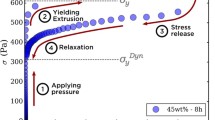
Abstract
Transient creep testing was used to differentiate the printability of block copolymer (BCP) containing epoxy inks for direct ink writing (DIW). Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide-b-ethylene oxide) (P123) BCPs were shown to form disordered micelles at 20 wt% in a 3D-printable epoxy ink. Oscillatory amplitude sweeps identified no obvious difference in the rheological properties of the inks; however, the P123 inks required less pressure to print quality parts. By contrast, transient creep testing identified significant differences and showed that the P123 ink had a lower apparent yield stress and a lower time-dependent decrease in the shear rate. Additionally, both inks showed re-entrant solid behavior. This behavior manifests in printing as a material that initially flows well, but the material flow eventually stops. The transient creep results correlate well with the printing results. We propose that studying the time-dependent flow properties using transient creep testing is critical for the evaluation of DIW inks.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Most data that was generated and analyzed during this study is included in this published article. Any additional datasets are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Balmforth NJ, Frigaard IA, Ovarlez G (2014) Yielding to stress: recent developments in viscoplastic fluid mechanics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 46:121–146. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-010313-141424
Barnes HA (1999) The yield stress-a review or ‘παντα ρει’-everything flows? J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 81:133–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0257(98)00094-9
Bauer T, Oberdisse J, Ramos L (2006) Collective rearrangement at the onset of flow of a polycrystalline hexagonal columnar phase. Phys Rev Lett 97:258303. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.258303
Bergenholtz J, Fuchs M (1999) Nonergodicity transitions in colloidal suspensions with attractive interactions. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics 59:5706–5715. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.59.5706
Bockstaller MR, Lapetnikov Y, Margel S, Thomas EL (2003) Size-selective organization of enthalpic compatibilized nanocrystals in ternary block copolymer/particle mixtures. J Am Chem Soc 125:5276–5277. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja034523t
Bonn D, Denn MM, Berthier L, Divoux T, Manneville S (2017) Yield stress materials in soft condensed matter. Rev Mod Phys 89:03505. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.89.035005
Caton F, Baravian C (2008) Plastic behavior of some yield stress fluids: from creep to long-time yield. Rheol Acta 47:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-008-0267-2
Christopoulou C, Petekidis G, Erwin B, Cloitre M, Vlassopoulos D (2009) Ageing and yield behaviour in model soft colloidal glasses. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 367:5051–5071. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2009.0166
Compton BG, Lewis JA (2014) 3D-printing of lightweight cellular composites. Adv Mater 26:5930–5935. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201401804
Coussot P (2014) Yield stress fluid flows: a review of experimental data. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 211:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2014.05.006
Coussot P (2018) Slow flows of yield stress fluids: yielding liquids or flowing solids? Rheol Acta 57:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-017-1055-7
Dinkgreve M, Denn MM, Bonn D (2017) “Everything flows?”: elastic effects on startup flows of yield-stress fluids. Rheol Acta 56:189–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-017-0998-z
Dinkgreve M, Paredes J, Denn MM, Bonn D (2016) On different ways of measuring “the” yield stress. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 238:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2016.11.001
Divoux T, Barentin C, Manneville S (2011) From stress-induced fluidization processes to Herschel-Bulkley behaviour in simple yield stress fluids. Soft Matter 7:8409–8418. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1sm05607g
Donley GJ, de Bruyn JR, McKinley GH, Rogers SA (2019a) Time-resolved dynamics of the yielding transition in soft materials. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 264:117–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2018.10.003
Donley GJ, Hyde WW, Rogers SA, Nettesheim F (2019b) Yielding and recovery of conductive pastes for screen printing. Rheol Acta 58:361–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-019-01148-w
Drummy LF, Koerner H, Farmer K, Tan A, Farmer BL, Vaia RA (2005) High-resolution electron microscopy of montmorillonite and montmorillonite/epoxy nanocomposites. J Phys Chem B 109:17868–17878. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp053133l
Duty C, Ajinjeru C, Kishore V, Compton B, Hmeidat N, Chen X, Liu P, Hassen AA, Lindahl J, Kunc V (2018) What makes a material printable? A viscoelastic model for extrusion-based 3D printing of polymers. J Manuf Process 35:526–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.08.008
Fernandes RR, Andrade DEV, Franco AT, Negrão COR (2017) The yielding and the linear-to-nonlinear viscoelastic transition of an elastoviscoplastic material. J Rheol 61:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.4991803
Guo Q, Thomann R, Gronski W, Thurn-Albrecht T (2002) Phase behavior, crystallization, and hierarchical nanostructures in self-organized thermoset blends of epoxy resin and amphiphilic poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(propylene oxide)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers. Macromolecules. 35:3133–3144. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma011971h
Hmeidat NS, Kemp JW, Compton BG (2018) High-strength epoxy nanocomposites for 3D printing. Compos Sci Technol 160:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.03.008
Jakus AE, Taylor SL, Geisendorfer NR, Dunand DC, Shah RN (2015) Metallic architectures from 3D-printed powder-based liquid inks. Adv Funct Mater 25:6985–6995. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201503921
Johnson KJ, Wiegart L, Abbott AC, Johnson EB, Baur JW, Koerner H (2019) In operando monitoring of dynamic recovery in 3D-printed thermoset nanocomposites by XPCS. Langmuir 35:8758–8768. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00766
Kim CS, Randow C, Sano T (eds) (2015) Hybrid and hierarchical composite materials. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12868-9
Koerner H, Misra D, Tan A, Drummy L, Mirau P, Vaia R (2006) Montmorillonite-thermoset nanocomposites via cryo-compounding. Polymer 47:3426–3435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.03.057
Landrum BJ, Russel WB, Zia RN (2016) Delayed yield in colloidal gels: creep, flow, and re-entrant solid regimes. J Rheol (N Y N Y) 60:783–807. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.4954640
Larrañaga M, Gabilondo N, Kortaberria G et al (2005) Micro- or nanoseparated phases in thermoset blends of an epoxy resin and PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymer. Polymer 46:7082–7093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.05.102
Larranaga M, Martín MD, Gabilondo N et al (2004) Cure kinetics of epoxy systems modified with block copolymers. Polym Int 53:1495–1502. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1574
Larrañaga M, Martin MD, Gabilondo N, Kortaberria G, Eceiza A, Riccardi CC, Mondragon I (2006) Toward microphase separation in epoxy systems containing PEO-PPO-PEO block copolymers by controlling cure conditions and molar ratios between blocks. Colloid Polym Sci 284:1403–1410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-006-1512-9
Lewis JA (2006) Direct ink writing of 3D functional materials. Adv Funct Mater 16:2193–2204. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200600434
Li L, Lin Q, Tang M, Duncan AJE, Ke C (2019) Advanced polymer designs for direct-ink-write 3D printing. Chem A Eur J 25:10768–10781. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201900975
Møller PCF, Fall A, Bonn D (2009) Origin of apparent viscosity in yield stress fluids below yielding. EPL 87:38004. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/87/38004
Nelson AZ, Schweizer KS, Rauzan BM, Nuzzo RG, Vermant J, Ewoldt RH (2019) Designing and transforming yield-stress fluids. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 23:100758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2019.06.002
Nguyen QD, Boger DV (1992) Measuring the flow properties of yield stress fluids. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 24:47–88. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fl.24.010192.000403
Orilall MC, Wiesner U (2011) Block copolymer based composition and morphology control in nanostructured hybrid materials for energy conversion and storage: solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells. Chem Soc Rev 40:520–535. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00034e
Raney JR, Compton BG, Mueller J, Ober TJ, Shea K, Lewis JA (2018) Rotational 3D printing of damage-tolerant composites with programmable mechanics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:1198–1203. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1715157115
Ruiz-Pérez L, Royston GJ, Fairclough JPA, Ryan AJ (2008) Toughening by nanostructure. Polymer. 49:4475–4488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.07.048
Taheri SM, Fischer S, Förster S (2011) Routes to nanoparticle-polymer superlattices. Polymers. 3:662–673. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3020662
Thompson RB, Ginzburg VV, Matsen MW, Balazs AC (2001) Predicting the mesophases of copolymer-nanoparticle composites. Science. 292:2469–2472. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060585
Vaia RA, Liu W, Koerner H (2003) Analysis of small-angle scattering of suspensions of organically modified montmorillonite: implications to phase behavior of polymer nanocomposites. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 41:3214–3236. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.10698
Wang J, Li W, Zhu J (2014) Encapsulation of inorganic nanoparticles into block copolymer micellar aggregates: strategies and precise localization of nanoparticles. Polymer 55:1079–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.01.027
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Sungsik Lee at Argonne National Laboratory for his help and support with the SAXS experiments. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. The Anton Paar Academic VIP program is gratefully acknowledged for the use of the MCR 702 rheometer.
Funding
This work is supported through a YIP award funded by the AFOSR Low Density Materials program under grant number FA9550-17-1-0128.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekbote, R.P., Donley, G.J., Liu, D.Y. et al. Re-entrant solid behavior of 3D-printable epoxy inks. Rheol Acta 59, 631–638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01227-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01227-3