Abstract
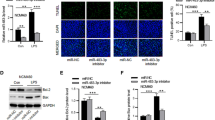
Dexmedetomidine inhibits the release of inflammatory cytokines and exerts a systemic anti-inflammatory effect and has potential protective effects on vital organs such as lung, heart, and kidneys. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-treated HK-2 cells in vitro and explore the potential mechanisms. The HK-2 cells were pretreated with dexmedetomidine before LPS induction. CCK-8, flow cytometry, ELISA, or qRT-PCR was performed to detect cell proliferation, apoptosis, and proinflammatory cytokine expression. The levels of MALAT1 in HK-2 cells under different stimulation were measured by qRT-PCR. Then, m6A RNA immunoprecipitation was performed to detect methylated MALAT1 in HK-2 cells. The results showed dexmedetomidine suppressed cell viability, induced cell apoptosis, and reduced inflammation cytokine production of LPS-treated HK-2 cells. Besides, dexmedetomidine reduced the expression of MALAT1 in HK-2 cells under LPS stimulation. In addition, ALKBH5 could up-regulate MALAT1 expression by demethylation. Furthermore, dexmedetomidine inhibited the expression of ALKBH5 in LPS-treated HK-2 cells. ALKBH5 knockdown inhibited cell viability, induced cell apoptosis, and decreased inflammation cytokine production of LPS-treated HK-2 cells. In short, dexmedetomidine suppressed the biological behavior of HK-2 cells treated with LPS by inhibiting the expression of ALKBH5 in vitro, which may provide potential targets for the prevention and treatment of sepsis-induced kidney injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonso, J., and F. Reis. 2012. Dexmedetomidine: Current role in anesthesia and intensive care. Revista Brasileira de Anestesiologia 62 (1): 118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-7094(12)70110-1.
Aik, W., J.S. Scotti, H. Choi, L. Gong, M. Demetriades, C.J. Schofield, and M.A. McDonough. 2014. Structure of human RNA N(6)-methyladenine demethylase ALKBH5 provides insights into its mechanisms of nucleic acid recognition and demethylation. Nucleic Acids Research 42 (7): 4741–4754. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku085.
Bagshaw, S.M., C. George, and R. Bellomo. 2008. Early acute kidney injury and sepsis: A multicentre evaluation. Critical Care 12 (2): R47. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc6863.
Bone, R.C., C.L. Sprung, and W.J. Sibbald. 1992. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure. Critical Care Medicine 20 (6): 724–726. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199206000-00002.
Chen, H., X. Wang, X. Yan, X. Cheng, X. He, and W. Zheng. 2018. LncRNA MALAT1 regulates sepsis-induced cardiac inflammation and dysfunction via interaction with miR-125b and p38 MAPK/NFkappaB. International Immunopharmacology 55: 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.038.
Feng, C., Y. Liu, G. Wang, Z. Deng, Q. Zhang, W. Wu, Y. Tong, C. Cheng, and Z. Chen. 2014. Crystal structures of the human RNA demethylase Alkbh5 reveal basis for substrate recognition. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 289 (17): 11571–11583. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.546168.
Gu, J., J. Chen, P. Xia, G. Tao, H. Zhao, and D. Ma. 2011. Dexmedetomidine attenuates remote lung injury induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 55 (10): 1272–1278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2011.02526.x.
Hanci, V., G. Yurdakan, S. Yurtlu, I.O. Turan, and E.Y. Sipahi. 2012. Protective effect of dexmedetomidine in a rat model of alpha-naphthylthiourea-induced acute lung injury. The Journal of Surgical Research 178 (1): 424–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.02.027.
He, Y., H. Hu, Y. Wang, H. Yuan, Z. Lu, P. Wu, D. Liu, L. Tian, J. Yin, K. Jiang, and Y. Miao. 2018. ALKBH5 inhibits pancreatic cancer motility by decreasing long non-coding RNA KCNK15-AS1 methylation. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 48 (2): 838–846. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491915.
Ji, P., S. Diederichs, W. Wang, S. Boing, R. Metzger, P.M. Schneider, N. Tidow, et al. 2003. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 22 (39): 8031–8041. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206928.
Lee, M., B. Kim, and V.N. Kim. 2014. Emerging roles of RNA modification: m(6)A and U-tail. Cell 158 (5): 980–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.005.
Maity, A., and B. Das. 2016. N6-methyladenosine modification in mRNA: Machinery, function and implications for health and diseases. The FEBS Journal 283 (9): 1607–1630. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13614.
Mantz, J., J. Josserand, and S. Hamada. 2011. Dexmedetomidine: New insights. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 28 (1): 3–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0b013e32833e266d.
Mattick, J.S., and J.L. Rinn. 2015. Discovery and annotation of long noncoding RNAs. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 22 (1): 5–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2942.
Mehta, R.L., J. Bouchard, S.B. Soroko, T.A. Ikizler, E.P. Paganini, G.M. Chertow, and J. Himmelfarb. 2011. Sepsis as a cause and consequence of acute kidney injury: Program to improve care in acute renal disease. Intensive Care Medicine 37 (2): 241–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-010-2089-9.
Meyer, K.D., and S.R. Jaffrey. 2014. The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology 15 (5): 313–326. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3785.
Rajapakse, S., C. Rodrigo, A. Rajapakse, D. Kirthinanda, and S. Wijeratne. 2009. Renal replacement therapy in sepsis-induced acute renal failure. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation 20 (4): 553–559.
Riker, R.R., Y. Shehabi, P.M. Bokesch, D. Ceraso, W. Wisemandle, F. Koura, P. Whitten, B.D. Margolis, D.W. Byrne, E.W. Ely, M.G. Rocha, and SEDCOM (Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine Compared With Midazolam) Study Group. 2009. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: A randomized trial. JAMA 301 (5): 489–499. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.56.
Riveros, R., N. Makarova, E. Riveros-Perez, P. Chodavarapu, W. Saasouh, H.O. Yilmaz, E. Cuko, R. Babazade, S. Kimatian, and A. Turan. 2017. Utility and clinical profile of dexmedetomidine in pediatric cardiac catheterization procedures: A matched controlled analysis. Seminars in Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 21 (4): 330–340. https://doi.org/10.1177/1089253217708035.
Roundtree, I.A., M.E. Evans, T. Pan, and C. He. 2017. Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell 169 (7): 1187–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.045.
Sanders, R.D., P. Sun, S. Patel, M. Li, M. Maze, and D. Ma. 2010. Dexmedetomidine provides cortical neuroprotection: Impact on anaesthetic-induced neuroapoptosis in the rat developing brain. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 54 (6): 710–716. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.02177.x.
Taniguchi, T., A. Kurita, K. Kobayashi, K. Yamamoto, and H. Inaba. 2008. Dose- and time-related effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality and inflammatory responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats. Journal of Anesthesia 22 (3): 221–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-008-0611-9.
van Zanten, A.R., S. Brinkman, M.S. Arbous, A. Abu-Hanna, M.M. Levy, and N.F. de Keizer. 2014. Guideline bundles adherence and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. Critical Care Medicine 42 (8): 1890–1898. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000297.
Yu, Z., A. Rayile, X. Zhang, Y. Li, and Q. Zhao. 2017. Ulinastatin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac microvascular endothelial cell dysfunction via downregulation of lncRNA MALAT1 and EZH2 in sepsis. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 39 (5): 1269–1276. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.2920.
Zhang, J., S. Guo, H.Y. Piao, Y. Wang, Y. Wu, X.Y. Meng, D. Yang, Z.C. Zheng, and Y. Zhao. 2019. ALKBH5 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by decreasing methylation of the lncRNA NEAT1. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry 75 (3): 379–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-019-00690-8.
Zhang, S., B.S. Zhao, A. Zhou, K. Lin, S. Zheng, Z. Lu, Y. Chen, E.P. Sulman, K. Xie, O. Bögler, S. Majumder, C. He, and S. Huang. 2017. m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell 31 (4): 591–606 e596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.013.
Zheng, G., J.A. Dahl, Y. Niu, P. Fedorcsak, C.M. Huang, C.J. Li, C.B. Vagbo, et al. 2013. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Molecular Cell 49 (1): 18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.015.
Zong, X., S. Nakagawa, S.M. Freier, J. Fei, T. Ha, S.G. Prasanth, and K.V. Prasanth. 2016. Natural antisense RNA promotes 3′ end processing and maturation of MALAT1 lncRNA. Nucleic Acids Research 44 (6): 2898–2908. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Sichuan Academy of Medical Science, Sichuan Province People’s Hospital.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Lu, Y. Dexmedetomidine Suppressed the Biological Behavior of HK-2 Cells Treated with LPS by Down-Regulating ALKBH5. Inflammation 43, 2256–2263 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01293-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01293-y