Abstract
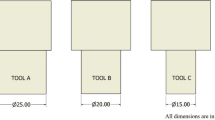
In this study, mechanical properties, macrostructure and microstructure of the friction stir spot weld joints were investigated under the influence of pinless tool geometry and different rotation speed parameters (1350, 1850 and 2530 rpm) using Al5754 plates. Tensile shear strength tests were carried out for joints of different process parameters, and fracture surfaces were inspected by scanning electron microscopy; in addition, fracture modes of the joints were also evaluated. According to the results, the maximum strength values were obtained at 1850 rpm rotation speed, and ductile and brittle fractures were observed together.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mert Ş, and Arıcı A, Sci Technol Weld J 16 (2011) 6.
Sun Y, Fujii H, Zhu S, and Guan S, J Mater Process Technol 264 (2019) 414.
Meran C, and Çolak M, J Fac Eng Arch Gazi Univ 23 (2008) 3.
Li Z, Yue Y, Ji S, Peng C, and Wang, L, Mater Des 94 (2016) 368.
Lakshminarayanan A K, Annamalai V E, and Elangovan K, J Mater Res Technol 4 (2015) 3.
Tozakı Y, Uematsu Y, and Tokajı K, Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 30 (2007) 2.
Piccini M J, and Svoboda H G, J Manuf Process 26 (2017).
Güler H, JOM (2014).
Klobčar D, Tušek J, Skumavc A, and Smolej A, Metalurgıja 53 (2014) 1.
Wang T, Sidhar H, Mishra R S, Hovanski Y, Upadhyay P, and Carlson B, Sci Technol Weld Join 24 (2018) 2.
Mubiayi M P, Akinlabi E T, and Makhatha M E, Microstructure and Chemical Analysis of Friction Stir Spot Welding Between Aluminium and Copper (Case Study), Structural Integrity, vol 6, Springer, Cham (2019), p 123.
Heydari F, Amadeh A A, Ojo O O, and Hasanniya, M H, Sādhanā, 44 (2019) 73.
Kang M, Yoon J, and Kim C, Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2019).
Gerlich A, Avramovic-Cingara G, and North T H, Mater Sci Forum 519-521 (2006).
Mahmoud T S, and Khalifa T A, JMEPEG 23 (2014).
Pathak N, Bandyopadhyay K, Sarangi M, and Panda S K, JMEPEG 22 (2013) 131.
Dedeoğlu O, and Güler Özgül H, J Manuf Mater Process 3 (2019) 8.
Güler H, Mater Technol 49 (2015) 3.
Klobčar D, Tušek J, Smolej A, and Simončič S, Weld World 59 (2015) 269.
Suryanarayanan R, and Sridhar V G, Metallogr Microstr Anal (2020).
Gerlich A P, and North T H, Innovations in Materials Manufacturing, Fabrication, and Environmental Safety, Friction Stir Spot Welding, vol 8, CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton (2010), p 193.
Ojo O O, Taban E, and Kaluc E, Mater Test 60 (2018) 10.
Lathabai S, Painter M J, Cantin G M D, and Tyagi V K, Scripta Mater 55 (2006) 10.
Zhikang S, Ding Y, and Gerlich A P, Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci (2019).
Tozaki Y, Uematsu Y, and Tokaji K, J Mater Process Technol 210 (2010) 844.
Ding M, Wang T, Maerz B, Robertson S, Sun Z, Fan L, Shi Y, and Wu H, Ceram Int 45 (2019) 21127.
Warke W R, and Elsea A R, Electron Microscopic Fractography, Ductile Fracture, Defense Metals Information Center Battele Memorial Institute, Ohio (1962), p 7.
Brooks C R, and McGill B L, Mater Charact 33 (1994) 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özgül, H.G., Dedeoğlu, O. Investigations of the Mechanical and Microstructural Effects of Pinless Tool Geometry on Friction Stir Spot Welding Process. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 2281–2289 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02034-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02034-3