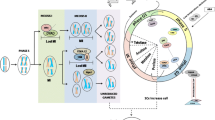
Abstract
Green plants provide food, fuel, materials, and medicine for humans. Amongst these, medicinal plants contain unique molecules with therapeutic applications. However, our understanding of these organisms is in its infancy. Landscaping plants also have a great impact on the human soul and emotional perception. These two groups of plants are part of natural wealth and have great economic value. One of the remarkable breeding strategies to improve the valuable properties of plants is artificial polyploidy induction. Medicinal and ornamental plants with duplicated whole sets of chromosomes, although not always, have more distinctive characteristics such as modified phytochemical profile, higher content of desired pharma molecules, plant form, flower color, size and style, fragrance, vase life, and prolonged flowering period. Therefore, artificial chromosome doubling (ACD) of ornamental and medicinal plants could have significant economic consequences. In medicinal plants with an ornamental flower/inflorescence, and/or in ornamental plants bearing essential oils, ACD is a dual beneficial breeding strategy. Working with both in vitro and in vivo chromosome doubling pathways, researchers are able to produce custom-designed plants with higher marketability. Some critical factors must be considered to establish a successful ACD protocol. The plant genotype and explant type are important parameters in this procedure. Type, dosage and duration of application (exposure time) of antimitotic agent (AMA) should also be considered as the main factors. Antimitotic agents can be classified according to their efficacy and toxicity. Although colchicine is the most applied and well-known AMA, there are other alternative mitotic spindle inhibitors with higher specificity for tubulin binding sites in plant materials and possessing less toxicity for animal tubulin. Testing the interaction effects of plant and AMA parameters is necessary for establishing an ACD breeding program and promoting the economic values of medicinal and ornamental plants. This paper reviews significant developments in polyploidization using different antimitotic agents over the last decade in the field of ornamental and medicinal plants.
Key message
Artificial polyploidy induction is one of the applicable breeding methods in ornamental and medicinal plants. Increasing the efficiency of chromosome doubling and fast-reliable screening of desired phenotypes are prerequisites for production of custom-designed medicinal and ornamental plants through artificial polyploidy induction.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACD:
-
Artificial chromosome doubling
- AMA:
-
Antimitotic agent
- APPI:
-
Artificial polyploidy induction
- BBBMs:
-
Biotechnology-based breeding methods
- CRISPR:
-
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- MOPs:
-
Medicinal and ornamental plants
- PGRs:
-
Plant growth regulators
References
Acanda Y, Martínez Ó, González MV, Prado MJ, Rey M (2015) Highly efficient in vitro tetraploid plant production via colchicine treatment using embryogenic suspension cultures in grapevine (Vitis vinifera cv Mencía). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 123(3):547–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0859-3
Adams KL, Wendel JF (2005) Novel patterns of gene expression in polyploid plants. Trends Genet 21(10):539–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2005.07.009
Ahmadi B, Ebrahimzadeh H (2020) In vitro androgenesis: spontaneous vs. artificial genome doubling and characterization of regenerants. Plant Cell Rep 39(3):299–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02509-z
Alagoz Y, Gurkok T, Zhang B, Unver T (2016) Manipulating the biosynthesis of bioactive compound alkaloids for next-generation metabolic engineering in opium poppy using CRISPR-Cas 9 genome editing technology. Sci Rep 6:30910. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30910
Aqafarini A, Lotfi M, Norouzi M, Karimzadeh G (2019) Induction of tetraploidy in garden cress: morphological and cytological changes. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 137(3):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01596-5
Ari E, Djapo H, Mutlu N, Gurbuz E, Karaguzel O (2015) Creation of variation through gamma irradiation and polyploidization in Vitex agnus-castus L. Scient Horticu 195:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.08.039
Atichart P (2013) Polyploid induction by colchicine treatments and plant regeneration of Dendrobium chrysotoxum. Thai J Agric Sci. 46(1):59–63
Azadi P, Bagheri H, Nalousi AM, Nazari F, Chandler SF (2016) Current status and biotechnological advances in genetic engineering of ornamental plants. Biotechnol Ad 34(6):1073–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.06.006
Ban Y, Morita Y, Ogawa M, Higashi K, Nakatsuka T, Nishihara M, Nakayama M (2019) Inhibition of post-transcriptional gene silencing of chalcone synthase genes in Petunia picotee petals by fluacrypyrim. J Exp Bot 70(5):1513–1523. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz009
Bhuvaneswari G, Thirugnanasampandan R, Gogulramnath M (2020) Effect of colchicine induced tetraploidy on morphology, cytology, essential oil composition, gene expression and antioxidant activity of Citrus limon (L.) Osbeck. Physiol Mol Biol Pla 26(2):271–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00718-9
Bicknell R, Boase M, Morgan E (2019) Developing polyploid genotypes of Leptospermum scoparium. New Z J Crop Hortic Sci 47(4):273–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671.2019.1683044
Borrill P, Harrington SA, Uauy C (2017) Genome-wide sequence and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in polyploid wheat. G3 Genes Genomes Genet 7(9):3019–3029. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.117.043679
Brandoli C, Petri C, Egea-Cortines M, Weiss J (2020) The clock gene Gigantea 1 from Petunia hybrida coordinates vegetative growth and inflorescence architecture. Sci Rep 10(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57145-9
Cai X, Cao Z, Xu S, Deng Z (2015) Induction, regeneration and characterization of tetraploids and variants in Tapestry caladium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120(2):689–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0636-8
Carbajal EM, Zuleta MC, Swayzer L, Schwartz BM, Chavarro MC, Ballen-Taborda AC, Milla-Lewis SR (2019) Development of colchicine-induced tetraploid St Augustinegrass (Stenotaphrum secundatum) lines. Plant Breedi 138(6):958–966. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12742
Castillo AM, Cistué L, Vallés MP, Soriano M (2009) Chromosome doubling in monocots. In: Touraev A, Forster BP, Jain SM (eds) Advances in haploid production in higher plants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8854-4
Chaikam V, Molenaar W, Melchinger AE, Boddupalli PM (2019) Doubled haploid technology for line development in maize: technical advances and prospects. Theor Appl Genet 132:3227–3243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03433-x
Chen ZJ, Ni Z (2006) Mechanisms of genomic rearrangements and gene expression changes in plant polyploids. BioEssays 28(3):240–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20374
Chen C, Hou X, Zhang H, Wang G, Tian (2011) Induction of Anthurium andraeanum “Arizona” tetraploid by colchicine in vitro. Euphytica 181(2):137–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0344-3
Chen F, Zhu Z, Tong L, Guo X, Xu S, Chen J, Wu J, Zhu Z (2020) Production of allohexaploid Brassica hybrid between tuber mustard (Brassica juncea L. var crassicaulis Chen & Yang) and Chinese kale (Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra Bailey). Sci Hortic 270:109412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109412
Cheng C, Gao J, Ma N (2018) Investigation of petal senescence by TRV-mediated virus-induced gene silencing in rose. Plant Senescence. Humana Press, New York, pp 49–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7672-0_4
Comstock RE, Robinson HF (1948) The components of genetic variance in populations of biparental progenies and their use in estimating the average degree of dominance. Biometrics 4:254–266. https://doi.org/10.2307/3001412
Denaeghel H, Van Laere K, Leus L, Van Huylenbroeck J, Van Labeke MC (2015) Induction of Tetraploids in Escallonia spp. In: XXV International EUCARPIA Symposium Section Ornamentals: Crossing Borders. 1087, 453–458. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2015.1087.61
Dhooghe E, Van Laere K, Eeckhaut T, Leus L, Van Huylenbroeck J (2011) Mitotic chromosome doubling of plant tissues in vitro. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult 104(3):359–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9786-5
Doležel J, Bartoš JAN (2005) Plant DNA flow cytometry and estimation of nuclear genome size. Ann Bot 95(1):99–110. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci005
Du Y, Cheng F, Zhong Y (2020) Induction of direct somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis and histological study in tree peony (Paeonia sect. Moutan). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 141:557–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01815-4
Ebrahimzadeh H, Soltanloo H, Shariatpanahi ME, Eskandari A, Ramezanpour SS (2018) Improved chromosome doubling of parthenogenetic haploid plants of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) using colchicine, trifluralin, and oryzalin. Plant CellTissue Organ Cult 135(3):407–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1473-y
Eng WH, Ho WS (2019) Polyploidization using colchicine in horticultural plants: a review. Scient Hortic 246:604–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.11.010
Esmaeili G, Van Laere K, Muylle H, Leus L (2020) Artificial chromosome doubling in allotetraploid Calendula officinalis. Front Plant Sci 11:622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00622
Feng S, Song W, Fu R, Zhang H, Xu A, Li J (2018) Application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 135(1):133–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1450-5
Fernando SC, Goodger JQ, Chew BL, Cohen TJ, Woodrow IE (2019) Induction and characterisation of tetraploidy in Eucalyptus polybractea RT Baker. Ind Crop Prod 140:111633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111633
Fetouh MI, Kareem A, Knox GW, Wilson SB, Deng Z (2016) Induction, identification, and characterization of tetraploids in Japanese privet (Ligustrum japonicum). Hort Sci 51(11):1371–1377. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI11138-16
Fu L, Zhu Y, Li M, Wang C, Sun H (2019) Autopolyploid induction via somatic embryogenesis in Lilium distichum Nakai and Lilium cernuum Komar. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 139:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01671-x
Fuentes P, Zhou F, Erban A, Karcher D, Kopka J, Bock R (2016) A new synthetic biology approach allows transfer of an entire metabolic pathway from a medicinal plant to a biomass crop. Elife 5:13664. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13664.002
Gaebelein R, Alnajar D, Koopmann B, Mason AS (2019) Hybrids between Brassica napus and B nigra show frequent pairing between the B and A/C genomes and resistance to blackleg. Chromosome Res 27(3):221–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-019-09612-2
Gallone A, Hunter A, Douglas GC (2014) Polyploid induction in vitro using colchicine and oryzalin on Hebe ‘Oratia Beauty’: production and characterization of the vegetative traits. Sci Horticu 179:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.09.014
Ghanbari MA, Jowkar A, Salehi H, Zarei M (2019) Effects of polyploidization on petal characteristics and optical properties of Impatiens walleriana (Hook.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 38:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01625-3
Głowacka K, Jeżowski S, Kaczmarek Z (2010) In vitro induction of polyploidy by colchicine treatment of shoots and preliminary characterisation of induced polyploids in two Miscanthus species. Indu Crop Prod 32(2):88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.03.009
Griffing B (1956) Concept of general and specific combining ability in relation to diallel crossing systems. Aus J Biol Sci 9(4):463–493. https://doi.org/10.1071/BI9560463
Grosso V, Farina A, Giorgi D, Nardi L, Diretto G, Lucretti S (2018) A high-throughput flow cytometry system for early screening of in vitro made polyploids in Dendrobium hybrids. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 132(1):57–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1310-8
Hannweg K, Visser G, de Jager K, Bertling I (2016) In vitro-induced polyploidy and its effect on horticultural characteristics, essential oil composition and bioactivity of Tetradenia riparia. S Afr J Bot 106:186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2016.07.013
Hayman BY (1958) The theory and analysis of diallel crosses. Genetics II:63–85
He H, Ke H, Keting H, Qiaoyan X, Silan D (2013) Flower colour modification of Chrysanthemum by suppression of F3′H and overexpression of the exogenous Senecio cruentus F3′5′H gene. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074395
He M, Gao W, Gao Y, Liu Y, Yang X, Jiao H, Zhou Y (2016) Polyploidy induced by colchicine in Dendranthema indicum var. Aromaticum, a scented chrysanthemum. Eur J Hortic Sci. 81(4):219–226
Hoang TK, Hwang YJ, Lim JH (2020) Chemical polyploidization of Chrysanthemum boreale. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 140(3):677–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01761-w
Hosseini HR, Chehrazi M, Ahmadi DN, Sorestani MM (2018) Colchicine-induced autotetraploidy and altered plant cytogenetic and morpho-physiological traits in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Adv in Hortic Sci 32(2):229–238. https://doi.org/10.13128/ahs-20845
Huang R, Liu D, Zhao M, Li Z, Li M, Sui S (2015) Artificially induced polyploidization in Lobularia maritima (L.) Desv. and its effect on morphological traits. Hort Sci 50(5):636–639. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.50.5.636
Huy NP, Luan VQ, Tung HT, Hien VT, Ngan HTM, Duy PN, Nhut DT (2019) In vitro polyploid induction of Paphiopedilum villosum using colchicine. Sci Hortic 252:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.03.063
Iannicelli J, Guariniello J, Tossi VE, Regalado JJ, Di Ciaccio L, van Baren CM, Álvarez SP, Escandón AS (2020) The “polyploid effect” in the breeding of aromatic and medicinal species. Sci Hortic 260:108854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108854
Jaleel CA, Sankar B, Murali PV, Gomathinayagam M, Lakshmanan GMA, Panneerselvam R (2008) Water deficit stress effects on reactive oxygen metabolism in Catharanthus roseus; impacts on ajmalicine accumulation. Colloids Surf B 62(1):105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.09.026
Jeloudar NI, Chamani E, Shokouhian AA, Zakaria RA (2019) Induction and identification of polyploidy by colchicine treatment in Lilium regale. Cytologia 84(3):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.84.271
Jinks JL (1954) The analysis of continuous variation in a diallel cross of Nicotiana rustica varieties. Genetics 39(6):767–788
Julião SA, Ribeiro CDV, Lopes JML, Matos EMD, Reis AC, Peixoto PHP, Machado MA, Azevedo ALS, Grazul RM, Campos JMSD, Viccini LF (2020) Induction of synthetic polyploids and assessment of genomic stability in Lippia alba. Front Plant Sci 11:292. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00292
Junping X, Naing AH, Kim CK (2018) Transcriptional activation of anthocyanin structural genes in Torenia ‘Kauai Rose’via overexpression of anthocyanin regulatory transcription factors. 3 Biotech 8(11):476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1505-7
Kanemaki A, Otani M, Takano M, Fujimoto T, Okuhara H, Nomizu T, Kondo M, Kobayashi H, Tatsuzawa F, Nakano M (2018) Ectopic expression of the R2R3-MYB gene from Tricyrtis sp. results in leaf color alteration in transgenic Pelargonium crispum. Sci Hortic 240:411–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.06.029
Kearsey MJ, Jinks JL (1968) A general method of detecting additive, dominance and epistatic variation for metrical traits I. Theory Hered. 22:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1968.52
Kearsey MJ, Pooni HS (1998) The genetical analysis of quantitative traits. Stanley Thornes Ltd., London, p 381
Kempthorne O (1957) An introduction to genetical statistics. Wiley, New York
Khalili S, Niazian M, Arab M, Norouzi M (2019) In vitro chromosome doubling of African daisy, Gerbera jamesonii Bolus cv. Mini Red. Nucleus 63:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-019-00282-3
Kooti W, Farokhipour M, Asadzadeh Z, Ashtary-Larky D, Asadi-Samani M (2016) The role of medicinal plants in the treatment of diabetes: a systematic review. Electron Phys 8(1):1832. https://doi.org/10.19082/1832
Kushwah KS, Verma RC, Patel S, Jain NK (2018) Colchicine induced polyploidy in Chrysanthemum carinatum L. J Phylogenet Evol Biol 6(193):2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-9002.1000193
Lan MO, Chen JH, Fei Chen XuQW, Tong ZK, Huang HH, DONG RH, Lou XZ, Lin EP (2020) Induction and characterization of polyploids from seeds of Rhododendron fortunei Lindl. J Integr Agric 19(8):2016–2026. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63210-5
Lattier JD, Touchell DH, Ranney TG, Smith JC (2013) Micropropagation and Polyploid Induction of Acer platanoides ‘Crimson Sentry. J Env Hortic 31(4):246–252
Lavania UC (1988) Enhanced productivity of the essential oil in the artificial autopolyploid of vetiver (Vetiveria zizanioides L. Nash). Euphytica 38(3):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023530
Lavania UC (2005) Genomic and ploidy manipulation for enhanced production of phyto-pharmaceuticals. Plant Genet Resour 3(2):170. https://doi.org/10.1079/PGR200576
Lavania UC, Srivastava S, Lavania S, Basu S, Misra NK, Mukai Y (2012) Autopolyploidy differentially influences body size in plants, but facilitates enhanced accumulation of secondary metabolites, causing increased cytosine methylation. Plant J 71(4):539–549. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05006.x
Levy M (1976) Altered glycoflavone expression in induced autotetraploids of Phlox drummondii. Biochem Syst Ecol 4(4):249–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-1978(76)90047-8
Li Z, Ruter JM (2017) Development and evaluation of diploid and polyploid Hibiscus moscheutos. Hort Sci 52(5):676–681. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI11630-16
Li Q, Yang Y, Wu H (2016) In Vitro segregation of tetraploid and octoploid plantlets from colchicine-induced ploidy chimeras in Echinacea purpurea L. Hort Sci 51(5):549–557
Li W, Liu J, TanH Luo L, Cui J, Hu J, Wang S, Liu Q, Hu F, Tang C, Ren L (2018a) Asymmetric expression patterns reveal a strong maternal effect and dosage compensation in polyploid hybrid fish. BMC Genomics 19(1):517. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4883-7
Li M, Ding B, Huang W, Pan J, Ding Z, Jiang F (2018b) Induction and characterization of tetraploids from seeds of Bletilla striata (Thunb.) Reichb. f. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3246398
Li H, Liu J, Pei T, Bai Z, Han R, Liang Z (2019a) Overexpression of SmANS enhances anthocyanin accumulation and alters phenolic acids content in Salvia miltiorrhiza and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge f. alba plantlets. Int J Mol Sci 20(9):2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092225
Li S, Li M, Li Z, Zhu Y, Ding H, Fan X, Li F, Wang Z (2019b) Effects of the silencing of CmMET1 by RNA interference in chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium). Plant Biotechnol Rep 13(1):63–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-019-00516-5
Li S, Lin Y, Pei H, Zhang J, Zhang J, Luo J (2020) Variations in colchicine-induced autotetraploid plants of Lilium davidii var. unicolor. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01805-6
Liu S, Chen S, Chen Y, Guan Z, Yin D, Chen F (2011) In vitro induced tetraploid of Dendranthema nankingense (Nakai) Tzvel. shows an improved level of abiotic stress tolerance. Sci Hortic 127(3):411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2010.10.012
Lu J, Liu JN, Sarsaiya S, Duns GJ, Han J, Jin L, Chen J (2020) Phenotypic and transcriptomic analysis of two Pinellia ternata varieties T2 line and T2Plus line. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61512-2
Lucía GR, Jesica I, Andrea C, Verónica B, Paula B, Sandra PÁ, Alejandro E (2015) A protocol for the in vitro propagation and polyploidization of an interspecific hybrid of Glandularia (G. peruviana × G. scrobiculata). Sci Hortic 184:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.12.032
Madani H, Hosseini B, Karimzadeh G, Rahimi A (2019) Enhanced thebaine and noscapine production and modulated gene expression of tyrosine/dopa decarboxylase and salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase genes in induced autotetraploid seedlings of Papaver bracteatum Lindl. Acta Physiol Plant 41(12):194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2984-9
Manzoor A, Ahmad T, Bashir MA, Baig MMQ, Quresh AA, Shah MKN, Hafiz IA (2018) Induction and identification of colchicine induced polyploidy in Gladiolus grandiflorus ‘White Prosperity’. Folia Horticulturae. 30(2):307–319. https://doi.org/10.2478/fhort-2018-0026
Manzoor A, Ahmad T, Bashir MA, Hafiz IA, Silvestri C (2019) Studies on colchicine induced chromosome doubling for enhancement of quality traits in ornamental plants. Plants 8(7):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8070194
Meng L, Guo Y, Liu S, Zhao Y, Pang X, Li Y (2019) Autotetraploidization in Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. spinosa enhances salt tolerance conferred by active, diverse stress responses. Environ Exp Bot 165:92–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.05.016
Miguel TP, Leonhardt KW (2011) In vitro polyploid induction of orchids using oryzalin. Sci Hortic 130(1):314–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2011.07.002
Mopuri R, Islam MS (2017) Medicinal plants and phytochemicals with anti-obesogenic potentials: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1442–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.108
Mwathi MW, Gupta M, Quezada-Martinez D, Pradhan A, Batley J, Mason AS (2020) Fertile allohexaploid Brassica hybrids obtained from crosses between B. oleracea and B. juncea via ovule rescue and colchicine treatment of cuttings. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 140(2):301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01728-x
Nadler JD, Pooler M, Olsen RT, Coleman GD (2012) In vitro induction of polyploidy in Cercis glabra Pamp. Sci Hortic 148:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.09.024
Niazian M (2019) Application of genetics and biotechnology for improving medicinal plants. Planta 249(4):953–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03099-1
Niazian M, Shariatpanahi EM (2020) In vitro-based doubled haploid production: recent improvements. Euphytica 216:69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02609-7
Niazian M, Noori SAS, Galuszka P, Tohidfar M, Mortazavian SMM (2017a) Genetic stability of regenerated plants via indirect somatic embryogenesis and indirect shoot regeneration of Carum copticum L. Ind Crop Prod 97:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.12.044
Niazian M, Sadat Noori SA, Tohidfar M, Mortazavian SMM (2017b) Essential oil yield and agro-morphological traits in some Iranian ecotypes of ajowan (Carum copticum L.). J Essent Oil Bear Pl 20(4):1151–1156. https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2017.1326849
Niazian M, Sadat-Noori SA, Abdipour M (2018) Artificial neural network and multiple regression analysis models to predict essential oil content of ajowan (Carum copticum L.). J Appl Res Med Aroma Plants 9:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2018.04.001
Niazian M, Sadat-Noori SA, Tohidfar M, Galuszka P, Mortazavian SMM (2019) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague): an important industrial medicinal plant. Ind Crop Prod 132:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.02.005
Ning GG, Shi XP, Hu HR, Yan Y, Bao MZ (2009) Development of a range of polyploid lines in petunia hybrida and the relationship of ploidy with the single-/double-flower trait. HortScience 44(2):250–255. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.44.2.250
Nomani M, Noori SAS, Tohidfar M, Ramshini H (2019) Overexpression of TPS2 gene to increase thymol content using Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation in Trachyspermum ammi (Qom ecotype). Ind Crop Prod 130:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.12.076
Noori SAS, Norouzi M, Karimzadeh G, Shirkool K, Niazian M (2017) Effect of colchicine-induced polyploidy on morphological characteristics and essential oil composition of ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 130(3):543–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1245-0
Nukui S, Kitamura S, Hioki T, Ootsuka H, Miyoshi K, Satou T, Takatori Y, Oomiya T, Okazaki K (2011) N2O induces mitotic polyploidization in anther somatic cells and restores fertility in sterile interspecific hybrid lilies. Breed Sci 61(4):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.61.327
Ochatt SJ, Patat-Ochatt EM, Moessner A (2011) Ploidy level determination within the context of in vitro breeding. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104(3):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9918-6
Opsahl B (1956) The discrimination of interactions and linkage in continuous variation. Biometrics 12(4):415–432
Osborn TC, Pires JC, Birchler JA, Auger DL, Chen ZJ, Lee HS, Comai L, Madlung A, Doerge RW, Colot V, Martienssen RA (2003) Understanding mechanisms of novel gene expression in polyploids. Trends Genet 19(3):141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(03)00015-5
Pan-pan H, Wei-xu L, Hui-hui L (2018) In vitro induction and identification of autotetraploid of Bletilla striata (Thunb.) Reichb. f by colchicine treatment. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 132(3):425–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1339-8
Parsons JL, Martin SL, James T, Golenia G, Boudko EA, Hepworth SR (2019) Polyploidization for the genetic improvement of Cannabis sativa. Front Plant Sci 10:476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00476
Podwyszyńska M (2011) In vitro tetraploid induction in tulip (Tulipa gesneriana L.). In: VII International Symposium on In Vitro Culture and Horticultural Breeding. 961: 391–396
Pradhan SK, Gupta RC, Goel RK (2018) Differential content of secondary metabolites in diploid and tetraploid cytotypes of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. Nat Prod Res 32(20):2476–2482. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1423298
Priyadarshan PM (2019) Induced mutations and polyploidy breeding. In: Priyadarshan PM (ed) Plant breeding: classical to modern. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7095-3_16
Qi-Qing LI, Zhang J, Ji-Hua LIU, Bo-Yang YU (2018) Morphological and chemical studies of artificial Andrographis paniculata polyploids. Chin J Natur Medic 16(2):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30033-5
Rahnema S, Sedaghathoor S, Allahyari MS, Damalas CA, El Bilali H (2019) Preferences and emotion perceptions of ornamental plant species for green space designing among urban park users in Iran. Urban Urban Gree 39:98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2018.12.007
Regalado JJ, Carmona-Martín E, Querol V, Veléz CG, Encina CL, Pitta-Alvarez SI (2017) Production of compact petunias through polyploidization. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 129(1):61–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1156-5
Sabu KK, Nadiya F (2020) Small RNA manipulation in plants: Techniques and recent developments. In: Guleria K, Kumar V (eds) Plant Small RNA. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 379–413
Sabzehzari M, Hoveidamanesh S, Modarresi M, Mohammadi V (2019a) Morphological, anatomical, physiological, and cytological studies in diploid and tetraploid plants of Plantago psyllium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 139(1):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-019-00846-x
Sabzehzari M, Hoveidamanesh S, Modarresi M, Mohammadi V (2019b) Morphological, anatomical, physiological, and cytological studies in diploid and tetraploid plants of Ispaghul (Plantago ovata Forsk.). Genet Resour Crop Ev 67:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-019-00846-x
Salma U, Kundu S, Mandal N (2017) Artificial polyploidy in medicinal plants: advancement in the last two decades and impending prospects. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 20(1):9–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-016-0080-1
Santeramo D, Howell J, Ji Y, Yu W, Liu W, Kelliher T (2020) DNA content equivalence in haploid and diploid maize leaves. Planta 251(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03320-1
Sattler MC, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2016) The polyploidy and its key role in plant breeding. Planta 243(2):281–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2450-x
Šedivá J, Mrázková M, Zahumenická P, Cusimamani EF, Zahradník D (2019) Identification of Phytophthora tolerance in the Anemone sylvestris tetraploid. Sci Hortic 256:108579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108579
Shahriari-Ahmadi F, Dehghan E, Farsi M, Azizi M (2008) Tetraploid induction of Hyoscyamus muticus L. using colchicine treatment. Pak J Biol Sci 11(24):2653
Shmeit YH, Fernandez E, Novy P, Kloucek P, Orosz M, Kokoska L (2020) Autopolyploidy effect on morphological variation and essential oil content in Thymus vulgaris L. Sci Hortic 263:109095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.109095
Sivakumar G, Alba K, Phillips GC (2017) Biorhizome: a biosynthetic platform for colchicine biomanufacturing. Front Plant Sci 8:1137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01137
Slamet A, Andarias SH, Bahrun AH, Mantja K (2019) Induction of Lili Hujan polyploid (Zephyranthes rosea Lindl) with ethanolic extract of Tapak Dara leaf (Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. don.) to increase its economic value. Earth and Environmental Science 235(1):12102
Soltani Howyzeh M, Sadat Noori SA, Shariati JV, Niazian M (2018) Essential oil chemotype of Iranian Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi L.). J Essent Oil Bear Pl 21(1):273–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2018.1433074
Talebi SF, Saharkhiz MJ, Kermani MJ, Sharafi Y, Fard FR (2016) Effect of ploidy level on the nuclear genome content and essential oil composition of anise hyssop (Agastache foeniculum [Pursh.] Kuntze). Anal Chem Lett 6(5):678–687. https://doi.org/10.1080/22297928.2016.1257953
Talebi SF, Saharkhiz MJ, Kermani MJ, Sharafi Y, Fard FR (2017) Effect of different antimitotic agent AMAs on polyploid induction of anise hyssop (Agastache foeniculum L.). Caryologia 70(2):184–193
Tang ZQ, Chen DL, Song ZJ, He YC, Cai DT (2010) In vitro induction and identification of tetraploid plants of Paulownia tomentosa. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 102(2):213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9724-6
Thomford NE, Senthebane DA, Rowe A, Munro D, Seele P, Maroyi A, Dzobo K (2018) Natural products for drug discovery in the 21st century: innovations for novel drug discovery. Int J Mol Sci 19(6):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061578
Tiwari AK, Mishra SK (2012) Effect of colchicine on mitotic polyploidization and morphological characteristics of Phlox drummondi. Afr J Biotechnol 11(39):9336–9342. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.3820
Tong J, Chen FZ (2012) Study on colchicines induced polyploid breeding of Callicarpa bodinieri. Hubei Agric Sci 10
Touchell DH, Palmer IE, Ranney TG (2020) In vitro ploidy manipulation for crop improvement. Front Plant Sci 11:722. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00722
Tsuro M, Kondo N, Noda M, Ota K, Nakao Y, Asada S (2016) In vitro induction of autotetraploid of Roman chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile L.) by colchicine treatment and essential oil productivity of its capitulum. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 52(5):479–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-016-9779-0
Tu HY, Zhang AL, Xiao W, Lin YR, Shi JH, Wu YW, Wu ST, Zhong CH, Mo SX (2018) Induction and identification of tetraploid Hedychium coronarium through thin cell layer culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 135(3):395–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1472-z
Urwin NA (2014) Generation and characterisation of colchicine-induced polyploid Lavandula × intermedia. Euphytica 197(3):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1069-5
Van Kleunen M, Essl F, Pergl J, Brundu G, Carboni M, Dullinger S, Early R, González-Moreno P, Groom QJ, Hulme PE, Kueffer C (2018) The changing role of ornamental horticulture in alien plant invasions. Biol Rev 93(3):1421–1437. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12402
Wang LJ, Sheng MY, Wen PC, Du JY (2017) Morphological, physiological, cytological and phytochemical studies in diploid and colchicine-induced tetraploid plants of Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn. Bot Stud 58(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-016-0157-3
Wang J, Guan Y, Ding L, Li P, Zhao W, Jiang J, Chen S, Chen F (2019) The CmTCP20 gene regulates petal elongation growth in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Plant Sci 280:248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.12.008
Wang LJ, Zhang Q, Cao QZ, Gao X, Jia GX (2020) An efficient method for inducing multiple genotypes of tetraploids Lilium rosthornii Diels. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01807-4
Wu QQ, Zheng SX, Wang JH, Xu C (2010) Polyploid induction of lily derived from intersectional hybrid. J West Chi Forest Sci 4:17
Xiong JS, Ding J, Li Y (2015) Genome-editing technologies and their potential application in horticultural crop breeding. Hortic Res 2:15019. https://doi.org/10.1038/hortres.2015.19
Xu C, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Yao P, Li Y, Kang X (2018) Impact of the leaf cut callus development stages of Populus on the tetraploid production rate by colchicine treatment. J Plant Growth Regul 37(2):635–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9763-x
Xu J, Kang BC, Naing AH, Bae SJ, Kim JS, Kim H, Kim CK (2020) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase1 enhances Petunia flower longevity. Plant Biotechnol J 18(1):287–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13197
Ye YM, Tong J, Shi XP, Yuan W, Li GR (2010) Morphological and cytological studies of diploid and colchicine-induced tetraploid lines of crape myrtle (Lagerstroemia indica L.). Sci Hortic 124(1):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.12.016
Yue Y, Fan X, Hu Y, Han C, Li H, Teng W, Zhang H, Teng K, Wen H, Yang X, Wu J (2020a) In vitro induction and characterization of hexaploid Pennisetum × advena, an ornamental grass. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01814-5
Yue Y, Ren M, Quan Y, Lian M, Piao X, Wu S, Zhou Y, Jin M, Gao R (2020b) Autopolyploidy in Chrysanthemum cv ‘Gongju’ improved cold tolerance. Plant Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01225-y
Zahumenická P, Fernández E, Šedivá J, Žiarovská J, Ros-Santaella JL, Martínez-Fernández D, Russo D, Milella L (2018) Morphological, physiological and genomic comparisons between diploids and induced tetraploids in Anemone sylvestris L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 132(2):317–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1331-3
Zhang X, Gao J (2020) In vitro tetraploid induction from multigenotype protocorms and tetraploid regeneration in Dendrobium officinale. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01786-6
Zhang F, Hua L, Fei J, Wang F, Liao Y, Fang W, Chen F, Teng N (2016a) Chromosome doubling to overcome the chrysanthemum cross barrier based on insight from transcriptomic and proteomic analyses. BMC Genomics 17(1):585. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2939-0
Zhang Q, Zhang F, Li B, Zhang L, Shi H (2016b) Production of tetraploid plants of Trollius chinensis Bunge induced by colchicine. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 52(1):34–38. https://doi.org/10.17221/89/2015-CJGPB
Zhang L, Shivute FN, Shahid MQ, Kamara N, Wu J, Liu X (2019) In vitro induction of auto-allotetraploid in a newly developed wild rice line from Oryza alta Swallen. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 139(3):577–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01701-8
Zhang YS, Chen JJ, Cao YM, Duan JX, Cai XD (2020) Induction of tetraploids in ‘Red Flash’caladium using colchicine and oryzalin: morphological, cytological, photosynthetic and chilling tolerance analysis. Sci Hortic 272:109524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109524
Zhao C, Tian M, Li Y, Zhang P (2017) Slow-growing pollen-tube of colchicine-induced 2n pollen responsible for low triploid production rate in Populus. Euphytica 213(4):94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1881-9
Zhao Q, Zhong M, He L, Wang B, Liu QL, Pan YZ, Jiang BB, Zhang L (2018) Overexpression of a chrysanthemum transcription factor gene DgNAC1 improves drought tolerance in chrysanthemum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 135(1):119–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1449-y
Zhou Z, Tan H, Li Q, Chen J, Gao S, Wang Y, Chen W, Zhang L (2018) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated efcient targeted mutagenesis of RAS in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Phytochem 148:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.01.015
Zhou Q, Wu J, Sang Y, Zhao Z, Zhang P, Liu M (2020) Effects of colchicine on Populus canescens ectexine structure and 2n pollen production. Front Plant Sci 11:295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00295
Zobayed SMA, Afreen F, Kozai T (2007) Phytochemical and physiological changes in the leaves of St. John’s wort plants under a water stress condition. Environ Exp Bot 59(2):109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.10.002
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Arman Beyraghdar Kashkooli for technical and language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MN and AMN conceived the idea and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests. All the authors read and approved the manuscript in its final form.
Additional information
Communicated by M. I. Beruto.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niazian, M., Nalousi, A.M. Artificial polyploidy induction for improvement of ornamental and medicinal plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 142, 447–469 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01888-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01888-1