Abstract
Background and aims
Behçet’s disease (BD) is an auto-immune vasculitis, characterized by episodic inflammation of multiple organs. The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is used as a marker of inflammation in several diseases nowadays. While nitric oxide (NO) seem to be involved in BD pathogenicity. Our study aims to investigate the NLR as an inflammatory marker of BD activity as well as to evaluate the relationship between the NO production and NLR in Algerian BD patients with different clinical manifestations before and under colchicine + corticosteroid treatment.
Methods
For this purpose, we evaluated the NLR as the ratio of neutrophil count to lymphocyte count in naïve and treated active BD patients with different clinical manifestations and in inactive ones. Furthermore, we assessed NO production by the Griess’ method in the same patients. Additionally, we evaluated in vivo interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-4 (IL-4) levels using ELISA.
Results and discussion
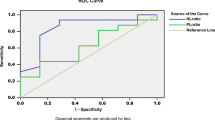
Our results indicate that the NLR and nitrite levels were higher in naïve active BD patients. Interestingly, this high ratio and NO production differed according to the clinical manifestations and was associated with an increased risk of mucocutaneous and vascular involvement. Importantly, in treated BD patients NLR was higher in active patients especially in those with mucocutaneous involvement while increased nitrites levels were regardless of the clinical manifestations studied. Both NLR and NO production decreased in these treated active patients. In addition, IL-4 production differed according to the clinical manifestations studied contrary to the IFN-γ production.
Conclusion
Collectively our results suggest that the NLR is a potential marker of BD activity in Algerian patients, predicting the disease severity. Moreover, the positive relationship between the NLR and NO production is related to an increased risk of mucocutaneous lesions and vascular involvement. Thus, the application of these two accessible tools could be benefit for the clinical prognosis and treatment of BD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acikgoz N (2016) The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and behcet disease. Angiology 67(3):297. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003319715611805
Ahsen A, Ulu MS, Yuksel S, Demir K, Uysal M, Erdogan M, Acarturk G (2013) As a new inflammatory marker for familial mediterranean fever: neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Inflammation 36(6):1357–1362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9675-2
Akkaya G, Bilen Ç (2019) Comments on: role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator for hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula failure. J Vasc Access 20(6):788–789. https://doi.org/10.1177/1129729819874998
Akkurt ZM, Bozkurt M, Uçmak D, Yüksel H, Uçak H, Sula B, Özkurt ZG, Yildiz M, Akdeniz D, Arica M (2015) Serum cytokine levels in Behçet’s disease. J Clin Lab Anal 29(4):317–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.21772
Alan S, Tuna S, Türkoğlu EB (2015) The relation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and mean platelet volume with the presence and severity of Behçet’s syndrome. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 31(12):626–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2015.10.010
Aridogan BC, Yildirim M, Vahide Baysal H, Inaloz S, Baz K, Kaya S (2003) Serum levels of IL-4, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13 and IFN-gamma in Behçet’s disease. J Dermatol 30(8):602–607
Asahina A, Kubo N, Umezawa Y, Honda H, Yanaba K, Nakagawa H (2017) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and mean platelet volume in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: response to therapy with biologics. J Dermatol 44(10):1112–1121. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.13875
Balkarli A, Kucuk A, Babur H, Erbasan F (2016) Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and mean platelet volume in Behçet’s disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(14):3045–3050
Balta S, Celik T, Mikhailidis DP, Ozturk C, Demirkol S, Aparci M, Iyisoy A (2016) The relation between atherosclerosis and the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio. Clin Appl Thrombosis/Hemost Off J Int Acad Clin Appl Thrombosis/Hemost 22(5):405–411. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029615569568
Bhat T, Teli S, Rijal J, Bhat H, Raza M, Khoueiry G, Meghani M, Akhtar M, Costantino T (2013) Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cardiovascular diseases: a review. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 11(1):55–59. https://doi.org/10.1586/erc.12.159
Celikbilek M, Dogan S, Ozbakır O, Zararsız G, Kücük H, Gürsoy S, Yurci A, Güven K, Yücesoy M (2013) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of disease severity in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Lab Anal 27(1):72–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.21564
Cetin A, Esin FC, Cefle A, Deniz G (2014) IL-22-secreting Th22 and IFN-γ-secreting Th17 cells in Behçet’s disease. Mod Rheumatol 24(5):802–807. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2013.879414
Cho S, Kim J, Cho SB, Zheng Z, Choi MJ, Kim DY, Bang D (2014) Immunopathogenic characterization of cutaneous inflammation in Behçet’s disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereo JEADV 28(1):51–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.12054
International Study Group for Behçet’s Disease (1990) Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet’s disease. Lancet 335(8697):1078–1080
Demir S, Sag E, Dedeoglu F, Ozen S (2018) Vasculitis in systemic autoinflammatory diseases. Front Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2018.00377
Djaballah-Ider F, Chaib S, Belguendouz H, Talbi D, Touil-Boukoffa C et al (2012) T cells activation and interferon-γ/nitric oxide production during Behçet disease: a study in Algerian patients. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 20(3):215–217. https://doi.org/10.3109/09273948.2012.671882
Djaballah-Ider F, Djeraba Z, Chemli M, Dammene-Debbihe N, Lounis D, Belguendouz H, Medour Y, Chaib S, Touil-Boukoffa C (2018) Influence of corticosteroid therapy on IL-18 and nitric oxide production during Behçet’s disease. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0472-2
Djaballah-Ider F, Djaballah A, Djeraba Z, Chaib S, Touil-Boukoffa C (2019) Auto-immunity profile evaluation during different clinical manifestations of Behçet disease in Algerian patients: effect of corticosteroid treatment. Inflammopharmacol Février. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00567-8
Djeraba Z, Boumedine K, Arroul-Lammali A, Otmani F, Belguendouz H, Touil-Boukoffa C (2014) Ex vivo immunomodulatory effect of all-trans-retinoic acid during Behçet’s disease: a study in Algerian patients. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 36(1):78–86. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2013.873048
Emmi G, Silvestri E, Della Bella C, Grassi A, Benagiano M, Cianchi F, Squatrito D et al (2016) Cytotoxic Th1 and Th17 cells infiltrate the intestinal mucosa of Behcet patients and exhibit high levels of TNF-α in early phases of the disease. Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000005516
Emmi G, Becatti M, Bettiol A, Hatemi G, Prisco D, Fiorillo C (2019) Behçet’s syndrome as a model of thrombo-inflammation: the role of neutrophils. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01085
Erdağ E, Şahin C, Küçükali Cİ, Bireller S, Küçükerden M, Kürtüncü M, Türkoğlu R, Cakmakoglu B, Tüzün E, Arıcıoğlu F (2017) Effects of in vivo and in vitro administration of neuro-Behcet’s disease IgG. Neurol Sci Off J Ital Neurol Soc Ital Soc Clin Neurophysiol 38(5):833–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2856-2
Furuya MY, Temmoku J, Fujita Y, Matsuoka N, Asano T, Sato S, Kobayashi H, Watanabe H, Migita K (2019) Vasculo-Behçet disease complicated by conversion disorder diagnosed with 18F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography (PET/CT). Fukushima J Med Sci 65(2):55–60. https://doi.org/10.5387/fms.2019-07
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Yessirkepov M, Kitas GD (2015) Colchicine as an anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective agent. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 11(11):1781–1794. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2015.1076391
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Mukanova U, Yessirkepov M, Kitas GD (2019) The platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as an inflammatory marker in rheumatic diseases. Ann Lab Med 39(4):345. https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.4.345
Gholijani N, Ataollahi MR, Samiei A, Aflaki E, Shenavandeh S, Kamali-Sarvestani E (2017) An elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines profile in Behcet’s disease: a multiplex analysis. Immunol Lett 186:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2016.12.001
Guenane H, Hartani D, Chachoua L, Lahlou-Boukoffa OS, Mazari F, Touil-Boukoffa C et al (2006) Production of Th1/Th2 cytokines and nitric oxide in Behçet’s uveitis and idiopathic uveitis. J Fr D’ophtalmologie 29(2):146–152
Guthrie GJK, Charles KA, Roxburgh CSD, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ (2013) The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol 88(1):218–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.03.010
Hammad M, Shehata OZ, Abdel-Latif SM, El-Din AMM (2018) Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and platelet/lymphocyte ratio in Behçet’s disease: which and when to use? Clin Rheumatol 37(10):2811–2817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4194-z
Hamzaoui K (2011) Th17 cells in Behçet’s disease: a new immunoregulatory axis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29(4 Suppl 67):S71–76
Hamzaoui K, Hamzaoui A, Guemira F, Bessioud M, Hamza MH, Ayed K (2002) Cytokine profile in Behçet’s disease patients. Relationship with disease activity. Scand J Rheumatol 31(4):205–210
Hamzaoui A, Ghraïri H, Ammar J, Zekri S, Guemira F, Hamzaoui K (2003) IL-18 MRNA expression and IFN-gamma induction in bronchoalveolar lavage from Behçet’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21(4 Suppl 30):S8–14
Horie Y, Meguro A, Ohta T, Lee EB, Namba K, Mizuuchi K, Iwata D et al (2017) HLA-B51 carriers are susceptible to ocular symptoms of Behçet disease and the association between the two becomes stronger towards the east along the silk road: a literature survey. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 25(1):37–40. https://doi.org/10.3109/09273948.2015.1136422
Inanir A, Tural S, Yigit S, Kalkan G, Pancar GS, Demir HD, Ates O (2013) Association of IL-4 gene VNTR variant with deep venous thrombosis in Behçet’s disease and its effect on ocular involvement. Mol Vis 19:675–683
İşcan Y, Yiğit U, Tuğcu BÇ, Erdoğan M, Erdoğan DA, Öner V, Taş M, Özyazgan Y (2012) Tear nitric oxide levels in Behçet’s disease. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 48(11):559–562
Koarada S, Haruta Y, Tada Y, Ushiyama O, Morito F, Ohta A, Nagasawa K (2004) Increased entry of CD4+ T cells into the Th1 cytokine effector pathway during T-cell division following stimulation in Behcet’s disease. Rheumatol (Oxf Engl) 43(7):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh195
Leccese P, Alpsoy E (2019) Behçet’s disease: an overview of etiopathogenesis. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01067
Merriman RC, Dissanayake O, Alnjar S, Burns F, Miller RF (2019) Incidence and significance of elevated platelet-to-lymphocyte and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios among hospitalised hiv-positive adult patients. Int J STD AIDS. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956462419868881
Murray NP, Fuentealba C, Reyes E, Lopez MA, Salazar A, Minzer S, Munoz L, Orrego S, Guzman E, Arzeno L (2019) Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in the diagnosis of significant prostate cancer at initial biopsy: a comparison with free percent prostate specific antigen prostate specific antigen density and primary circulating prostate cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 20(11):3385–3389. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.11.3385
Na SY, Park M-J, Park S, Lee E-S (2013) Up-regulation of th17 and related cytokines in Behçet’s disease corresponding to disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(3 Suppl 77):32–40
Neves FS, Spiller F (2013) Possible mechanisms of neutrophil activation in Behçet’s disease. Int Immunopharmacol 17(4):1206–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2013.07.017
Perazzio SF, PV Soeiro-Pereira, VC dos Santos, de Brito MV, Salu B, Vilela Oliva ML, Stevens AM et al (2017) Soluble CD40L is associated with increased oxidative burst and neutrophil extracellular trap release in Behçet’s disease. PubMed NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29052524
Rifaioglu EN, Şen BB, Ekiz Ö, Dogramaci AC (2014) Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in Behçet’s disease as a marker of disease activity. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannon Adriat 23(4):65–67
Safi R, Kallas R, Bardawil T, Mehanna CJ, Abbas O, Hamam R, Uthman I, Kibbi A-G, Nassar D (2018) Neutrophils contribute to vasculitis by increased release of neutrophil extracellular traps in Behçet’s disease. J Dermatol Sci 92(2):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.08.010
Sanda GE, Belur AD, Teague HL, Mehta NN (2017) Emerging associations between neutrophils, atherosclerosis, and psoriasis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 19(12):53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-017-0692-8
Sen BB, Rifaioglu EN, Ekiz O, Inan MU, Sen T, Sen N (2014) Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a measure of systemic inflammation in psoriasis. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 33(3):223–227. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569527.2013.834498
Shahram F, Nikoopour E, Rezaei N, Saeedfar K, Ziaei N, Davatchi F, Amirzargar A (2011) Association of interleukin-2, interleukin-4 and transforming growth factor-beta gene polymorphisms with Behcet’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29(4 Suppl 67):S28–31
Shimizu J, Takai K, Fujiwara N, Arimitsu N, Ueda Y, Wakisaka S, Yoshikawa H, Kaneko F, Suzuki T, Suzuki N (2012) Excessive CD4+ T cells co-expressing interleukin-17 and interferon-γ in patients with Behçet’s disease. Clin Exp Immunol 168(1):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04543.x
Sun JY, Mu N, Mu J, Zhang CG, Wang DM (2019) Significance of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and platelet/lymphocyte ratio in patients with multiple myeloma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 27(4):1185–1189. https://doi.org/10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2019.04.031
Takeuchi M, Kastner DL, Remmers EF (2015) The immunogenetics of Behçet’s disease: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 64:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.013
Takeuchi M, Karasawa Y, Harimoto K, Tanaka A, Shibata M, Sato T, Caspi RR, Ito M (2017) Analysis of Th Cell-related cytokine production in Behçet disease patients with uveitis before and after infliximab treatment. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 25(1):52–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/09273948.2016.1158276
Talaat RM, Sibaii H, Bassyouni IH, El-Wakkad A (2019) IL-17, IL-10, IL-6, and IFN-γ in Egyptian Behçet’s disease: correlation with clinical manifestations. Eur Cytokine Netw 30(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1684/ecn.2019.0421
Taysi S, Sari RA, Dursun H, Yilmaz A, Keles M, Cayir K, Akyuz M, Uyanik A, Guvenc A (2008) Evaluation of nitric oxide synthase activity, nitric oxide, and homocysteine levels in patients with active Behcet’s disease. Clin Rheumatol 27(12):1529–1534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0963-4
Touil-Boukoffa C, Bauvois B, Sancéau J, Hamrioui B, Wietzerbin J (1998) Production of nitric oxide (NO) in human hydatidosis: relationship between nitrite production and interferon-gamma levels. Biochimie 80(8–9):739–744
Trottier MD, Newsted MM, King LE, Fraker PJ (2008) Natural glucocorticoids induce expansion of all developmental stages of murine bone marrow granulocytes without inhibiting function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):2028–2033. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0712003105
Zeb A, Khurshid S, Bano S, Rasheed U, Zammurrad S, Khan MS, Aziz W, Tahir S (2019) The role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as markers of disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. Cureus 11(10):e6025. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.6025
Zeidan MJ, Saadoun D, Garrido M, Klatzmann D, Six A, Cacoub P (2016) Behçet’s disease physiopathology: a contemporary review. Auto Immun Highlights 7(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13317-016-0074-1
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients and the controls. They also express their gratitude to the Department of Internal Medicine of Mustapha Pacha Hospital and that of Dr Md Seghir NEKKACHE Hospital in Algiers, and to the Hematology Department of Dr Md Seghir NEKKACHE Hospital in Algiers.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Agency for Research and Development (ATRSS, ex ANDRS), project code number 58-DFPR-ATRSS-AAP-2014 Algeria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with regard to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This manuscript was approved by the co-author. The local ethics committee “Algerian National Agency for Research in Health Sciences, ATRSS ex-ANDRS” in compliance with Helsinki declaration has approved our study (Code number 58-DFPR-ATRSS-AAP-2014).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djaballah-Ider, F., Touil-Boukoffa, C. Effect of combined colchicine-corticosteroid treatment on neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio: a predictive marker in Behçet disease activity. Inflammopharmacol 28, 819–829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00701-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00701-x