Abstract
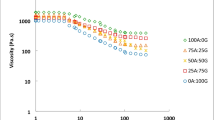
The interactions between sodium caseinate (NaCas) and basil seed gum (BSG) in the presence of calcium chloride (CaCl2) were investigated. The phase behavior of the mixed aqueous dispersions and their gels revealed a homogeneous mixture, obtained at the higher concentrations of both CaCl2 and BSG. The Herschel-Bulkley model sufficiently fitted the flow behavior of the mixture solution data. Apparent viscosity increased significantly (p < 0.05) by increasing the concentration of BSG, where the addition of CaCl2 had no significant effect on the viscosity of the samples (p > 0.05). Furthermore, there was an increase in thixotropy due to the higher concentrations of BSG and CaCl2. Based on the frequency sweep test, at the low frequencies, a more gel-like behavior was observed in the case of the higher concentrations of either BSG or CaCl2. The rheological and SEM data suggested that the stronger structure of NaCas-BSG gel in the presence of the higher concentrations of CaCl2 was related to the induction of complex formation between the two biopolymers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
C.C. Sánchez, J.M.R. Patino, Food Hydrocoll. 19(3), 407–416 (2005)
E. Dickinson, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 288(1), 3–11 (2006)
E. Dickinson, C. Eliot, Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 29(2), 89–97 (2003)
B. Lo, E. Gorczyca, S. Kasapis, B. Zisu, Ultrason. Sonochem. 58, 104525 (2019)
A.L.M. Braga, M. Menossi, R.L. Cunha, Int. Dairy J. 16(5), 389–398 (2006)
A.J. Carr, P.A. Munro, O.H. Campanella, Int. Dairy J. 12(6), 487–492 (2002)
P. Thomar, T. Nicolai, L. Benyahia, D. Durand, Int. Dairy J. 31(2), 100–106 (2013)
S. Mirarab Razi, A. Motamedzadegan, A. Shahidi, A. Rashidinejad, Food Hydrocoll. 82, 268–277 (2018a)
E. Dickinson, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 9(10), 347–354 (1998)
K. K. T. Goh, A. Teo, A. Sarkar and H. Singh, in Milk Proteins (Third Edition), edited by M. Boland and H. Singh (Academic Press, 2020), pp. 499–535
A.A. Perez, C.R. Carrara, C.C. Sánchez, J.M. Rodríguez Patino, L.G. Santiago, Food Chem. 116(1), 104–113 (2009)
H. Khalesi, B. Emadzadeh, R. Kadkhodaee, Y. Fang, Food Hydrocoll. 59, 45–49 (2016)
Q. Zhao, Z. Long, J. Kong, T. Liu, D. Sun-Waterhouse, M. Zhao, Food Hydrocoll. 43, 137–145 (2015)
L. Liu, Q. Zhao, T. Liu, Z. Long, J. Kong, M. Zhao, Food Hydrocoll. 27(2), 339–346 (2012)
S.M. Loveday, A. Ye, S.G. Anema, H. Singh, Food Res. Int. 54(1), 111–117 (2013)
C. Schmitt, S.L. Turgeon, Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 167(1), 63–70 (2011)
W. Xiong, C. Ren, M. Tian, X. Yang, J. Li, B. Li, Food Hydrocoll. 73, 41–50 (2017)
S.M. Razi, A. Motamedzadegan, L. Matia-Merino, S.-A. Shahidi, A. Rashidinejad, Food Hydrocoll. 94, 399–410 (2019)
A. Ye, International Journal of Food Science & Technology 43(3), 406–415 (2008)
R.N. Tharanathan, Y.V. Anjaneyalu, Aust. J. Chem. 28(6), 1345–1350 (1975)
S. Mirarab Razi, A. Motamedzadegan, S. Shahidi and A. Rashidinejad, Food Nutr J: FDNJ-192. , DOI 10, 2575–7091. (2018b)
A. Rafe, S.M.A. Razavi, R. Farhoosh, Food Hydrocoll. 30(1), 134–142 (2013)
R. Farahmandfar, S. Naji-Tabasi, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 149, 101–107 (2020)
M. Hatami, M. Nejatian, M.A. Mohammadifar, H. Pourmand, Carbohydr. Polym. 101, 1068–1073 (2014)
J. Li, Y. Wu, Y. Ma, N. Lu, J.M. Regenstein, P. Zhou, Food Funct. 8(8), 2897–2904 (2017)
D.N. López, M. Galante, E.M. Alvarez, P.H. Risso, V. Boeris, Carbohydr. Polym. 173, 1–6 (2017)
M. Khemakhem, H. Attia, M.A. Ayadi, Food Hydrocoll. 87, 11–19 (2019)
F. Weinbreck, R. de Vries, P. Schrooyen, C.G. de Kruif, Biomacromolecules 4(2), 293–303 (2003)
C.G. de Kruif, R. Tuinier, Food Hydrocoll. 15(4), 555–563 (2001)
S.H. Hosseini-Parvar, L. Matia-Merino, K.K.T. Goh, S.M.A. Razavi, S.A. Mortazavi, J. Food Eng. 101(3), 236–243 (2010)
S. Sharabiani, S. Razavi, K. Behzad and M. Tehrani, Iranian Food Science & Technology Research Journal 6 (1), 27–36. (2010)
M. Bourne, Food texture and viscosity: concept and measurement. . (Elsevier., 2002)
L. van den Berg, Y. Rosenberg, M.A.J.S. van Boekel, M. Rosenberg, F. van de Velde, Food Hydrocoll. 23(5), 1288–1298 (2009)
A. Pitkowski, D. Durand, T. Nicolai, Colloid and Interface Science 326, 96–102 (2008)
A. Rafe, S.M.A. Razavi, International Journal of Food Science & Technology 48(9), 1924–1931 (2013)
F. Javidi, S. M. Razavi, F. Behrouzian and A. Alghooneh, Food Hydrocolloids 52, 625–633. (2016)
S. M. A. Razavi and S. Naji-Tabasi, in Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications, edited by J. Ahmed, P. Ptaszek and S. Basu (Woodhead Publishing, 2017), pp. 405–435
C. Schmitt, C. Sanchez, S. Desobry-Banon and J. Hardy, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 38 (8), 689–753. (1998)
A. Rafe, S.M.A. Razavi, S. Khan, Food Res. Int. 49(1), 32–38 (2012)
C. J. Souza and E. E. Garcia-Rojas, Food Hydrocolloids 66, 268–275. (2017)
M. Tunick, C. Onwulata and P. Cooke, Abstracts of papers of the american chemical society. amer chemical soc 1155 16th st, nw, washington, dc 20036 USA. (2012)
I. Heertje, Food Structure 1 (1), 3–23. (2014)
S. Banerjee and S. Bhattacharya, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 52 (4), 334–346. (2012)
S. M. Razi, A. Motamedzadegan, S.-A. Shahidi and A. Rashidinejad, Int. J. Chem. Eng. (2019)
S. M. Razi, A. Motamedzadegan, S.-A. Shahidi and A. Rashidinejad, Rheologica Acta, 1–15 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Tabarestan Technology Incubator (TTI), Sari Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources University (SANRU), Sari, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarabi-Aghdam, V., Hosseini-Parvar, S.H., Motamedzadegan, A. et al. Characterization of Aqueous Dispersions and Gels Made of Sodium Caseinate and Basil Seed Gum: Phase Behavior, Rheology, and Microstructure. Food Biophysics 15, 495–508 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09644-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09644-w