2017-HZ-802), the ministry of education Yangtze river scholars and innovation team development plan (IRT-17R62) funding, international cooperation and communion department of project (teaching department letter [2017] 860).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chengyi Li, Yang, Y., Li, X. et al. Effects of Simulated Climate Warming and Grazing on Photosynthesis and Respiration of Permafrost Meadow Plant Community. Russ J Ecol 51, 224–232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413620030042
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413620030042