Abstract
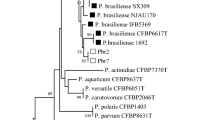
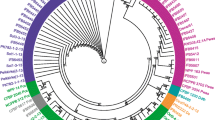
Recent observations of increasing incidences of potato plants showing blackleg symptoms have caused serious concern for potato growers and traders in Egypt. Potato plants showing blackleg and soft rot symptoms were sampled from main potato-growing areas in Egypt during three successive seasons. Dickeya spp., Pectobacterium carotovorum and Pectobacterium atrosepticum were successfully isolated and identified from symptomatic potato plants (tubers and stems). The identity of bacterial isolates was reviled by identification methods based on different biological principles: cultural, biochemical and molecular methods. Specific primers targeting different genomic loci were selected for molecular identification, utilizing either conventional or real-time PCR. Multiple species were isolated from some infected samples revealing complex infection, which confirm the complexity and interaction of soft rot and blackleg diseases. Given that no previous reports on Dickeya diseases in Egypt were confirmed since the recent revision of its taxonomy, the result of PCR with Dickeya spp. was furtherly confirmed using DNA sequencing assay. BLASTn analyses of 16S rDNA sequences showed similarity to several species of Dickeya, with 99% nucleotide similarity to strains of, D. chrysanthemi, D. dianthicola and D. solani, respectively. Furthermore, the most commonly identified bacterial pathogen in the tested samples was P. carotovorum followed by P. atrosepticum and Dickeya spp., while P. brasiliense was never detected in any of the collected samples confirmed by real-time PCR assay. The results of such field survey suggested to help the decision makers in Egypt to establish an action plan to face the increasing risk of potato diseases caused by Dickeya spp. for the benefit of Egyptian domestic production.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Elhak MZ (2005) Potato production and storage in Egypt. Bulletin of the General Administration of Agricultural Culture, Egyptian Ministry of Agriculture and Land Reclamation, No (9) p 84 (in Arabic)
Adeolu M, Seema A, Naushad S, Gupta RS (2016) Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the “Enterobacteriales”: proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:5575–5599
Agrios GN (2005) Plant pathology, 5th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Agrios GN (2006) Bacterial soft rots, 5th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Ahmed Asia RE (2009) Pathological studies on potato soft rot disease caused by Erwiniacarotovora subsp. carotovora. Msc thesis, Alex Univ, Fac of Agric, Damnhour branch, Egypt
Ashmawy NA, Nagia MJ, Alia AS, ElBebany AF (2015) Identification and genetic characterization of Pectobacterium spp. and related Enterobacteriaceae causing potato soft rot diseases in Egypt. J Pure Appl Microbiol 9:1847–1858
Behiry SI (2009) Studies on potato bacterial soft rot disease in Egypt. M.Sc. thesis. Alex University, Agricultural Botany Department, Faculty of Agric, Egypt
Chapman D, Purse BV, Roy HE, Bullock JM (2017) Global trade networks determine the distribution of invasive non-native species. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 26(8):907–917
Charkowski A, Sharma K, Parker ML, Secor GA, Elphinstone J (2020) Bacterial diseases of potato, chp 11. In: Campos H, Hortis O (eds) The potato crop, pp 353–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28683-5_10
Czajkowski R, Grzegorz G, van der Wolf J (2009) Distribution of Dickeya spp. and Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. carotovorum in naturally infected seed potatoes. Eur J Plant Pathol 125:263–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9480-9
Czajkowski R, de Boer WJ, Velvis H, van der Wolf J (2010) Systemic colonization of potato plants by a soilborne, green fluorescent protein-tagged strain of Dickeya sp. biovar 3. Phytopathology 100:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-100-2-0134
Czajkowski R, Pérombelon MC, van Veen JA, van der Wolf JM (2011) Control of blackleg and tuber soft rot of potato caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya species: a review. Plant Pathol 60(6):999–1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2011.02470.x
Darrasse A, Priou S, Kotoujansky A, Bertheau Y (1994) PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism of a pel gene as a tool to identify Erwinia carotovora in relation to potato diseases. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1437–1443
De Boer SH, Rubio I (2004) Blackleg of potato. Plant Health Instr. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHI-I-2004-0712-01
De Boer SH, Ward LJ (1995) PCR detection of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica associated with potato tissue. Phytopathology 85(8):854–858
De Boer SH, Li X, Ward LJ (2012) Pectobacterium spp. associated with bacterial stem rot syndrome of potato in Canada. Phytopathology 102:937–947. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-04-12-0083-R
Degefu Y, Potrykus M, Golanowska M, Virtanen E, Lojkowska E (2013) A new clade of Dickeya spp. plays a major role in potato blackleg outbreaks in North Finland. Ann Appl Biol 162:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12020
Deutsch CA, Tewksbury JJ, Tigchelaar M, Battisti DS, Merrill SC, Huey RB, Naylor RL (2018) Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate. Science 361(6405):916–919. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat3466
du Raan S, Coutinho TA, van der Waals JE (2016) Cardinal temperature differences, determined in vitro, between closely related species and subspecies of pectinolytic bacteria responsible for blackleg and soft rot on potatoes. Eur J Plant Pathol 144:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0773-x
Duarte V, de Boer SH, Ward LJ, de Oliveira AM (2004) Characterization of atypical Erwinia carotovora strains causing blackleg of potato in Brazil. J Appl Microbiol 96:535–545. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02173.x
Dupuis B, Michelante D, Garcia N, Nimal C, Stilman D (2005) Evolution of Erwinia’s potato contaminations in the Walloon Region during the seasons 2003 and 2004: analysis of field and storage infections. Paper presented at the 16th triennial conference of the EAPR. European Association for Potato Research, Bilbao, Spain
El-Kazazz SA (1984) Physiopathological studies on soft rot bacteria with special reference to the possible production of toxin. Ph.D. thesis. Alex Univ, Plant Pathol Dep, Fac Agric, Egypt
Fahy PC, Hayward AC (1983) Plant bacterial disease (a diagnostic guide). Academic Press, Sydney, p 349
FAO STAT (2018). http://www.fao.org/statistics/en/
Hélias V, Andrivon D, Jouan B (2000) Internal colonization pathways of potato plants by Erwinia carotovora ssp. atroseptica. Plant Pathol 49:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3059.2000.00431.x
Hélias V, Le Roux AC, Boishardy M, Aujean JM, Copin P, Perramant M et al. (2004) Erwinias causing blackleg in France: species/subspecies and their distribution in 2003. Paper presented at the E.A.P.R. pathology section meeting, Lille, France
Heuer H, Smalla K (1997) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis for studying soil microbial communities. In: Van Elsas JD, Trevors JT, Wellington MH (eds) Modern soil microbiology. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 353–373
Hiddink GA, Termorshuizen AJ, Raaijmakers JM, van Bruggen AHC (2005) Effect of mixed and single crops on disease suppressiveness of soils. Phytopathology 95:1325–1332. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-95-1325
Hyman LJ, Toth IK, Pérombelon MC (1998) Isolation and identification. In: Methods for the detection and quantification of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica on Potato. Laboratory Manual, Scottish Crop Research Institute Annual Report, Dundee, Scotland, United Kingdom pp 64–71
Janse JD, Ruissen MA (1988) Characterization and classification of Erwinia chrysanthemi strains from several hosts in the Netherlands. Phytopathology 78:800–808
Kang HW, Kwon SW, Go SJ (2003) PCR-based specific and sensitive detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. carotovorum by primers generated from a URP-PCR fingerprinting-derived polymorphic band. Plant Pathol 52:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3059.2003.00822.x
King E, Ward M, Raney D (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Laurila J, Hannukkala A, Nykyri J, Pasanen M, Hélias V, Garlant L, Pirhonen M (2010) Symptoms and yield reduction caused by Dickeya spp. strains isolated from potato and river water in Finland. Eur J Plant Pathol 126:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9537-9
Lee YA, Yu CP (2006) A differential medium for the isolation and rapid identification of a plant soft rot pathogen, Erwinia chrysanthemi. J Microbiol Methods 64:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2005.04.031
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S, Citovsky V, Sriariyanum M, Ronald P, Dow M, Verdier V, Beer SV, Machado MA, Toth I, Salmond G, Foster GD (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:614–629. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00804.x
Nassar A, Darrasse A, Lemattre M, Kotoujansky A, Dervin C, Vedel R, Bertheau Y (1996) Characterization of Erwinia chrysanthemi by pectinolytic isozyme polymorphism and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified fragments of pel genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2228–2235
Ngadze E, Brady CL, Coutinho T, Van Der Waals JE (2012) Pectinolytic bacteria associated with potato soft rot and blackleg in South Africa and Zimbabwe. Eur J Plant Pathol 134:533–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-012-0036-z
Pérombelon MC (1974) The role of the seed tuber in the contamination by Erwinia carotovora of potato crops in Scotland. Potato Res 17:187–199
Pérombelon MC (1992) Potato blackleg: epidemiology, host-pathogen interaction and control. Neth J Plant Pathol 98:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974480
Pérombelon MC (2002) Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: an overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol 51:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0032-0862.2001.Shorttitle.doc.x
Pérombelon MC, Kelman A (1980) Ecology of the soft rot erwinias. Annu Rev Phytopathol 18:361–387
Pérombelon MC, Van Der Wolf JM (2002) Methods for the detection and quantification of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. atrosepticum) on potatoes: a laboratory manual. Scot Crop Res Instit Ann Report 10
Pickup RW (1991) Development of molecular methods for the detection of specific bacteria in the environment. J Gen Microbiol 137:1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-137-5-1009
Prior P, Steva H (1990) Characteristics of strains of Pseudomonas solanacearum from the French West Indies. Plant Dis 74:1317
Pritchard L, Humphris S, Saddler GS, Parkinson NM, Bertrand V, Elphinstone JG, Toth IK (2012) Detection of phytopathogens of the genus Dickeya using a PCR primer prediction pipeline for draft bacterial genome sequences. Plant Pathol 62:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2012.02678.x
Rosado AS, Duarte GR, Seldin L, Van Elsas JD (1998) Genetic diversity of nifH gene sequences in Paenibacillus azotofixans strains and soil samples analyzed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2770–2779
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Samson R, Legendre JB, Christen R, Fischer-Le Saux M, Achouak W, Gardan L (2005) Transfer of Pectobacterium chrysanthemi (Burkholder et al. 1953; Brenner et al. 1973) and Brenneria paradisiaca to the genus Dickeya gen. nov. as Dickeya chrysanthemi comb. nov. and Dickeya paradisiaca comb. nov. and delineation of four novel species, Dickeyadadantii sp. nov., Dickeya dianthicola sp. nov., Dickeya dieffenbachiae sp. nov. and Dickeya zeae sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1415–1427. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02791-0
Schaad NW (1988) Laboratory guide for the identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 2nd edn. APS Press, Minnesota
Schaad N, Jones J, Chun W (2001) Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 3rd edn. APS, St Paul. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3059.2001.00635.x
Slawiak M, Beckhoven JRCM, Speksnijder AGCL, Czajkowski R, Grabe G, van der Wolf JM (2009) Biochemical and genetical analysis reveal a new clade of biovar 3 Dickeya spp. strains isolated from potato in Europe. Eur J Plant Pathol 125:245–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9479-2
Suslow TW, Schroth MN, Isaka M (1982) Application of a rapid method of Gram differentiation of plant pathogenic and saprophytic bacteria without staining. Phytopathology 72:917–918. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-72-917
Toth IK, van der Wolf JM, Saddler G, Lojkowska E, Hélias V, Pirhonen M, Tsror L, Elphinstone JG (2011) Dickeya species: an emerging problem for potato production in Europe. Plant Pathol 60:385–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2011.02427.x
Tsror L, Erlich O, Lebiush S, Hazanovsky M, Zig U, Slawiak M et al (2008) Assessment of recent outbreaks of Dickeya spp. (syn. Erwinia chrysanthemi) slow wilt in potato crops in Israel. Eur J Plant Pathol 123(3):311–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9368-0
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (2016) UNECE standard s-1 concerning the marketing and commercial quality control of seed potatoes, 2016 ed, New York and Geneva. https://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trade/agr/standard/potatoes/S-1_SeedPotatoes_2016_E.pdf
van der Merwe JJ, Coutinho TA, Korsten L, van der Waals JE (2010) Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp brasiliensis causing blackleg on potatoes in South Africa. Eur J Plant Pathol 126:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9531-2
van der Wolf JM, De Boer SH (2007) Bacterial pathogens of potato. In: Vreugdenhil D (ed) Potato biology and biotechnology, advances and perspectives. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 595–619
van der Wolf JM, Nijhuis EH, Kowalewska MJ, Saddler GS, Parkinson N, Elphinstone JG, Pritchard L, Toth IK, Lojkowska E, Potrykus M, Waleron M, de Vos P, Cleenwerck I, Pirhonen M, Garlant L, Hélias V, Pothier JF, Pflüger V, Duffy B, Tsror L, Manulis S (2013) Dickeya solani sp. nov., a pectinolytic plant pathogenic bacterium isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.052944-0
Waleron M, Waleron K, Lojkowska E (2013) Occurrence of Pectobacterium wasabiae in potato field samples. Eur J Plant Pathol 137:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0227-2
Acknowledgements
The work was partially supported by Potato Brown Rot Project (PBRP), Ministry of Agriculture, Dokki, Giza, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elhalag, K., Elbadry, N., Farag, S. et al. Etiology of potato soft rot and blackleg diseases complex in Egypt. J Plant Dis Prot 127, 855–871 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-020-00354-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-020-00354-6