Abstract
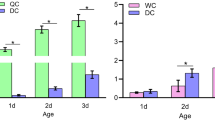
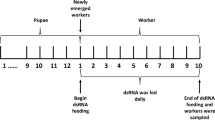
9-Oxo-2-decenoic acid (9-ODA, the predominant component of honeybee queen mandibular pheromones) acts as a sex pheromone attracting drones during mating flights in midair. Odorant receptor 11 (Or11), which is located on the membrane of antennal olfaction receptor neurons in bees, can specifically recognize 9-ODA. At present, the molecular pathway of honeybee drones responding to 9-ODA is still unclear. Studies have demonstrated that 9-ODA could downregulate the expression of Krüppel-homolog1 (Kr-h1, a transcription factor related to the regulation of reproduction and division of labor mediated by juvenile hormone) gene in the mushroom of honeybee brain. We speculate that Kr-h1 may be the downstream gene of Or11, which is involved in the pathway of drones responding to 9-ODA. Therefore, we analyzed the influence of 9-ODA on the expression of Or11 and Kr-h1 in the antennae of sexually immature (4 days) and mature (14 days) male honeybees (Apis mellifera) by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). The results demonstrated that 9-ODA significantly downregulated the expression of Or11 and Kr-h1 in the antennae of sexually immature and mature drones. Additionally, siRNA-Or11 was injected into the antennae and brain tissues of 8-day-old drone pupae, and the expression patterns of Or11, Kr-h1 and Broad-Complex (Br–c, downstream gene of Kr-h1) were determined by qPCR at 72 h. The RNAi-induced knockdown of Or11 significantly decreased the expression of Or11, Kr-h1 and Br–c in the antennae and brains of drones. This study suggests that the transcription factor Kr-h1 is downstream of Or11, Kr-h1, which may play an important role in the signal transduction process of drones responding to 9-ODA.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and material are fully available without restriction.
References
Abdou MA, He Q, Wen D et al (2011) Drosophila Met and Gce are partially redundant in transducing juvenile hormone action. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:938–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.09.003
Belles X, Santos CG (2014) The MEKRE93 (Methoprene tolerant-Krüppel homolog 1–E93) pathway in the regulation of insect metamorphosis, and the homology of the pupal stage. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 52:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.06.009
Beye M, Hartel S, Hagen A et al (2002) Specific developmental gene silencing in the honey bee using a homeobox motif. Insect Mol Biol 11:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2583.2002.00361.x
Brockmann A, Brückner D, Crewe RM (1998) The EAG response spectra of workers and drones to queen honeybee mandibular gland components: the evolution of a social signal. Naturwissenschaften 85:283–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001140050500
Brockmann A, Dietz D, Spaethe J, Tautz J (2006) Beyond 9-ODA: SEX pheromone communication in the European honey bee Apis mellifera L. J Chem Ecol 32:657–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-005-9027-2
Butler CG (1971) The mating behaviour of the honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). J Entomol Ser A, Gen Entomol 46:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3032.1971.tb00103.x
Butler CG, Callow RK, Johnston NC (1962) The isolation and synthesis of queen substance, 9-oxodec-trans-2-enoic acid, a honeybee pheromone. Proceed Royal Soc B: Biol Sci 155:417–432. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1962.0009
Butler CG, Callow RK, Johnston NC (1959) Extraction and purification of “queen substance” from queen bees. Nature 184:1871–1871. https://doi.org/10.1038/1841871a0
Carlisle DB, Butler CG (1956) The “queen-substance” of honeybees and the ovary-inhibiting hormone of crustaceans. Nature 178:323
Claudianos C, Lim J, Young M et al (2014) Odor memories regulate olfactory receptor expression in the sensory periphery. Eur J Neurosci 39:1642–1654. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12539
Erezyilmaz DF, Riddiford LM, Truman JW (2006) The pupal specifier broad directs progressive morphogenesis in a direct-developing insect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6925–6930. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509983103
Gary NE (1962) Chemical mating attractants in the queen honey bee. Science 136:773–774. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.136.3518.773
Gary NE, Marston J (1971) Mating behaviour of drone honey bees with queen models (Apis mellifera L.). Anim Behav 19:299–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-3472(71)80010-6
Grozinger CM, Fischer P, Hampton JE (2007) Uncoupling primer and releaser responses to pheromone in honey bees. Naturwissenschaften 94:375–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-006-0197-8
Grozinger CM, Robinson GE (2007) Endocrine modulation of a pheromone-responsive gene in the honey bee brain. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 193:461–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-006-0202-x
Grozinger CM, Sharabash NM, Whitfield CW, Robinson GE (2003) Pheromone-mediated gene expression in the honey bee brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:14519–14525. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2335884100
Guo X, Wang Y, Sinakevitch I et al (2018) Comparison of RNAi knockdown effect of tyramine receptor 1 induced by dsRNA and siRNA in brains of the honey bee, Apis mellifera. J Insect Physiol 111:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2018.10.005
Harwood G, Amdam G, Freitak D (2019) The role of Vitellogenin in the transfer of immune elicitors from gut to hypopharyngeal glands in honey bees (Apis mellifera). J Insect Physiol 112:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2018.12.006
Huang JH, Lozano J, Belles X (2013) Broad-complex functions in postembryonic development of the cockroach Blattella germanica shed new light on the evolution of insect metamorphosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1830:2178–2187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.09.025
Kaatz HH, Hildebrandt H, Engels W (1992) Primer effect of queen pheromone on juvenile hormone biosynthesis in adult worker honey bees. J Comp Physiol B 162:588–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296638
Keeling CI, Slessor KN, HigoWinston HaML (2003) New components of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) queen retinue pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4486–4491. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0836984100
Kilaso M, Remnant EJ, Chapman NC et al (2017) DNA methylation of Kr-h1 is involved in regulating ovary activation in worker honeybees (Apis mellifera). Insectes Soc 64:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-016-0518-7
Liu JF, Yang L, Li M et al (2019) Cloning and expression pattern of odorant receptor 11 in Asian honeybee drones, Apis cerana (Hymenoptera, Apidae). J Asia-Pac Entomol 22:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2018.12.014
Loper GM, Wolf WW, Taylor OR (1993) Radar detection of drones responding to honeybee queen pheromone. J Chem Ecol 19:1929–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00983797
Lourenço AP, Mackert A, Cristino ADS, Simões ZLP (2008) Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in the honey bee, Apis mellifera, by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Apidologie 39:372–385. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2008015
Martins JR, Nunes FMF, Cristino AS et al (2010) The four hexamerin genes in the honey bee: structure, molecular evolution and function deduced from expression patterns in queens, workers and drones. BMC Mol Biol 11:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-11-23
Minakuchi C, Namiki T, Shinoda T (2009) Krüppel homolog 1, an early juvenile hormone-response gene downstream of Methoprene-tolerant, mediates its anti-metamorphic action in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Dev Biol 325:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.016
Minakuchi C, Zhou X, Riddiford LM (2008) Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) mediates juvenile hormone action during metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. Mech Dev 125:91–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2007.10.002
Nunes FMF, Simões ZLP (2009) A non-invasive method for silencing gene transcription in honeybees maintained under natural conditions. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.10.011
Pankiw T, Huang Z, Winston M, Robinson G (1998) Queen mandibular gland pheromone influences worker honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) foraging ontogeny and juvenile hormone titers. J Insect Physiol 44:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1910(98)00040-7
Pankiw T, Page RE (2003) Effect of pheromones, hormones, and handling on sucrose response thresholds of honey bees ( Apis mellifera L.). J Comp Physiol A 189:675–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-003-0442-y
Paul RK, Takeuchi H, Kubo T (2006) Expression of two ecdysteroid-regulated genes, broad-complex and E75, in the brain and ovary of the honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). Zoolog Sci 23:1085–1092. https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.23.1085
Plettner E, Otis GW, Wimalaratne PDC et al (1997) Species- and caste-determined mandibular gland signals in honeybees (Apis). J Chem Ecol 23:363–377. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006365.20996.a2
Rangel J, Böröczky K, Schal C, Tarpy DR (2016) Honey bee (Apis mellifera) queen reproductive potential affects queen mandibular gland pheromone composition and worker retinue response. PLoS ONE 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156027
Sandoz J-C (2006) Odour-evoked responses to queen pheromone components and to plant odours using optical imaging in the antennal lobe of the honey bee drone Apis mellifera L. J Exp Biol 209:3587–3598. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.02423
Sandoz J-C, Deisig N, de Brito Sanchez MG, Giurfa M (2007) Understanding the logics of pheromone processing in the honeybee brain: from labeled-lines to across-fiber patterns. Front Behav Neurosci 1:5. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.08.005.2007
Scharlaken B, de Graaf DC, Goossens K et al (2008) Reference gene selection for insect expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR: the head of the honeybee, Apis mellifera, after a bacterial challenge. J Insect Sci 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.008.3301
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Schuh R, Aicher W, Gaul U et al (1986) A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell 47:1025–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2
Slessor KN, Winston ML, Le Conte Y (2005) Pheromone communication in the honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). J Chem Ecol 31:2731–2745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-005-7623-9
Villar G, Baker TC, Patch HM, Grozinger CM (2015) Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying sex- and maturation-related variation in pheromone responses in honey bees (Apis mellifera). J Comp Physiol A 201:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-1006-7
Villar G, Grozinger CM (2017) Primer effects of the honeybee, Apis mellifera, queen pheromone 9-ODA on drones. Anim Behav 127:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.03.023
Wang Y, Baker N, Amdam GV (2013) RNAi-mediated double gene knockdown and gustatory perception measurement in honey bees (Apis mellifera). J Vis Exp 77:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3791/50446
Wanner KW, Nichols AS, Walden KKO et al (2007) A honey bee odorant receptor for the queen substance 9-oxo-2-decenoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14383–14388. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705459104
Whitfield CW, Cziko A-M, Robinson GE (2003) Gene expression profiles in the brain predict behavior in individual honey bees. Science 302:296–299. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1086807
Acknowledgements
We thank Frederick Partridge and anonymous reviewers for their comments that improved this manuscript. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572469) and the Earmarked Fund for the China Agricultural Research System (CARS-44-KXJ15).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572469) and the Earmarked Fund for the China Agricultural Research System (CARS-44-KXJ15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: ZJZ. Performed the experiments: JFL. Analyzed the data: JFL XJW. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: ZLW XJH. Wrote the paper: JFL XJW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Ethics approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Jiangxi Agricultural University (JXAULL-2017002).
Consent to participate
All authors have consented to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented for publication.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
40_2020_775_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 (TIF 1429 kb) SI Fig. 3 The developmental state of drone pupae at 0 h (A), 24 h (B), 48 h (C) and 72 h (D) after injection
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J.F., Wan, X.J., Wang, Z.L. et al. Influence of RNA interference-mediated reduction of Or11 on the expression of transcription factor Kr-h1 in Apis mellifera drones. Insect. Soc. 67, 411–418 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-020-00775-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-020-00775-4