Abstract
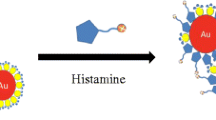
The development of a gold nanoparticle aptamer assay is persued for rapid and sensitive determination of histamine in foodstuffs, which could be deployed for on-site use. The assay is based on a histamine-specific aptamer and gold nanoparticles and the salt-induced aggregation of the particles in the presence of histamine indicated by the color change from red to blue. Gold nanoparticle size, salt type, and concentration as well as aptamer concentration were optimized, and using optimum conditions, a limit of detection of 8 nM (~ 0.05 mg/kg) was obtained. Finally, the aptamer AuNP assay was applied to the determination of histamine in quality control fish samples. The histamine levels of these samples had previously been determined using HPLC and commercial ELISA kits by numerous independent laboratories and a good correlation was obtained. The developed AuNP assay is rapid, sensitive, and reproducible.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez MA, Moreno-Arribas MV (2014) The problem of biogenic amines in fermented foods and the use of potential biogenic amine-degrading microorganisms as a solution. Trends Food Sci Technol 39:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.07.007
Ordóñez JL, Troncoso AM, García-Parilla MDC (2016) Recent trends in the determination of biogenic amines in fermented beverages – a review. Anal Chim Acta 939:10–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.07.045
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2019) Fish and fishery products hazards and controls guidance - fourth edition. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781847558398-00136
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2005) Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off J Eur Union 48:1–26
Mohammed GI, Bashammakh AS, Alsibaai AA, Alwael H, El-Shahawi MS (2016) A critical review on the chemistry, clean-up and recent advances in analysis of biogenic amines in foodstuffs. Trends Anal Chem 78:84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.02.007
Gone S, Kosa N, Krebs J, Hungerford J, Trucksess M, DeWitt C (2018) Validation study of MaxSignal® histamine enzymatic assay for the detection of histamine in fish/seafood. J AOAC Int 101:783–792. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.17-0289
Ye W, Xu Y, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Yang M, Sun P (2016) A nanoporous alumina membrane based electrochemical biosensor for histamine determination with biofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticles concentration and signal amplification. Sensors 16:1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101767
Luo L, Yang JY, Xiao ZL, Zeng DP, Li YJ, Shen YD, Sun YM, Lei HT, Wang H, Xu ZL (2015) A sensitivity-enhanced heterologous immunochromatographic assay based on a monoclonal antibody for the rapid detection of histamine in saury samples. RSC Adv 5:78833–78840. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403566e
Moyano A, Salvador M, Martínez-García J, Socoliuc V, Vékás L, Peddis D, Alvarez MA, Fernández M, Rivas M, Blanco-López MC (2019) Magnetic immunochromatographic test for histamine detection in wine. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:6615–6624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02031-6
Hungerford J, Wu WH (2012) Comparison study of three rapid test kits for histamine in fish: BiooScientific MaxSignal enzymatic assay, Neogen Veratox ELISA, and the Neogen Reveal Histamine Screening test. Food Control 25:448–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.11.007
Alkhamis O, Canoura J, Yu H, Liu Y, Xiao Y (2019) Innovative engineering and sensing strategies for aptamer-based small-molecule detection. Trends Anal Chem 121:115699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115699
Wu Y, Belmonte I, Sykes KS, Xiao Y, White RJ (2019) Perspective on the future role of aptamers in analytical chemistry. Anal Chem 91:15335–15344. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03853
Chang CC, Chen CP, Wu TH, Yang CH, Lin CW, Chen CY (2019) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assays for chemical and biological sensing applications. Nanomaterials 9:861. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9060861
Sabela M, Balme S, Bechelany M, Janot JM, Bisetty K (2017) A review of gold and silver nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensing assays. Adv Eng Mater 19:1700270. https://doi.org/. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700270
Ma Q, Wang Y, Jia J, Xiang Y (2018) Colorimetric aptasensors for determination of tobramycin in milk and chicken eggs based on DNA and gold nanoparticles. Food Chem 249:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.022
Ragavan KV, Selvakumar LS, Thakur MS (2013) Functionalized aptamers as nano-bioprobes for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol-A. Chem Commun 49:5960–5962. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc42002g
Wu YY, Huang P, Wu FY (2020) A label-free colorimetric aptasensor based on controllable aggregation of AuNPs for the detection of multiple antibiotics. Food Chem 304:125377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125377
Wang H, Zhang Y, Li R, Nie J, El-Sagheer AH, Brown T, Liu Z, Xiao W (2017) Instrument-free quantitative gold nanoparticle-based liquid-phase colorimetric assays for use in resource-poor environments. Chem Commun 53:8407–8410. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc03240d
Mairal Lerga T, Jauset-Rubio M, Skouridou V, Bashammakh AS, El-Shahawi MS, Alyoubi AO, O’Sullivan CK (2019) High affinity aptamer for the detection of the biogenic amine histamine. Anal Chem 91:7104–7111. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00075
Dwidar M, Yokobayashi Y (2019) Development of a histamine aptasensor for food safety monitoring. Sci Rep 9:16659. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52876-1
Ho SJ, Fogel R, Limson JL (2020) Generation and screening of histamine-specific aptamers for application in a novel impedimetric aptamer-based sensor. Talanta 208:120474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120474
Apetrei IM, Apetrei C (2016) Amperometric biosensor based on diamine oxidase/platinum nanoparticles/graphene/chitosan modified screen-printed carbon electrode for histamine detection. Sensors 16:442. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040422
Liu J (2012) Adsorption of DNA onto gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide: surface science and applications. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:10485–10496. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp41186e
Zhao W, Chiuman W, Lam JC, McManus SA, Chen W, Cui Y, Pelton R, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) DNA aptamer folding on gold nanoparticles: from colloid chemistry to biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 19:3610–3618. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja710241b
Xu C, Ying Y, Ping J (2019) Colorimetric aggregation assay for kanamycin using gold nanoparticles modified with hairpin DNA probes and hybridization chain reaction-assisted amplification. Microchim Acta 186:448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3574-7
Wang W, Ding X, Xu Q, Wang J, Wang L, Lou X (2016) Zeta-potential data reliability of gold nanoparticle biomolecular conjugates and its application in sensitive quantification of surface absorbed protein. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 148:541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.09.021
Turkevich J (1985) Colloidal gold. Part I Gold Bull 18:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03214690
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110:15700–15707. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp061667w
Bastús NG, Comenge J, Puntes V (2011) Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: size focusing versus Ostwald ripening. Langmuir 27:11098–11105. https://doi.org/10.1021/la201938u
Perrault SD, Chan WCW (2009) Synthesis and surface modification of highly monodispersed, spherical gold nanoparticles of 50-200 nm. J Am Chem Soc 131:17042–17043. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja907069u
Niu S, Lv Z, Liu J, Bai W, Yang S, Chen A (2014) Colorimetric aptasensor using unmodified gold nanoparticles for homogenous multiplex detection. PLoS One 9(10):e109263. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109263
Huang C, Wang S, Zhao W, Zong C, Liang A, Zhang Q, Liu X (2017) Visual and photometric determination of histamine using unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:2249–2254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2253-9
Venza M, Visalli M, Cucinotta M, Cicciù D, Passi P, Teti D (2006) Salivary histamine level as a predictor of periodontal disease in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. J Periodontol 77:1564–1571. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2006.050373
Friedman BS, Steinberg C, Meggs WJ, Kaliner MA, Frieri M, Metcalfe DE (1989) Analysis of plasma histamine levels in patients with mast cell disorders. Am J Med 87:649–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9343(89)80398-5
Lin RY, Schwartz LB, Curry A, Pesola GR, Knight RJ, Lee HS, Bakalchuk L, Tenenbaum C, Westfal ER (2000) Histamine and tryptase levels in patients with acute allergic reactions: an emergency department-based study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2000.107600
Myers G, Donlon M, Kaliner M (1981) Measurement of urinary histamine: development of methodology and normal values. J Allergy Clin Immunol 67:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(81)90026-9
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to King Abdulaziz University (Saudi Arabia) for financing the collaborative project “Ultrasensitive, extremely rapid lateral flow assays exploiting nanoparticles for the detection of biogenic amines, detection of adulteration of food with meat products and identification of contaminating meat and viruses.”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 948 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lerga, T.M., Skouridou, V., Bermudo, M.C. et al. Gold nanoparticle aptamer assay for the determination of histamine in foodstuffs. Microchim Acta 187, 452 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04414-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04414-4