Abstract
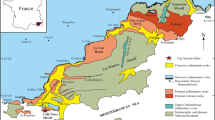
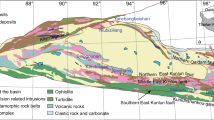
The Huaishuping gold deposit is located in the Xiong’ershan Mountains of the Qinling-Dabie Orogen of central China. The mineralisation is structurally controlled and hosted by faulted rhyolite, quartz andesite, volcaniclastic rocks and volcanic breccia assigned to the Jidanping Formation towards the top the Palaeoproterozoic Xiong’er Group. The deposit has a resource of around 32 t with an average grade of 5.5 g/t Au. Alteration at the deposit progressed from an early K-feldspar–quartz–pyrite assemblage through quartz–pyrite–gold, quartz–base-metal sulfides, to a late-stage assemblage of quartz–carbonate. The δ34S (V-CDT) values for pyrite in the ore range from − 13.3 to + 1.6‰. The calcite has C-isotopes ranging from − 6.1 to + 2.5‰ (V-PDB) and O-isotopes from + 10.6 to + 15.8‰ (V-SMOW). The δ18O quartz ranges from 10.5 to 15.1‰, and the δD values for fluid inclusions in quartz range from − 93 to − 76‰. The δ56Fe value for the mineralisation varies between 0.1 and 0.5‰ with corresponding δ57Fe values between 0.2 and 0.7‰. The isotope systematics indicates that the hydrothermal fluids were derived from metamorphic fluid, but the source of gold remains uncertain. Re–Os dating of molybdenite yields a date of 202 ± 8 Ma interpreted as the age of the gold mineralisation. This age is consistent with the Triassic onset of extensional tectonics following the collision between North and South China.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AJ, Fallick AG (1989) Evidence from Lewisian limestones for isotopically heavy carbon in ten-thousand-million-year-old seawater. Nature 337:352–354
Beard BL, Johnson CM (2004a) Inter-mineral Fe isotope variations in mantle-derived rocks and implications for the Fe geochemical cycle. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:4727–4743
Beard BL, Johnson CM (2004b) Fe isotope variations in the modern and ancient Earth and other planetary bodies. In: Johnson CM, Beard BL, Albare’de F (eds) Geochemistry of non-traditional stable isotopes. Rev Mineral Geochem 55:319–357
Beard BL, Johnson CM, Skulan JL, Nealson KH, Cox L, Sun H (2003) Application of Fe isotopes to tracing the geochemical and biological cycling of Fe. Chem Geol 195:87–117
Bierlein FP, Foster DA, Gray DR, Davidson GJ (2005) Timing of orogenic gold mineralisation in northeast Tasmania—implications for the tectonic and metallogenic evolution of Palaeozoic SE Australia. Mineral Deposita 39:890–903
Bierlein FP, Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Dubé D (2006) Lithospheric controls on the formation of provinces hosting giant orogenic gold deposits. Mineral Deposita 40:874–886
Bilenker LD, Simon AC, Reich M, Lundstrom CC, Gajos N, Bindeman I, Barra F, Munizaga R (2016) Fe–O stable isotope pairs elucidate a high-temperature origin of Chilean iron oxide-apatite deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 177:94–104
Biondi JA, Santos CLF (2013) The Paleoproterozoic Aripuanã Zn-Pb-Ag (Au, Cu) volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Mato Grosso, Brazil: geology, geochemistry of alteration, carbon and oxygen isotope modeling, and implications for genesis. Econ Geol 108:781–811
Cao J, Ye HS, Li HY, Li ZY, Zhang XK, He W, Li C (2014) Geological characteristics and molybdenite Re–Os isotopic dating of Huangshui'an carbonatite vein-type Mo (Pb) deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province. Mineral Deposits 33:53–69 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cao MP, Yao JM, Deng XH, Yang FJ, Mao GZ, Mathur R (2017) Diverse and multistage Mo, Au, Ag–Pb–Zn and Cu deposits in the Xiong'er Terrane, East Qinling: from Triassic Cu mineralization. Ore Geol Rev 81:565–574
Chen YJ, Santosh M (2014) Triassic tectonics and mineral systems in the Qinling orogen, Central China. Geol J 49:338–358
Chen YJ, Chen HY, Zaw K, Pirajno F, Zhang ZJ (2007) Geodynamic settings and tectonic model of skarn gold deposits in China: an overview. Ore Geol Rev 31:139–169
Chen L, Li XH, Li JW, Hofstra AH, Liu Y, Koenig AE (2015) Extreme variation of sulfur isotopic compositions in pyrite from the Qiuling sediment-hosted gold deposit, West Qinling orogen, Central China: an in situ SIMS study with implications for the source of sulfur. Mineral Deposita 50:643–656
Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1963) The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 27:43–52
Clayton RN, O’Neil JR, Mayeda TK (1972) Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water. J Geophys Res 77:3057–3067
Cohen KM, Finney SC, Gibbard L, Fan JX (2013) The ICS International Chronostratigraphic Chart. Episodes 36:199–204
Corbett GJ, Leach TM (1998). Southwest Pacific rim gold-copper systems: structure, alteration, and mineralisation. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication 6, 234 p
Das Sharma S, Srinivasan R, Ahmad SM, Patil DJ (1994) Carbon and oxygen isotopic compositions of regionally metamorphosed Archaean carbonate rocks of the Dharwar Craton. Curr Sci 66:857–860
Das A, Krishnaswami S, Bhattacharya SK (2005) Carbon isotope ratio of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in rivers draining the Deccan Traps, India: sources of DIC and their magnitudes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 236:419–429
Dauphas N, van Zuilen M, Wadhwa M, Davis AM, Marty B, Janney PE (2004) Clues from Fe isotope variations on the origin of Early Archean BIFs from Greenland. Science 306:2077–2080
Demeny A, Ahijado A, Casillas R, Vennemann TW (1998) Crustal contamination and fluid/rock interaction in the carbonatites of Fuerteventura (Canary Islands, Spain): C, O, H isotope study. Lithos 44:101–115
Deng J, Qiu K, Wang Q, Goldfarb R, Yang L, Zi J, Geng J, Ma Y (2020) In Situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold Province, eastern China. Econ Geol 115:671–685
Deng J, Gong QJ, Wang CM, Carranza EJM, Santosh M (2013) Sequence of Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous magmatic–hydrothermal events in the Xiong’ershan region, Central China: an overview with new zircon U–Pb geochronology data on quartz porphyries. J Asian Earth Sci 79:161–172
Deng J, Wang CM, Leon B, Carranza EJM, Lu YJ (2015) Cretaceous–Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong peninsula, China: constraints from zircon U–Pb, illite K–Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineral Deposita 50:987–1006
Deng J, Wang CM, Leon B, Vikraman S, Heejin J, Wu B, Yang LF (2017) Insights into ore genesis of the Jinding Zn–Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, China: evidence from Zn and in-situ S isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 90:943–957
Deng J, Wang CM, Leon B, Santosh M, Yao EN (2018) Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Sci Rev 182:251–272
Dong YP, Santosh M (2016) Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Res 29:1–40
Dong YP, Liu XM, Zhang GW, Chen Q, Zhang XN, Li W, Yang C (2011) Triassic diorites and granitoids in the Foping area: constraint on the conversion from subduction to collision in the Qinling orogen, China. J Asian Earth Sci 47:123–142
Du AD, Wu SQ, Sun DZ, Wang SX, Qü WJ, Markey R, Stein H, Morgan JW, Malinovskiy D (2004) Preparation and certification of Re-Os dating reference materials: molybdenite HLP and JDC. Geostand Geoanal Res 28:41–52
Fan HR, Xie YH, Zhao R, Wang YL (1994) Stable isotope geochemistry of rocks and gold deposits in the Xiong’ershan area, western Henan Province. Contrib Geol Mineral Res 9:54–64 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fiorentini ML, Bekker A, Rouxel O, Wing BA, Maier W, Rumble D (2012a) Multiple sulfur and iron isotope composition of magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide mineralization from eastern Botswana. Econ Geol 107:105–116
Fiorentini ML, Beresford S, Barley M, Duuring P, Bekker A, Rosengren A, Cas R, Hronsky J (2012b) District to camp controls on the genesis of komatiite-hosted nickel sulfide deposits, Agnew-Wiluna greenstone belt, Western Australia. Econ Geol 107:781–796
Foden J, Sossi PA, Wawryk CM (2015) Fe isotopes and the contrasting petrogenesis of A-, I- and S-type granite. Lithos 212–215:32–44
Gagnevin D, Boyce AJ, Barrie CD, Menuge JF, Blakeman RJ (2012) Zn, Fe and S isotope fractionation in a large hydrothermal system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 88:183–198
Ghosh P, Brand AW (2003) Stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry in global climate change research. Int J Mass Spectrom 228:1–33
Goldfarb RJ, Groves DI (2015) Orogenic gold: common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. Lithos 233:2–26
Goldfarb RJ, Ayuso R, Miller ML, Ebert SH, Masrsh EE, Miller LD, Bradley D, Johnson C, McClelland W (2004) The Late Cretaceous Donlin Creek gold deposit, southwestern Alaska: controls on epizonal ore formation. Econ Geol 99:643–671
Graham S, Pearson N, Jackson S, Griffin W, O'Reilly SY (2004) Tracing Cu and Fe from source to porphyry: in situ determination of Cu and Fe isotope ratios in sulfides from the Grasberg Cu-Au deposit. Chem Geol 207:147–169
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Gebre-Mariam M, Hagemann SG, Robert F (1998) Orogenic gold deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geol Rev 13:7–27
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Knox-Robinson CM, Ojala J, Gardoll S, Yun GY, Holyland P (2000) Late-kinematic timing of orogenic gold deposits and significance for computer-based exploration techniques with emphasis on the Yilgarn Block, Western Australia. Ore Geol Rev 17:1–38
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Robert F, Hart CJR (2003) Gold deposits in metamorphic belts: overview of current understanding, outstanding problems, future research, and exploration significance. Econ Geol 98:1–29
Hacker BR, Wang X, Eide EA, Ratschbacher L (1996) The Qinling–Dabie ultra-high-pressure collisional orogen. In: Yin A, Harrison M (eds) The tectonic evolution of Asia. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 345–370
He XY (2017) Gold-molybdenum mineral system in the ore-forming concentration district of the Xiong’ershan and Waifangshan. Ph.D. dissertation, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, 231p (in Chinese)
Hedenquist JW (1987) Mineralization associated with volcanic-related hydrothermal systems in the Circum-Pacific basin. In Horn MK (Ed), Transactions of the Fourth Circum-Pacific Energy and Mineral Resources Conference August, 1986, Singapore. Am. Assoc. Petroleum Geol., Tulsa, Oklahoma, pp. 513–524
Hedenquist JW, Arribas RA, Gonzalez-Urien E (2000) Exploration for epithermal gold deposits. Rev Econ Geol 13:245–277
Henan BGMED (Henan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development) (1989) Regional geology of Henan Province. Geological Publication House, Beijing, p 722 (in Chinese)
Hodgson CJ (1989) The structure of shear-related, vein type gold deposits: a review. Ore Geol Rev 4:231–273
Hodson JD (1977) Stable isotopes and limestone lithification. J Geol Soc Lond 133:637–660
Hoefs J (1997) Stable isotope geochemistry. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 1–214
Huang DH, Wu CY, Du AD, He HL (1994) Re–Os isotope ages of molybdenum deposits in east Qinling and their significance. Mineral Deposits 13:221–230 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang DH, Hou ZQ, Yang ZM, Li ZQ, Xu DX (2009) Geological and geochemical characteristics, metallogenetic mechanism and tectonic setting of carbonatite vein type Mo (Pb) deposits in the east Qinling molybdenum ore belt. Acta Geol Sin 83:1968–1984 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jian W, Lehmann B, Mao JW, Ye HS, Li ZY, He HJ, Zhang JG, Zhang H, Feng JW (2015) Mineralogy, fluid characteristics, and Re-Os age of the Late Triassic Dahu Au-Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling region, Central China: evidence for a magmatic-hydrothermal origin. Econ Geol 110:119–145
Jin XY, Li JW, Hofstra AH, Sui JX (2017) Magmatic–hydrothermal origin of the early Triassic Laodou lode gold deposit in the Xiahe–Hezuo district, West Qinling Orogen, China: implications for gold metallogeny. Mineral Deposita 52:883–902
Kesarwani M, Sarangi S, Srinivasan R, George BG, Singh SK, Bhattacharya S, Vasudev VN (2019) Origin of granodiorite hosted Neoarchaean orogenic gold ore deposits: stable isotopic and geochemical constraints with example from the Dharwar craton, southern India. Ore Geol Rev 107:754–779
Laflamme C, Jeon H, Reddy SM, Caruso S, Bui TH, Roberts MP, Voute F, Wacey D, Littman S, Hagemann S, Wacey D, Wing B, Kilburn MR (2016) In situ multiple sulfur isotope analysis by SIMS of pyrite, chalcopyrite, pyrrhotite, and pentlandite to refine magmatic ore genetic models. Chem Geol 444:1–5
LaFlamme C, Sugiono D, Thébaud N, Caruso S, Fiorentini M, Selvaraja V, Jeon H, Voute F, Martin L (2018) Multiple sulfur isotopes monitor fluid evolution of an Archean orogenic gold deposit. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 222:436–446
Li N, Pirajno F (2017) Early Mesozoic Mo mineralization in the Qinling Orogen: an overview. Ore Geol Rev 81:431–450
Li JW, Bi SJ, Sebly D, Chen L, Vasconcelos P, Thiede D, Zhou MF, Zhao XF, Li ZK, Qiu HN (2012a) Giant Mesozoic gold provinces related to the destruction of the North China craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 349–350:26–37
Li JW, Li ZK, Zhou MF, Chen L, Bi SJ, Deng XD, Qiu HN, Cohen B, Sebly D, Zhao XF (2012b) The Early Cretaceous Yangzhaiyu lode gold deposit, North China craton: a link between craton reactivation and gold veining. Econ Geol 107:43–79
Li DY, Xiao YL, Li WY, Zhu X, Williams HM, Li YL (2016) Iron isotopic systematics of UHP eclogites respond to oxidizing fluid during exhumation. J Metamorph Geol 34:987–997
Li JS, Xu D, Liang Z, Yang CL (2017) The fluid inclusion characteristics and significance of the Huaishuping gold deposit in Song County, Henan Province. Northwest Geol 50:115–127 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu HY, Hu SX, Guo K, He JR (2010) Metamorphism of Xiong'er group volcanic rocks in Machaoyin fault zone and its northern side. Volcanol Mineral Resour 21:275–285 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu SA, Li D, Li S, Teng FZ, Ke S, He Y, Lu Y (2014) High-precision copper and iron isotope analysis of igneous rock standards by MC–ICP–MS. J Anal Atom Spectrom 29:122–133
Lu XX, Wei XD, Dong Y, Yu ZP, Chang QL, Zhang GS (2004) Characteristics of gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling-Xiong’ershan area and mantle-derived ore fluids. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, p 128 (in Chinese)
Ludwig KR (2003) Isoplot 3.0, a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel, Berkeley Geochronological Centre Special Publication 4:1–71
Mao JW, Qiu YM, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang ZH, Garwin S, Ren FS (2002) Geology, distribution, and classification of gold deposits in the western Qinling belt, Central China. Mineral Deposita 37:352–377
Mattauer M, Matte P, Malavieille J, Tapponnier P, Maluski H, Xu Z, Lu Y, Tang Y (1985) Tectonics of the Qinling Belt: build-up and evolution of eastern Asia. Nature 317:496–500
McCuaig T, Kerrich R (1998) P-T-t-deformation-fluid characteristics of lode gold deposits: evidence from alteration systematics. Ore Geol Rev 12:381–453
Molnár F, Mänttäri I, O'Brien H, Lahaye Y, Pakkanen L, Johanson B, Käpyaho A, Sorjonen W, Whitehouse M, Sakellaris G (2016) Boron, sulphur and copper isotope systematics in the orogenic gold deposits of the Archaean Hattu schist belt, eastern Finland. Ore Geol Rev 77:133–162
No. 1 Geological Surveying Team (1989) Study on the geological characteristics of gold deposits and metallogenic prediction in the Northern Xiong’er mountains: Zhengzhou, Henan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development, 112 p (in Chinese)
Ohmoto H, Rye RO (1979) Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In: Barnes HL (ed) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits. Wiley, New York, pp 509–567
Pang XC, Yang CL, Zhang HJ, Xu D (2016) Zircon U-Pb dating for Wuzhangshan rock mass in Xiong’ershan of western Henan Province, and its geological significance. J Mineral Petrol 36:57–65 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Poitrasson F, Freydier R (2005) Heavy iron isotope composition of granites determined by high resolution MC-ICP-MS. Chem Geol 222:132–147
Poitrasson F, Halliday AN, Lee DC, Levasseur S, Teutsch N (2004) Iron isotope differences between Earth, Moon, Mars and Vesta as possible records of contrasted accretion mechanisms. Earth Planet Sci Lett 222:253–266
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Deng J, McIntire D, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Chang ZS, Zhu R, Li KN, Goldfarb R (2020) The giant Zaozigou Au–Sb deposit in West Qinling, China: magmatic- or metamorphic–hydrothermal origin? Mineral Deposita 55:345–362.
Ray JS, Ramesh R (1999) A fluid–rock interaction model for carbon and oxygen isotopic variations in altered carbonatites. J Geol Soc India 54:179–186
Ray JS, Ramesh R, Pande K (1999) Carbon isotopes in Kerguelen plume derived carbonatites: evidence for recycled inorganic carbon. Earth Planet Sci Lett 170:205–214
Ridley J, Diamond L (2000) Fluid chemistry of orogenic lode gold deposits and implications for genetic models. Soc Econ Geol Rev 13:141–162
Santos RV, Clayton RN (1995) Variations of oxygen and carbon isotopes in carbonatites: a study of Brazilian alkaline complexes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1339–1352
Schuessler JA, Schoenberg R, Sigmarsson O (2009) Iron and lithium isotope systematics of the Hekla volcano, Iceland: evidence for Fe isotope fractionation during magma differentiation. Chem Geol 258:78–91
Selvaraja V, Fiorentini ML, Jeon H, Savard DD, LaFlamme CK, Guagliardo P, Caruso S, Bui TH (2017) Evidence of local sourcing of sulfur and gold in an Archaean sediment-hosted gold deposit. Ore Geol Rev 89:909–930
Sillitoe RH, Thompson JFH (1998) Intrusion-related vein gold deposits: types, tectono-magmatic settings and difficulties of distinction from orogenic gold deposits. Resour Geol 48:237–250
Smoliar MI, Walker RJ, Morgan JW (1996) Re-Os ages of group IIA, IIIA, IVA and VIB iron meteorites. Science 271:1099–1102
Stein HJ, Markey RJ, Morgan JW, Du A, Sun Y (1997) Highly precise and accurate Re–Os ages for molybdenite from the East Qinling molybdenum belt, Shaanxi Province, China. Econ Geol 92:827–835
Stüwe K (1998) Tectonic constraints on the timing relationships of metamorphism, fluid production and gold-bearing quartz vein emplacement. Ore Geol Rev 13:219–228
Sun WD, Li SG, Chen YD, Li YJ (2002) Timing of syn–orogenic granitoids in the South Qinling, Central China: constraints on the evolution of the Qinling–Dabie orogenic belt. J Geol 110:457–468
Sun J, Zhu XK, Li SZ (2015) Fe isotope biogeochemistry and its applications. Acta Petrol Mineral 34:777–784 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Swain SK, Sarangi S, Srinivasan R, Sarkar A, Bhattacharya S, Patel SC, Sawkar RH (2015) Isotope (C and O) composition of auriferous quartz carbonate veins, central lode system, Gadag Gold Field, Dharwar Craton, India: implications to source of ore fluids. Ore Geol Rev 70:305–320
Syverson DD, Pester NJ, Craddock PR, Seyfried JWE (2014) Fe isotope fractionation during phase separation in the NaCl–H2O system: an experimental study with implications for seafloor hydrothermal vents. Earth Planet Sci Lett 406:223–232
Syverson DD, Luhmann AJ, Tan C, Borrok DM, Ding K, Seyfried JWE (2017) Fe isotope fractionation between chalcopyrite and dissolved Fe during hydrothermal recrystallization: an experimental study at 350 °C and 500 bars. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 200:87–109
Taylor HP (1974) The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition. Econ Geol 69:843–883
Taylor HE, Frechen J, Degens ET (1967) Oxygen and carbon isotope studies of carbonatites fromthe Laacher See District, West Germany and the Alno District Sweden. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 31:407–430
Thode HG, Monster J, Durford HB (1961) Sulphur isotope geochemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 25:150–174
Valley JW (1986) Stable isotope geochemistry of metamorphic rocks. In: Walley JW, Taylor HP, O’Neil JR (eds) Stable isotopes on high temperature geological processes. Rev Mineral 16:445–489
Wang XX, Wang T, Castro A, Pedreira R, Lu XX, Xiao QH (2011a) Triassic granitoids of the Qinling orogen, Central China: genetic relationship of enclaves and rapakivi textured rocks. Lithos 126:369–387
Wang Y, Zhu XK, Mao JW, Li ZH, Cheng YB (2011b) Iron isotope fractionation during skarn-type metallogeny: a case study of Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe–Au deposit in the middle-lower Yangtze valley. Ore Geol Rev 43:194–202
Wang CM, Zhang D, Wu GG, Santosh M, Zhang J, Xu YG, Zhang YY (2014) Geological and isotopic evidence for a magmatic–hydrothermal origin of the Ag–Pb–Zn deposits in the Lengshuikeng district, east-central China. Mineral Deposita 49:733–749
Wang Y, Zhu XK, Cheng YB (2015) Fe isotope behaviours during sulfide-dominated skarn-type mineralization. J Asian Earth Sci 103:374–392
Wang CM, Bagas L, Lu YJ, Santosh M, Du B, McCuaing TC (2016a) Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen: insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping. Earth-Sci Rev 156:39–65
Wang CM, Chen L, Bagas L, He XY, Lai XR (2016b) Zircon U–Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes for the Taishanmiao aluminous A-type granites: implications for Early Cretaceous lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton. Int J Earth Sci 105:1563–1589
Wang CM, Lu YJ, He XY, Wang QH, Zhang J (2016c) The Paleoproterozoic diorite dykes in the southern margin of the North China Craton: insight into rift-related magmatism. Precambrian Res 227:26–46
Wang JH, Chen L, Su QW, Wang HR, Liu YF, Lai SH (2016d) Geology, isotopic geochemistry and metallogenesis of Huaishuping gold deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province. Mineral Deposits 35:524–538 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang CM, Deng J, Bagas L, Wang Q (2017) Zircon Hf–isotopic mapping for understanding crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the Eastern Qinling Orogen. Gondwana Res 50:293–310
Wang CM, He XY, Carranza EJM, Cui CM (2019) Paleoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the southern margin of the North China Craton, Central China: implications for the Columbia supercontinent. Geosci Front 10:1543–1560
Wawryk CM, Foden JD (2015) Fe-isotope fractionation in magmatic-hydrothermal mineral deposits: a case study from the Renison Sn–W deposit, Tasmania. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 150:285–298
Zhang LG (1989) Petrogenic and Minerogenic theories and prospecting. Beijing University of Technology Press, Beijing, p 200 (in Chinese with detailed English abstract)
Zhang GJ, Guo AS, Yang SD, Xu D (2016) Zoning characteristics of the primary halos and geological significance in Huaishuping gold deposit, Henan Province. Gold Sci Tech 24:37–43 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao GC, He YH, Sun M (2009) The Xiong'er volcanic belt at the southern margin of the North China Craton: petrographic and geochemical evidence for its outboard position in the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia supercontinent. Gondwana Res 17:145–152
Zhou Q, Fan ZY (2015) Discovery of a large-scale gold deposit in Huaishuping district, Songxian. Resources Guide 9:49
Zhu ZY, Jiang SY, Mathur R, Cook NJ, Yang T, Wang M, Ma L, Ciobanu Cristiana L (2018) Iron isotope behavior during fluid/rock interaction in K-feldspar alteration zone – a model for pyrite in gold deposits from the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 222:94–116
Acknowledgements
This study is jointly sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Number 41872080), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Number 2652019197), Most Special Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources in China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (Number MSFGPMR201804) and the 111 Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (Number BP0719021). We are grateful to Heejin Jeon, Vikraman Selvaraja, Shengao Liu, Mu Liu and Xu Wang for their help with the C–H–O–S–Fe–Os–Re isotope analysis. We are also grateful to the Editor Prof. Georges Beaudoin and Associate Editor Prof. Frank Melcher for their valuable help in handling this paper, and Prof. Franco Pirajno and the anonymous referees for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: F. Melcher
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Deng, J., Bagas, L. et al. Origin and classification of the Late Triassic Huaishuping gold deposit in the eastern part of the Qinling-Dabie Orogen, China: implications for gold metallogeny. Miner Deposita 56, 725–742 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-020-01004-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-020-01004-5