Abstract
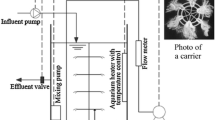
This study investigated and compared the microbial communities between a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) without carriers and a hybrid SBR with addition of carriers for the treatment of saline wastewater. The two systems were operated over 292 days with alternating aerobic/anoxic mode (temperature: 28℃, salinity: 0.0–3.0%). High removal efficiency of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total inorganic nitrogen (TIN) was achieved in both the SBR (above 86.7 and 95.4% respectively) and hybrid SBR (above 84.4 and 94.0%) at 0.0–2.5% salinity. Further increasing salinity to 3.0% decreased TIN removal efficiency to 78.4% in the hybrid SBR. Steep decline of biodiversity and relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) contributed to the worse performance. More genera related to sulfide-oxidizing and sulfate-reducing bacteria were detected in the hybrid SBR than the SBR at 3.0% salinity. The abundance of halotolerant bacteria increased with the salinity increase for both reactors, summing up to 25.5% in the suspended sludge (S-sludge) from the SBR, 28.9 and 22.9% in the S-sludge and biofilm taken from the hybrid SBR, respectively. Nitrification and denitrification via nitrate was the main nitrogen removal pathway in the SBR and hybrid SBR at 0.0 and 0.5% salinity, while partial nitrification and denitrification via nitrite became the key process for nitrogen removal in the two reactors when the salinity was increased to 1.0–3.0%. Higher abundance of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (ANAMMOX) and sulfide-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification (SOAD) bacteria were found in the hybrid SBR at 3.0% salinity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang P, Fang F, Chen YP, Shen Y, Zhang W, Yang JX, Li C, Guo JS, Liu SY, Huang Y, Li S, Gao X, Yan P (2014) Composition of EPS fractions from suspended sludge and biofilm and their roles in microbial cell aggregation. Chemosphere 117:59–65
Huang C, Shi Y, Gamal El-Din M, Liu Y (2017) Performance of flocs and biofilms in integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS) systems for the treatment of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW). Chem Eng J 314:368–377
Huang C, Shi Y, Xue J, Zhang Y, Gamal El-Din M, Liu Y (2017) Comparison of biomass from integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS), moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) treating recalcitrant organics: Importance of attached biomass. J Hazard Mater 326:120–129
Lo IW, Lo KV, Mavinic DS, Shiskowski D, Ramey W (2010) Contributions of biofilm and suspended sludge to nitrogen transformation and nitrous oxide emission in hybrid sequencing batch system. J Environ Sci 22:953–960
Zhang H, Wang H, Jie M, Zhang K, Qian Y, Ma J (2020) Performance and microbial communities of different biofilm membrane bioreactors with pre-anoxic tanks treating mariculture wastewater. Bioresour Technol 295:122302
He H, Chen Y, Li X, Cheng Y, Yang C, Zeng G (2017) Influence of salinity on microorganisms in activated sludge processes: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 119:520–527
Zhang X, Liang Y, Ma Y, Du J, Pang L, Zhang H (2016) Ammonia removal and microbial characteristics of partial nitrification in biofilm and activated sludge treating low strength sewage at low temperature. Ecol Eng 93:104–111
Zhang P, Guo JS, Shen Y, Yan P, Chen YP, Wang H, Yang JX, Fang F, Li C (2015) Microbial communities, extracellular proteomics and polysaccharides: a comparative investigation on biofilm and suspended sludge. Bioresour Technol 190:21–28
Hong J, Li W, Lin B, Zhan M, Liu C, Chen B-Y (2013) Deciphering the effect of salinity on the performance of submerged membrane bioreactor for aquaculture of bacterial community. Desalination 316:23–30
Cortés-Lorenzo C, González-Martínez A, Smidt H, González-López J, Rodelas B (2016) Influence of salinity on fungal communities in a submerged fixed bed bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 285:562–572
She Z, Zhao L, Zhang X, Jin C, Guo L, Yang S, Zhao Y, Gao M (2016) Partial nitrification and denitrification in a sequencing batch reactor treating high-salinity wastewater. Chem Eng J 288:207–215
Wang J, Liu Q, Wu B, Hu H, Dong D, Yin J, Ren H (2019) Effect of salinity on mature wastewater treatment biofilm microbial community assembly and metabolite characteristics. Sci Total Environ 711:134437
Chen Y, He H, Liu H, Li H, Zeng G, Xia X, Yang C (2018) Effect of salinity on removal performance and activated sludge characteristics in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour Technol 249:890–899
Li H, Wu S, Yang C (2020) Performance and biomass characteristics of SBRs treating high-salinity wastewater at presence of anionic surfactants. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:2689
Xia Z, Wang Q, She Z, Gao M, Zhao Y, Guo L, Jin C (2019) Nitrogen removal pathway and dynamics of microbial community with the increase of salinity in simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process. Sci Total Environ 697:134047
Wang Y, Chen J, Zhou S, Wang X, Chen Y, Lin X, Yan Y, Ma X, Wu M, Han H (2017) 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing reveals shift in nitrogen conversion related microorganisms in a CANON system in response to salt stress. Chem Eng J 317:512–521
Guo J, Peng Y, Huang H, Wang S, Ge S, Zhang J, Wang Z (2010) Short- and long-term effects of temperature on partial nitrification in a sequencing batch reactor treating domestic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 179:471–479
Huang W, She Z, Gao M, Wang Q, Jin C, Zhao Y, Guo L (2019) Effect of anaerobic/aerobic duration on nitrogen removal and microbial community in a simultaneous partial nitrification and denitrification system under low salinity. Sci Total Environ 651:859–870
APHA A, WPCF (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn, American Public Health Association Washington, DC, USA
Tang B, Chen Q, Bin L, Huang S, Zhang W, Fu F, Li P (2018) Insight into the microbial community and its succession of a coupling anaerobic-aerobic biofilm on semi-suspended bio-carriers. Bioresour Technol 247:591–598
Song W, Lee LY, You H, Shi X, Ng HY (2020) Microbial community succession and its correlation with reactor performance in a sponge membrane bioreactor coupled with fiber-bundle anoxic bio-filter for treating saline mariculture wastewater. Bioresour Technol 295:122284
Lujan-Facundo MJ, Fernandez-Navarro J, Alonso-Molina JL, Amoros-Munoz I, Moreno Y, Mendoza-Roca JA, Pastor-Alcaniz L (2018) The role of salinity on the changes of the biomass characteristics and on the performance of an OMBR treating tannery wastewater. Water Res 142:129–137
Chen L, Hu Q, Zhang X, Chen Z, Wang Y, Liu S (2019) Effects of salinity on the biological performance of anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J Environ Manag 238:263–273
Miao Y, Liao R, Zhang X-X, Liu B, Li Y, Wu B, Li A (2015) Metagenomic insights into salinity effect on diversity and abundance of denitrifying bacteria and genes in an expanded granular sludge bed reactor treating high-nitrate wastewater. Chem Eng J 277:116–123
Zhang Y, Li B, Xu R-X, Wang G-X, Zhou Y, Xie B (2016) Effects of pressurized aeration on organic degradation efficiency and bacterial community structure of activated sludge treating saline wastewater. Bioresour Technol 222:182–189
Sun H, Wang T, Yang Z, Yu C, Wu W (2019) Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and pharmaceutical and personal care products from the effluent of waste water treatment plants using aerated solid-phase denitrification system. Bioresour Technol 287:121389
Jeong D, Cho K, Lee C-H, Lee S, Bae H (2018) Effects of salinity on nitrification efficiency and bacterial community structure in a nitrifying osmotic membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 73:132–141
Li C, Zhang Z, Cao J, Li Y (2016) Study on poultry manure wastewater treatment by two-stage aerobic coupled process and its microbial community analysis. Biochem Eng J 110:107–114
He Q, Zhang J, Gao S, Chen L, Lyu W, Zhang W, Song J, Hu X, Chen R, Wang H, Yu J (2019) A comprehensive comparison between non-bulking and bulking aerobic granular sludge in microbial communities. Bioresour Technol 294:122151
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Ren HQ, Geng JJ, Xu K, Huang H, Ding LL (2015) Physicochemical characteristics and microbial community evolution of biofilms during the start-up period in a moving bed biofilm reactor. Bioresour Technol 180:345–351
He Q, Chen L, Zhang S, Chen R, Wang H (2019) Hydrodynamic shear force shaped the microbial community and function in the aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors for low carbon to nitrogen (C/N) municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 271:48–58
Yoshie S, Makino H, Hirosawa H, Shirotani K, Tsuneda S, Hirata A (2006) Molecular analysis of halophilic bacterial community for high-rate denitrification of saline industrial wastewater. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:182–189
Wang HG, Huang H, Liu RL, Mao YP, Biswal BK, Chen GH, Wu D (2019) Investigation on polyphosphate accumulation in the sulfur transformation-centric EBPR (SEBPR) process for treatment of high-temperature saline wastewater. Water Res 167:115138
Zhang L, Fu G, Zhang Z (2019) Simultaneous nutrient and carbon removal and electricity generation in self-buffered biocathode microbial fuel cell for high-salinity mustard tuber wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 272:105–113
Zhang S, Huang Z, Lu S, Zheng J, Zhang X (2017) Nutrients removal and bacterial community structure for low C/N municipal wastewater using a modified anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (mA2/O) process in North China. Bioresour Technol 243:975–985
Kostrytsia A, Papirio S, Morrison L, Ijaz UZ, Collins G, Lens PNL, Esposito G (2018) Biokinetics of microbial consortia using biogenic sulfur as a novel electron donor for sustainable denitrification. Bioresour Technol 270:359–367
Wang Z, Luo G, Li J, Chen SY, Li Y, Li WT, Li AM (2016) Response of performance and ammonia oxidizing bacteria community to high salinity stress in membrane bioreactor with elevated ammonia loading. Bioresour Technol 216:714–721
Tian H, Xu X, Qu J, Li H, Hu Y, Huang L, He W, Li B (2020) Biodegradation of phenolic compounds in high saline wastewater by biofilms adhering on aerated membranes. J Hazard Mater 392:122463
Wang J, Gong B, Huang W, Wang Y, Zhou J (2017) Bacterial community structure in simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and organic matter removal process treating saline mustard tuber wastewater as revealed by 16S rRNA sequencing. Bioresour Technol 228:31–38
Aslan S, Simsek E (2012) Influence of salinity on partial nitrification in a submerged biofilter. Bioresour Technol 118:24–29
Watsuntorn W, Ruangchainikom C, Rene ER, Lens PNL, Chulalaksananukul W (2019) Comparison of sulphide and nitrate removal from synthetic wastewater by pure and mixed cultures of nitrate-reducing, sulphide-oxidizing bacteria. Bioresour Technol 272:40–47
Lu H, Huang H, Yang W, Mackey HR, Khanal SK, Wu D, Chen GH (2018) Elucidating the stimulatory and inhibitory effects of dissolved sulfide on sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) driven autotrophic denitrification. Water Res 133:165–172
Cui YX, Biswal BK, van Loosdrecht MCM, Chen GH, Wu D (2019) Long term performance and dynamics of microbial biofilm communities performing sulfur-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification in a moving-bed biofilm reactor. Water Res 166:115038
Cui Y-X, Guo G, Biswal BK, Chen G-H, Wu D (2019) Investigation on sulfide-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification in moving-bed biofilm reactors: An innovative approach and mechanism for the process start-up. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 140:90–98
Xu X, Zhang R, Jiang H, Yang F (2020) Sulphur-based autotrophic denitrification of wastewater obtained following graphite production: Long-term performance, microbial communities involved, and functional gene analysis. Bioresour Technol 306:123117
Ma J, Wang K, Gong H, Yuan Q, Yang M, He C, Shi C, San E (2020) Integrating floc, aggregate and carrier to reap high-quality anammox biofilm. Bioresour Technol 309:123325
Chen K, Zhang L, Sun S, Li J, Jia T, Peng Y (2020) In situ enrichment of anammox bacteria in anoxic biofilms are possible due to the stable and long-term accumulation of nitrite during denitrification. Bioresour Technol 300:122668
Yang S, Guo B, Shao Y, Mohammed A, Vincent S, Ashbolt NJ, Liu Y (2019) The value of floc and biofilm bacteria for anammox stability when treating ammonia-rich digester sludge thickening lagoon supernatant. Chemosphere 233:472–481
Hao TW, Xiang PY, Mackey HR, Chi K, Lu H, Chui HK, van Loosdrecht MC, Chen GH (2014) A review of biological sulfate conversions in wastewater treatment. Water Res 65:1–21
Qian Z, Tianwei H, Mackey HR, van Loosdrecht MCM, Guanghao C (2019) Recent advances in dissimilatory sulfate reduction: from metabolic study to application. Water Res 150:162–181
Wang L, Zheng B, Nan B, Hu P (2014) Diversity of bacterial community and detection of nirS- and nirK-encoding denitrifying bacteria in sandy intertidal sediments along Laizhou Bay of Bohai Sea, China. Mar Pollut Bull 88:215–223
Wu Z, Guo G, Kumar Biswal B, Dai J, Chen G (2020) Denitrifying sulfur conversion-EBPR (DS-EBPR) process for treatment of seawater-based highly saline wastewater: evaluation on performance, kinetics and microbial community structure. Bioresour Technol 313:123574
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 201964003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51978636).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Guo, Z., She, Z. et al. Comparison of the effects of salinity on microbial community structures and functions in sequencing batch reactors with and without carriers. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 2175–2188 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02403-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02403-8