Abstract
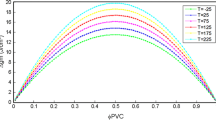
A novel blend flat-sheet ultrafiltration (UF) membrane was prepared by immersion precipitation phase inversion using polyacrylonitrile (PAN) and polysulfone (PSF) as membrane materials. The relationship between casting solution formula and separation performance of blend UF membranes was analyzed. Experimental results show that the different casting solution formula such as polymer concentration, blending ratio, organic additives and inorganic nanometer had a significant effect on the performance of blend UF membranes. With the increase of polymer concentration, the water flux and porosity of blend UF membrane decreased obviously while the rejection rate showed an upward trend. The separation performance of blend UF membrane exhibited the opposite trend when the proportion of PAN and PSF increased. The water flux of blend UF membrane prepared with 0.04% NaA zeolite was 176.9 L/m2h, which was nearly three times higher than that of the original membrane. The optimum formulation of blend UF membrane is as follows: polymer concentration of 20%, PAN to PSF mass ratio of 8:2, PEG additive content of 0.5%, NaA zeolite content of 0.04%. The novel blend UF membrane exhibits good pressure stability and pollution resistance performance.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng P, Li X, Su J et al (2018) Recent water quality trends in a typical semi-arid river with a sharp decrease in streamflow and construction of sewage treatment plants. Environ Res Lett 13(1):1–10
Tang C, Yang Z, Guo H et al (2018) Potable water reuse through advanced membrane technology. Environ Sci Technol 52(18):10215–10223
Wu X, Xie Z, Wang H, Zhao C, Ng D, Zhang K (2018) Improved filtration performance and antifouling properties of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes by blending with carboxylic acid functionalized polysulfone. RSC Adv 8(14):7774–7784
Martín J, Montaña E, Asuero AG (2018) Recovery of anthocyanins using membrane technologies: a review. Crit Rev Anal Chem 48(3):143–175
Yang J, Li HN, Chen ZX, He A, Zhong QZ, Xu ZK (2019) Janus membranes with controllable asymmetric configuration for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J Mater Chem A 7:7907–7917
Atkinson S (2018) Coated UF membranes improve virus removal from treated municipal wastewater. Membr Technol 2:6
Wang L, Li G, Li Y (2019) Enhanced treatment of composite industrial wastewater using anaerobic-anoxic-oxic membrane bioreactor: performance, membrane fouling and microbial community. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94:2292–2304
Mercer E, Davey CJ, Campo P et al (2018) Quantification of liquid phase faecal odourants to evaluate membrane technology for wastewater reuse from decentralised sanitation facilities. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 5(1):161–171
Moideen IK, Isloor AM, Qaiser AA et al (2018) Separation of heavy metal and protein from wastewater by sulfonated polyphenylsulfone ultrafiltration membrane process prepared by glycine betaine enriched coagulation bath. Korean J Chem Eng 35(6):1–9
Han R, Wu P (2019) High-performance graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with continuous nanochannels prepared by in situ oxidation of MXene. J Mater Chem A 7:6475–6481
Rahimpour A, Madaeni SS, Mansourpanah Y (2010) High performance polyethersulfone UF membrane for manufacturing spiral wound module: preparation, morphology, performance, and chemical cleaning. Polym Adv Technol 18(5):403–410
Yiantsios SG, Sioutopoulos D, Karabelas AJ (2005) Colloidal fouling of RO membranes: an overview of key issues and efforts to develop improved prediction techniques. Desalination 183(1):257–272
Reverberi AP, Maga L, Cerrato C, Fabiano B (2014) Membrane processes for water recovery and decontamination. Curr Opin Chem Eng 6:75–82
Wang K, Lin X, Jiang G, Liu JZ, Jiang L, Doherty CM, Hill AJ, Xu T, Wang H (2014) Slow hydrophobic hydration induced polymer ultrafiltration membranes with high water flux. J Membr Sci 471(6):27–34
Yi Y, Ramos TL, Heo J et al (2018) Zwitterionic poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymer/poly(arylene ether sulfone) blends for fouling-resistant desalination membranes. J Membr Sci 561:69–78
Xinya W, Changfa X, Hailiang L et al (2018) A study on fabrication of PVDF-HFP/PTFE blend membranes with controllable and bicontinuous structure for highly effective water-in-oil emulsion separation. RSC Adv 8(49):27754–27762
Mohsen A, Mahdi PC, Morteza S (2015) Surface modification of PAN hollow fiber membrane by chemical reaction. Fibers Polym 16(4):788–793
Zhao X, Su Y, Chen W et al (2012) Grafting perfluoroalkyl groups onto polyacrylonitrile membrane surface for improved fouling release property. J Membr Sci s 415–416:824–834
Liang B, Zhan W, Qi G, Lin S, Nan Q, Liu Y, Cao B, Pan K (2015) High performance graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile composite pervaporation membranes for desalination applications. J Mater Chem A 3(9):5140–5147
Zhang X, Yang S, Bing Y et al (2018) Advanced modified polyacrylonitrile membrane with enhanced adsorption property for heavy metal ions. Sci Rep 8(1):1260
Zhao L, Liu M, Xu Z et al (2015) Modification of polysulfone hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes using hyperbranched polyesters with different molecular weights. Polym Adv Technol 26(4):353–361
Lock SSM, Lau KK, Shariff AM, Yeong YF, Bustam MA (2018) Thickness dependent penetrant gas transport properties and separation performance within ultrathin polysulfone membrane: insights from atomistic molecular simulation. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 56(2):131–158
Wang H, Lu X, Lu D, Wang P, Ma J (2019) Development of a high-performance polysulfone hybrid ultrafiltration membrane using hydrophilic polymer-functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 as filler. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47353
Hoffmann C, Silau H, Pinelo M, Woodley JM, Daugaard AE (2018) Surface modification of polysulfone membranes applied for a membrane reactor with immobilized alcohol dehydrogenase. Materials-today Commun 14:160–168
Moideen IK, Isloor AM, Ismail AF et al (2016) Fabrication and characterization of new PSF/PPSU UF blend membrane for heavy metal rejection. Desalin Water Treat 57(42):19810–19819
Zhang J, Xu Y, Chen S et al (2018) Enhanced antifouling and antibacterial properties of poly (ether sulfone) membrane modified through blending with sulfonated poly (aryl ether sulfone) and copper nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 434:806–815
Qin Y, Yang H, Xu Z, Li F (2018) Surface modification of polyacrylonitrile membrane by chemical reaction and physical coating: comparison between static and pore-flowing procedures. ACS Omega 3(4):4231–4241
Xiao C (2013) Preparation and properties of polysulfone/polyacrylonitrile blend membrane and its modification with hydrolysis. Desalinat Water Treat 51(19–21):3979–3987
Güneşdurak S, Ormancıacar T, Tüfekci N (2018) Effect of PVP content and polymer concentration on polyetherimide (PEI) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN) based ultrafiltration membrane fabrication and characterization. Water Sci Technol 142:329–339
Klein F, Ricketts RT, Rohrer TR, Jones Jr WI, Clark PM, Flickinger MC (1984) Membrane ultrafiltration: concentration of interleukin-3. Appl Environ Microbiol 47(5):1023–1026
Liu P, Zhang S, Wang Y, Lu Y, Jian X (2015) Preparation and characterization of thermally stable copoly(phthalazinone biphenyl ether sulfone) hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes. Appl Surf Sci 335:189–197
Madhuri AP, Sudhir SK, Sandeep KK et al (2010) Poly(acrylonitrile) ultrafiltration membranes. II. Membrane morphology and permeation characteristics. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 43(15):2074–2085
Tarus B, Fadel N, Al-Oufy A et al (2016) Effect of polymer concentration on the morphology and mechanical characteristics of electrospun cellulose acetate and poly (vinyl chloride) nanofiber mats. Alexandria Eng J 55:2975–2984
Liu T, Lin W, Huang L et al (2005) Surface characteristics and hemocompatibility of PAN/PVDF blend membranes. Polym Adv Technol 16(5):413–419
Hwang LL, Tseng HH, Chen JC (2011) Fabrication of polyphenylsulfone /polyetherimide blend membranes for ultrafiltration applications: the effects of blending ratio on membrane properties and humic acid removal performance. J Membr Sci 384(1):72–81
Han R, Zhang S, Cheng L et al (2009) Effect of NaA zeolite particle addition on poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) composite ultrafiltration (UF) membrane performance. J Membr Sci 345(1):5–12
Qu F, Rui S, Li P et al (2017) Understanding the effect of zeolite crystal expansion/contraction on separation performance of NaA zeolite membrane: a combined experimental and molecular simulation study. J Membr Sci 539:14–23
Muntha ST, Siddiq M, Kausar A et al (2018) Mixed matrix membranes of polysulfone /polyimide reinforced with modified zeolite based filler: preparation, properties and application. Chin J Polym Sci 36(1):1–13
Basu S, Mukherjee S, Balakrishnan M et al (2018) Polysulfone/nanocomposites mixed matrix ultrafiltration membrane for the recovery of Maillard reaction products. Membrane Water Treat 9(2):105–113
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a project of Liaoning Science and Technology Department Fund-funded Projects (2020-BS-158, 20180550432), and Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project for College Students (201910153082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Niu, W., Wang, L. et al. Influence of casting solution formula on the performance of novel polyacrylonitrile/polysulfone blend ultrafiltration membrane. J Polym Res 27, 213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02192-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02192-4